UPSC Prelims 2017 Analysis
Subject wise MCQ distribution
- Polity and Governance: The highest weightage in the exam, with questions focusing on core constitutional concepts like democracy and rights, highlighting a return to traditional themes. Many followed the assertion-reasoning format, testing analytical abilities.
Economy: Heavily current affairs-based, covering topics such as GST, Monetary Policy Committee, and post-1991 reforms. Conceptual clarity was crucial for elimination-based questions.
Geography and Environment: Required conceptual clarity and linkages with current affairs, such as the Indian Ocean Dipole. Many questions incorporated maps for better understanding.
History: Weightage remained consistent, but factual knowledge was essential, especially for match the following and multi-statement questions.
Science & Technology: Mostly news-based, testing awareness of recent developments in biotechnology, AI, and space technology.
Government Schemes & Initiatives: A prominent focus area, covering policies related to education, health, and nutrition. Many questions were framed using the elimination technique.

Difficulty analysis
- Easy: Some Polity and Economy questions were straightforward for those who had covered NCERT and standard sources.
- Moderate: Many required linking static and dynamic aspects, such as governance and current affairs.
- Difficult: Environment, Geography, and factual History questions were particularly challenging.
- Tricky: Questions on conventions and alliances where India is not a member, along with misleadingly framed government initiative questions, posed difficulties.

Variations in Question framing
- Direct Questions: 42 direct questions, emphasizing understanding over rote memorization.
- Multi-Statement Based Questions: A significant 58 multi-statement questions, requiring a mix of static and current affairs knowledge. These took longer to solve but allowed option elimination.
- Application-Oriented Questions: Required candidates to link current events with static concepts, testing analytical abilities.
- Elimination-Based Questions: Many options were closely framed, making elimination techniques challenging.
- Deceptively Worded Questions: Designed to test deep knowledge, especially in areas like the National Investment and Infrastructure Fund.

Key learning for Future Preparation
- Strengthen Static Concepts: Read NCERTs and standard books thoroughly for a solid foundation.
- Follow a Reliable Newspaper: Sources like The Hindu, Indian Express, PIB, and PRS are essential for current affairs integration.
- Regularly Revise Government Schemes: Many questions are framed around policies from the India Year Book.
- Adopt a Balanced Approach: Expect a mix of analytical and factual questions; both require preparation.
- Use the Elimination Technique Wisely: Read questions carefully and systematically eliminate options to maximize accuracy.
- Avoid Over-Attempting: The tricky nature of the paper means reckless attempts can lead to penalties through negative marking.
- Strengthen Core Subjects: Excelling in Polity or History can help maximize scores in difficult papers.
- Solve Previous Year Papers: Recurring themes like the Trade Disputes Act and Liberalization highlight the importance of PYQs.
Subject-Wise Answer Key
QUESTION 1
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2017
The term 'M-STRIPES’ is sometimes seen in the news in the context of
A. Captive breeding of Wild Fauna
B. Maintenance of Tiger Reserves
C. Indigenous Satellite Navigation System
D. Security of National Highways
QUESTION 2
Easy
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2017
In India, if a species of tortoise is declared protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, what does it imply?
A. It enjoys the same level of protection as the tiger.
B. It no longer exists in the wild, a few individuals are under captive protection, and now it is impossible to prevent its extinction.
C. It is endemic to a particular region of India.
D. Both b and c stated above are correct in this context.
QUESTION 3
Hard
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2017
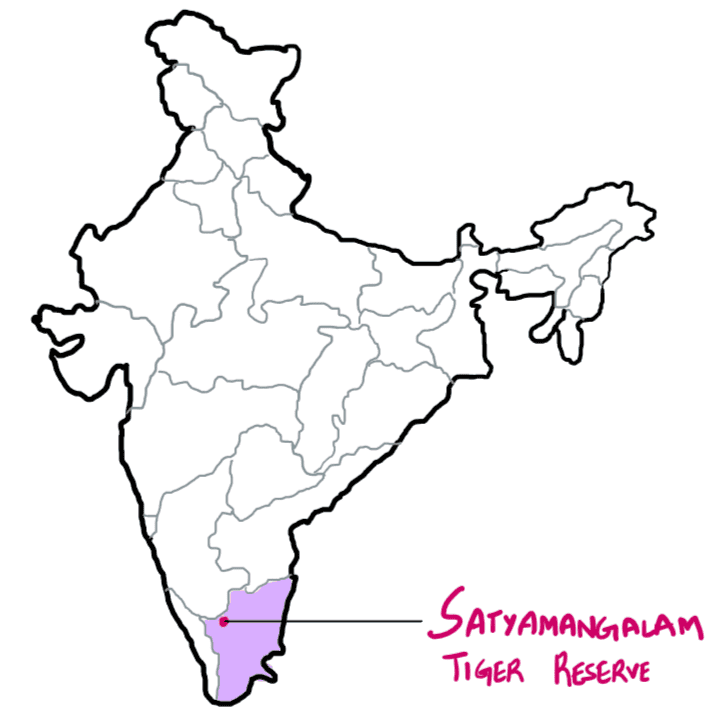
From the ecological point of view, which one of the following assumes importance in being a good link between the Eastern Ghats and the Western Ghats?
A. Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve
B. Nallamala Forest
C. Nagarhole National Park
D. Seshachalam Biosphere Reserve
QUESTION 4
Hard
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2017
Consider the following statements in respect of Trade-Related Analysis of Fauna and Flora in Commerce (TRAFFIC):
- TRAFFIC is a bureau under the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
- The mission of TRAFFIC is to ensure that trade in wild plants and animals is not a threat to the conservation of nature.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 5
Easy
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2017
If you want to see gharials in their natural habitat, which one of the following is the best place to visit?
A. Bhitarkanika Mangroves
B. Chambal River
C. Pulicat Lake
D. Deepor Beel
QUESTION 6
Hard
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2017
Consider the following statements:
- Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC) to Reduce Short-Lived Climate Pollutants is a unique initiative of G20 group of countries.
- The CCAC focuses on methane, black carbon and hydrofluorocarbons.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 7
Hard
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2017
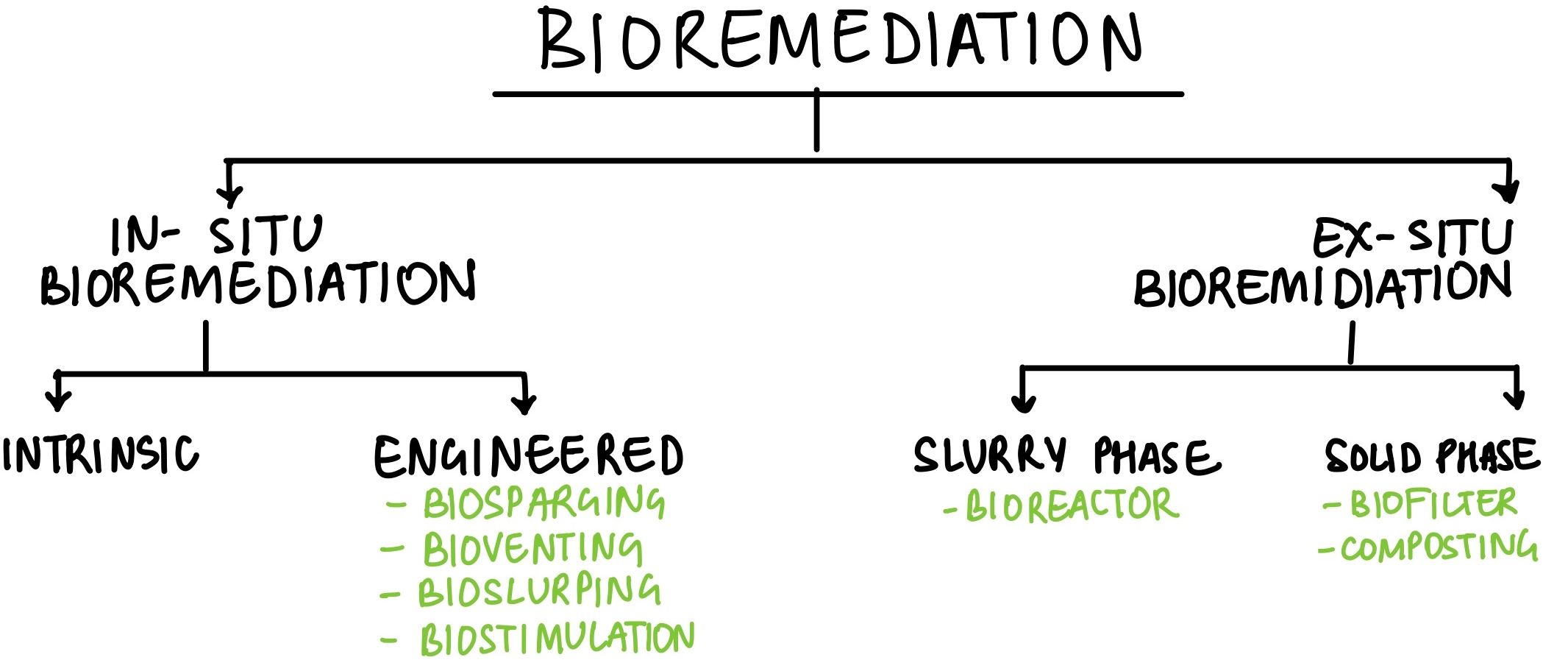
In the context of solving pollution problems, what is/are the advantage/advantages of bioremediation technique?
- It is a technique for cleaning up pollution by enhancing the same biodegradation process that occurs in nature.
- Any contaminant with heavy metals such as cadmium and lead can be readily and completely treated by bioremediation using microorganisms.
- Genetic engineering can be used to create microorganisms specifically designed for bioremediation.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 8
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2017
Recently there was a proposal to translocate some of the lions from their natural habitat in Gujarat to which one of the following sites?
A. Corbett National Park
B. Sariska National Park
C. Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary
D. Kuno Palpur Wildlife Sanctuary
QUESTION 9
Hard
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2017
With reference to ‘Global Climate Change Alliance’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- It is an initiative of the European Union.
- It provides technical and financial support to targeted developing countries to integrate climate change into their development policies and budgets.
- It is coordinated by the World Resources Institute (WRI) and World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD).
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 10
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2017
Which of the following practices can help in water conservation in agriculture?
- Reduced or zero tillage of the land
- Applying gypsum before irrigating the field
- Allowing crop residue to remain in the field
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 11
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2017
Due to some reasons if there is a huge fall in the population of species of butterflies, what could be its likely consequence/consequences?
- Pollination of some plants could be adversely affected.
- There could be a drastic increase in the fungal infections of some cultivated plants.
- It could lead to a fall in the population of some species of wasps, spiders and birds.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 12
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2017
In the context of mitigating the impending global warming due to anthropogenic emissions of carbon dioxide, which of the following can be the potential sites for carbon sequestration?
- Abandoned and uneconomic coal seams
- Depleted oil and gas reservoirs
- Subterranean deep saline formations
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 13
Easy
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2017
According to the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, which of the following animals cannot be hunted by any person except under some provisions provided by law?
- Gharial
- Indian wild ass
- Wild Buffalo
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 14
Easy
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2017
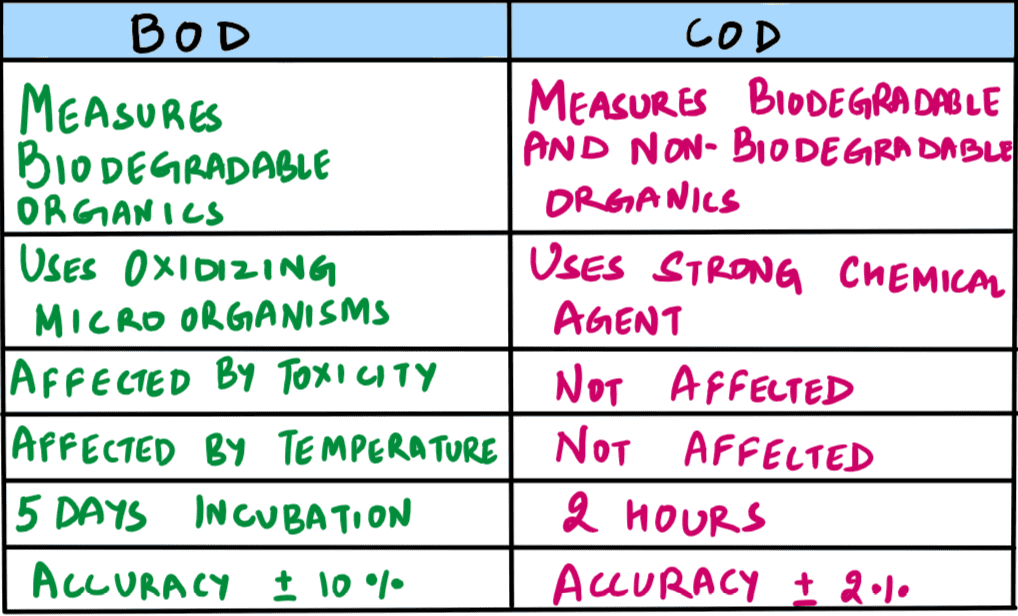
Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) is a standard criterion for -
A. Measuring oxygen levels in the blood
B. Computing oxygen levels in forest ecosystems
C. Pollution assay in aquatic ecosystems
D. Assessing oxygen levels in high altitude regions