UPSC Prelims 2017 Analysis
Subject wise MCQ distribution
- Polity and Governance: The highest weightage in the exam, with questions focusing on core constitutional concepts like democracy and rights, highlighting a return to traditional themes. Many followed the assertion-reasoning format, testing analytical abilities.
Economy: Heavily current affairs-based, covering topics such as GST, Monetary Policy Committee, and post-1991 reforms. Conceptual clarity was crucial for elimination-based questions.
Geography and Environment: Required conceptual clarity and linkages with current affairs, such as the Indian Ocean Dipole. Many questions incorporated maps for better understanding.
History: Weightage remained consistent, but factual knowledge was essential, especially for match the following and multi-statement questions.
Science & Technology: Mostly news-based, testing awareness of recent developments in biotechnology, AI, and space technology.
Government Schemes & Initiatives: A prominent focus area, covering policies related to education, health, and nutrition. Many questions were framed using the elimination technique.

Difficulty analysis
- Easy: Some Polity and Economy questions were straightforward for those who had covered NCERT and standard sources.
- Moderate: Many required linking static and dynamic aspects, such as governance and current affairs.
- Difficult: Environment, Geography, and factual History questions were particularly challenging.
- Tricky: Questions on conventions and alliances where India is not a member, along with misleadingly framed government initiative questions, posed difficulties.

Variations in Question framing
- Direct Questions: 42 direct questions, emphasizing understanding over rote memorization.
- Multi-Statement Based Questions: A significant 58 multi-statement questions, requiring a mix of static and current affairs knowledge. These took longer to solve but allowed option elimination.
- Application-Oriented Questions: Required candidates to link current events with static concepts, testing analytical abilities.
- Elimination-Based Questions: Many options were closely framed, making elimination techniques challenging.
- Deceptively Worded Questions: Designed to test deep knowledge, especially in areas like the National Investment and Infrastructure Fund.

Key learning for Future Preparation
- Strengthen Static Concepts: Read NCERTs and standard books thoroughly for a solid foundation.
- Follow a Reliable Newspaper: Sources like The Hindu, Indian Express, PIB, and PRS are essential for current affairs integration.
- Regularly Revise Government Schemes: Many questions are framed around policies from the India Year Book.
- Adopt a Balanced Approach: Expect a mix of analytical and factual questions; both require preparation.
- Use the Elimination Technique Wisely: Read questions carefully and systematically eliminate options to maximize accuracy.
- Avoid Over-Attempting: The tricky nature of the paper means reckless attempts can lead to penalties through negative marking.
- Strengthen Core Subjects: Excelling in Polity or History can help maximize scores in difficult papers.
- Solve Previous Year Papers: Recurring themes like the Trade Disputes Act and Liberalization highlight the importance of PYQs.
Subject-Wise Answer Key
QUESTION 1
At one of the places in India if you stand on the seashore and watch the sea, you will find that the sea water recedes from the shoreline a few kilometres and comes back to the shore, twice a day, and you can actually walk on the sea floor when the water recedes. This unique phenomenon is seen at -
A. Bhavnagar
B. Bheemunipatnam
C. Chandipur
D. Nagapattinam
QUESTION 2
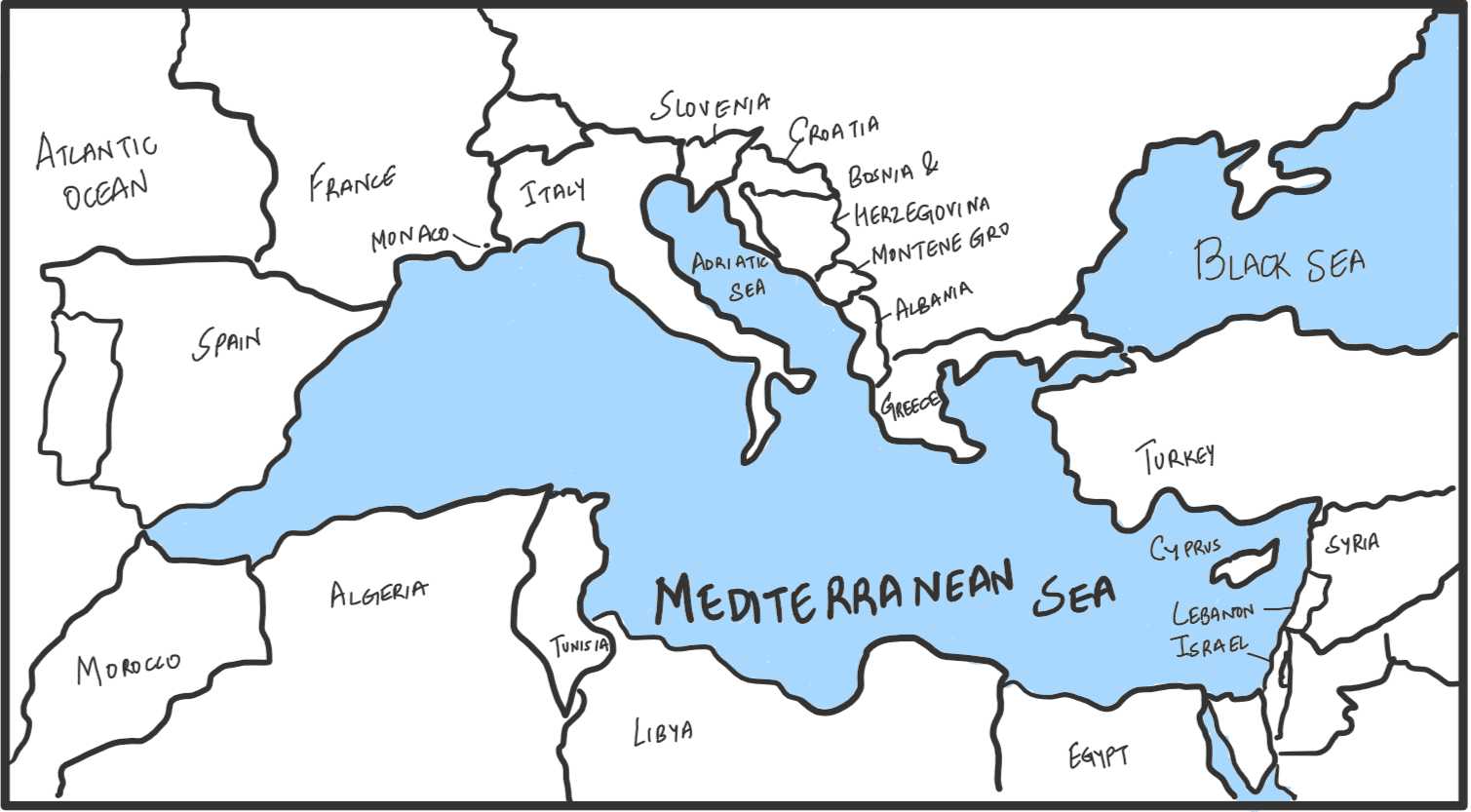
The Mediterranean Sea is a border of which of the following countries?
- Jordan
- Iraq
- Lebanon
- Syria Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1, 2 and 3 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 3 and 4 only
QUESTION 3
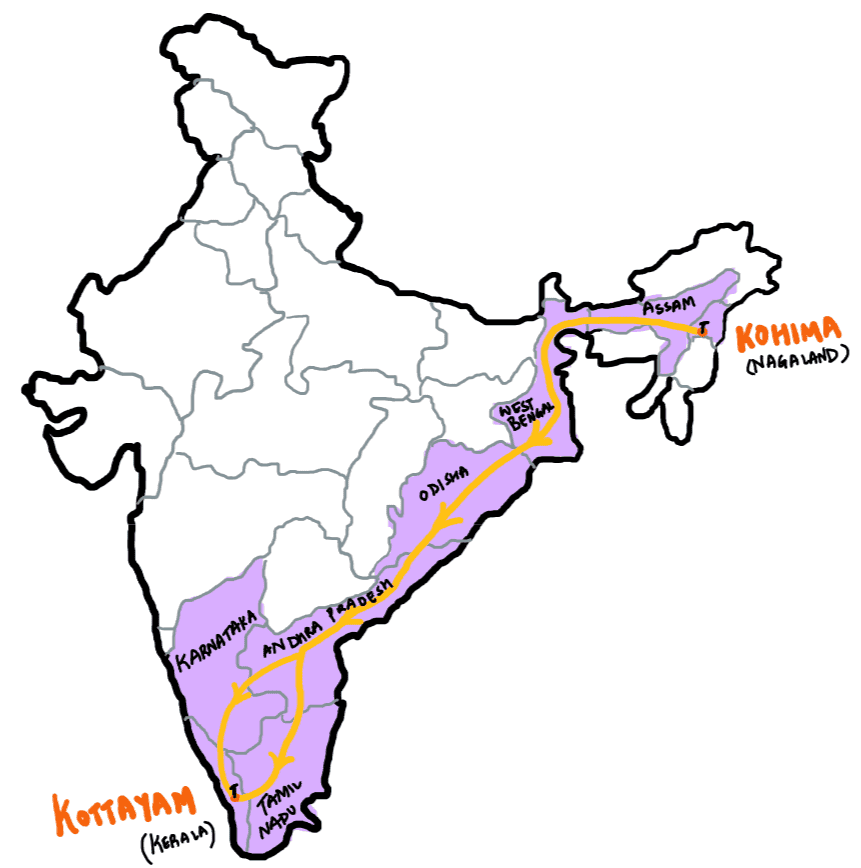
If you travel by road from Kohima to Kottayam, what is the minimum number of States within India through which you can travel, including the origin and the destination?
A. 6
B. 7
C. 8
D. 9
QUESTION 4
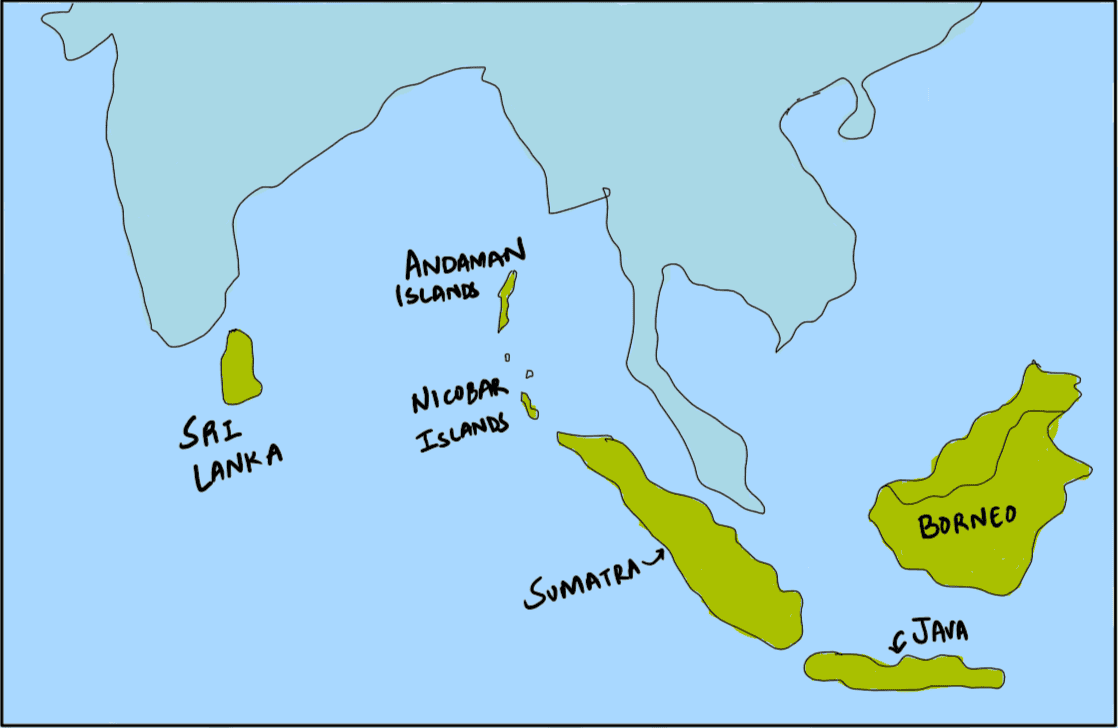
Which of the following is geographically closest to Great Nicobar?
A. Sumatra
B. Borneo
C. Java
D. Sri Lanka
QUESTION 5
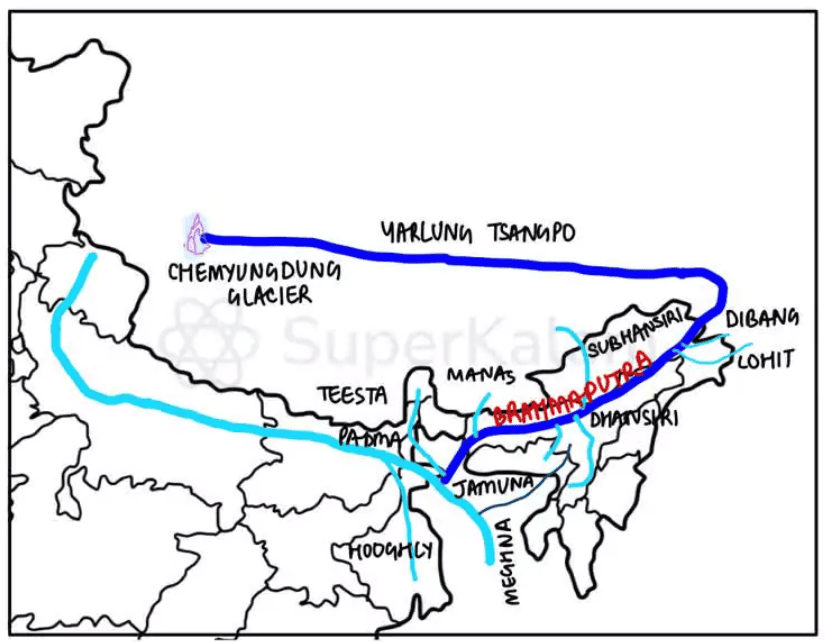
With reference to river Teesta, consider the following statements:
- The source of river Teesta is the same as that of Brahmaputra but it flows through Sikkim.
- River Rangeet originates in Sikkim and it is a tributary of river Teesta.
- River Teesta flows into Bay of Bengal on the border of India and Bangladesh. Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 6
Consider the following statements:
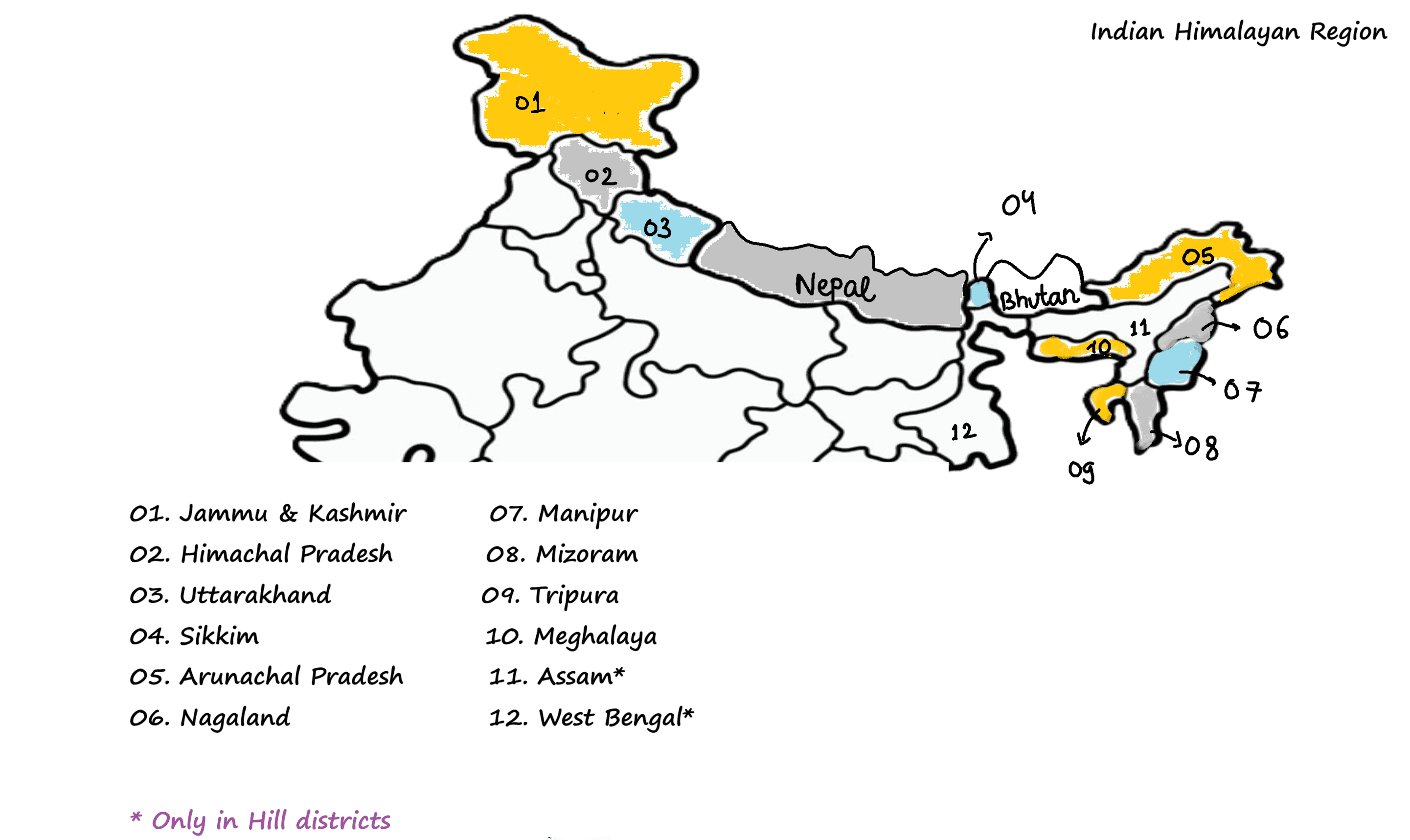
- In India, the Himalayas are spread over five States only.
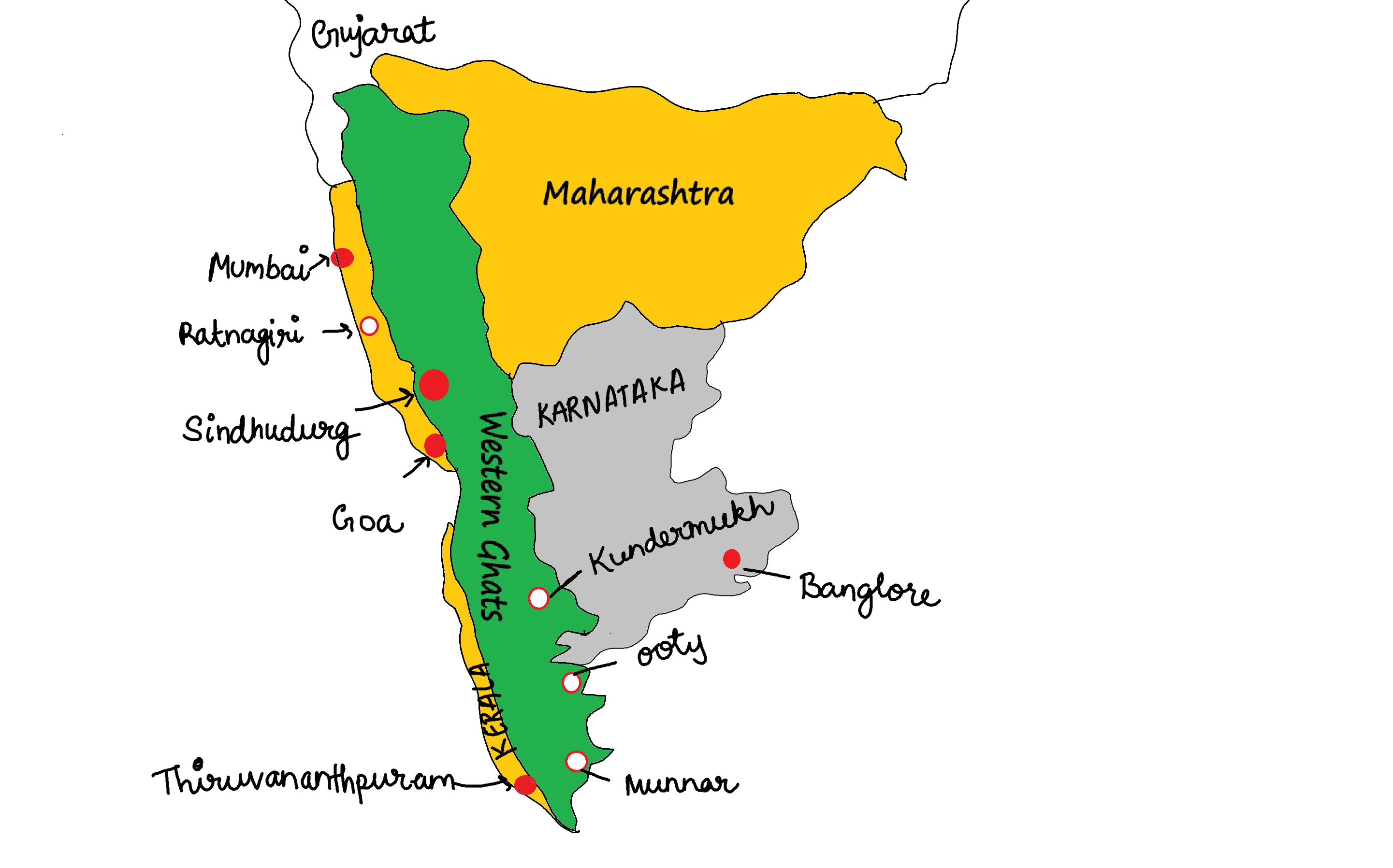
- The Western Ghats are spread over five States only.
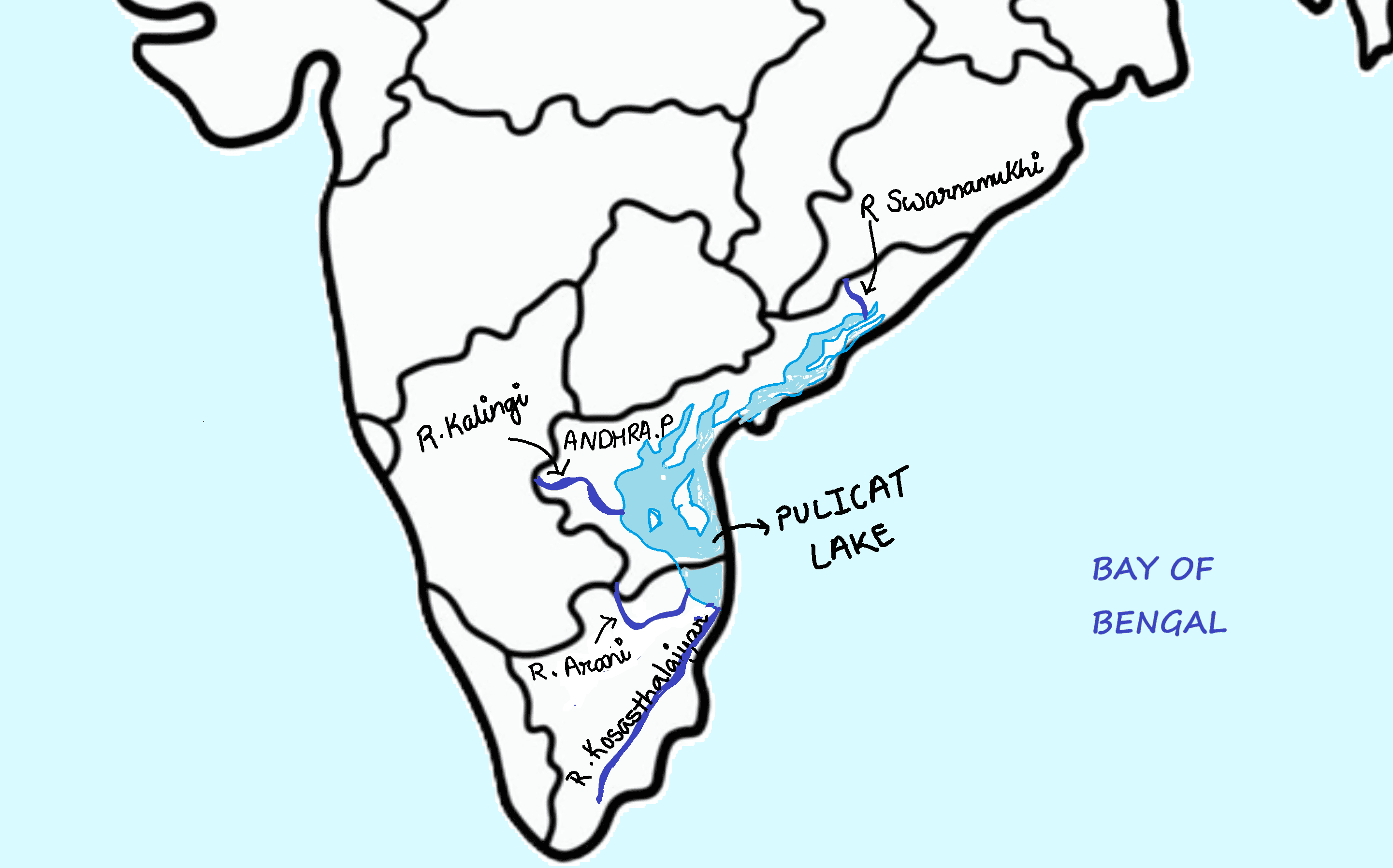
- Pulicat Lake is spread over two States only. Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1 and 3 only
QUESTION 7
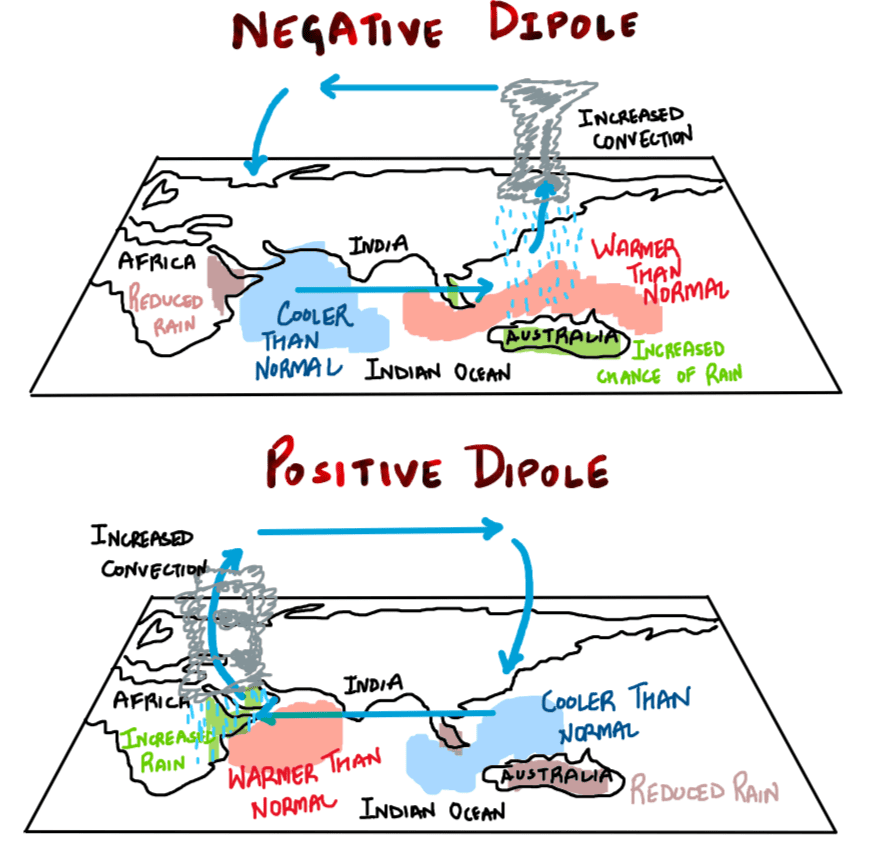
With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)’ sometimes mentioned in the news while forecasting Indian monsoon, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- IOD phenomenon is characterized by a difference in sea surface temperature between tropical Western Indian Ocean and tropical Eastern Pacific Ocean.
- An IOD phenomenon can influence El Nino’s impact on the monsoon. Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2