UPSC Prelims 2024 Analysis
Subject-Wise MCQ Distribution
- Polity: High representation with 15-20 questions, focusing on constitutional articles, governance, and recent amendments. Analytical abilities were essential to tackle assertion-based and statement-type questions.
- Economy: Approximately 12-15 questions, heavily tilted towards current economic developments, policies, and budget-related topics. A mix of static concepts from NCERT and dynamic updates was necessary.
- Environment & Ecology: 18-20 questions, with a strong emphasis on climate change, international agreements, and conservation efforts. Match the following questions played a significant role in this section.
- History: 12-14 questions, balanced between ancient, medieval, and modern, with increasing weightage on cultural aspects. Many questions required a combination of NCERT knowledge and historical maps for better context.
- Geography: 10-12 questions, mostly applied concepts like map-based and environmental geography questions.
- Science & Technology: 8-10 questions, leaning towards application-based knowledge on recent innovations and space technology.
- Current Affairs: 15-18 questions, interwoven with other subjects, often requiring assertion-reasoning skills to connect facts.

Difficulty Analysis
- Easy: ~30% of questions were straightforward and could be attempted with basic NCERT knowledge.
- Moderate: ~50% required analytical abilities, conceptual clarity, and elimination tactics.
- Difficult: ~20% were tricky, involving multi-layered reasoning or obscure facts.

Variations in Question Framing
- Statement-based MCQs: 60% of questions were framed in a two-statement or three-statement format, testing comprehension, elimination skills, and analytical abilities.
- Assertion-Reasoning: 13% of the questions assessed logical connections between concepts, requiring critical thinking.
- Match the Following: 10% of the questions required mapping terms with their definitions, locations, or features, particularly in Geography and Environment.
- Standalone Questions: 25% were direct, fact-based questions, but even these often required cross-referencing with maps or historical events.
- Notably, in 2024, UPSC introduced three-column Match the Following MCQs, increasing question complexity and demanding better comprehension skills.

Key Learnings for Future Preparation
- Integrated Approach: Focus on interlinking static NCERT subjects with current affairs, as many questions have contextual relevance.
- Master the Basics: A strong foundation in NCERTs is crucial for tackling conceptual questions, especially in Polity, History, and Geography.
- Develop Analytical Abilities: Statement-based and assertion-reasoning questions require critical thinking and elimination tactics.
- Focus on Trends: Emphasize high-yield topics like Environment, Economy, and Current Affairs to maximize scoring potential.
- Revise Maps and Schematics: Geography and Environmental questions often require map-based knowledge and spatial reasoning to answer correctly.
Subject-Wise Answer Key
QUESTION 1
GS
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2024
A Writ of Prohibition is an order issued by the Supreme Court or High Courts to :
A. a government officer prohibiting him from taking a particular action.
B. the Parliament/Legislative Assembly to pass a law on Prohibition.
C. the lower court prohibiting continuation of proceedings in a case.
D. the Government prohibiting it from following an unconstitutional policy.
QUESTION 2
GS
Medium
Indian Polity
Prelims 2024
Who was the Provisional President of the Constituent Assembly before Dr. Rajendra Prasad took over?
A. C. Rajagopalachari
B. Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
C. T.T. Krishnamachari
D. Dr. Sachchidananda Sinha
QUESTION 3
GS
Medium
Indian Polity
Prelims 2024
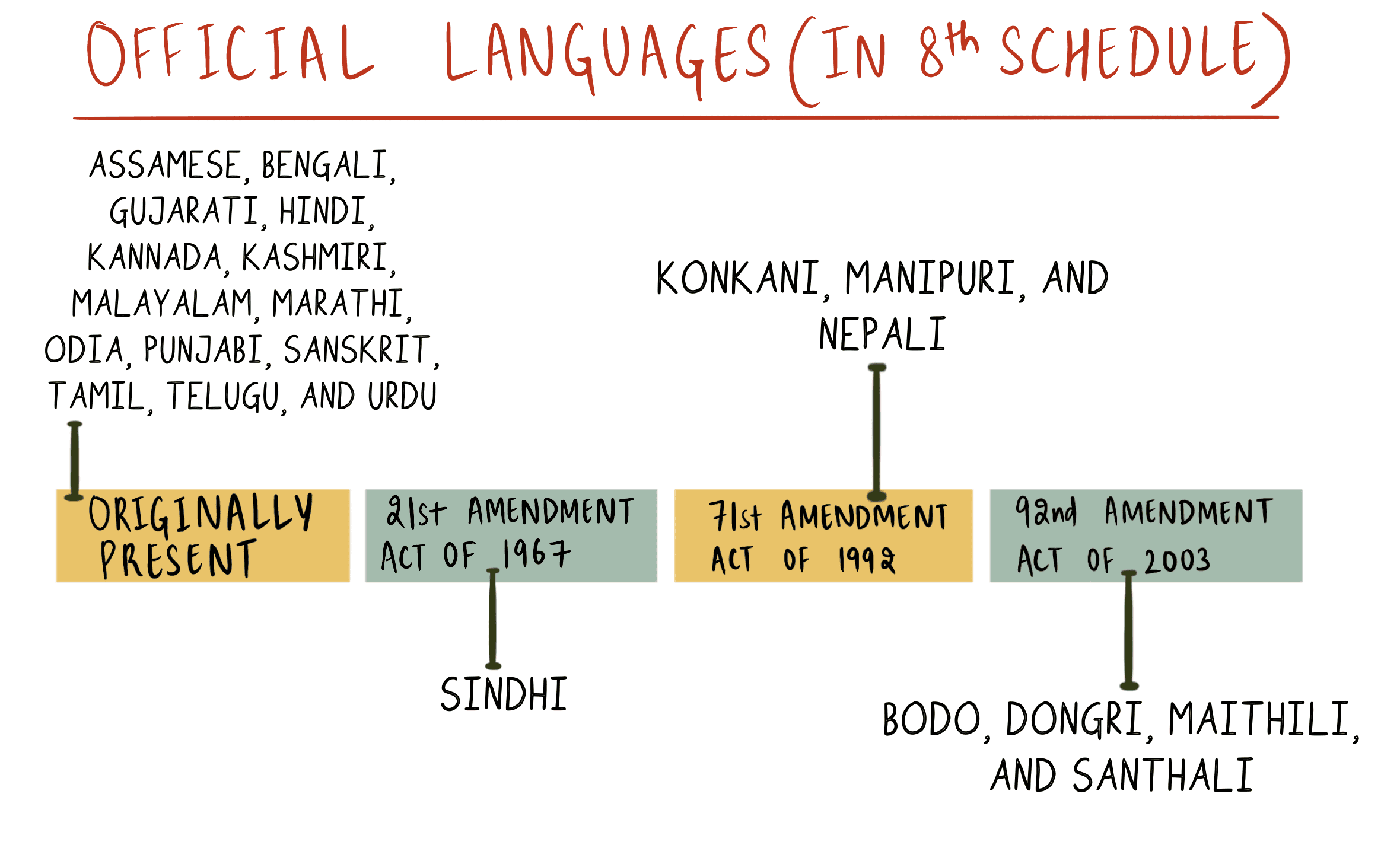
The Constitution (71st Amendment) Act, 1992 amends the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution to include which of the following languages?
- Konkani
- Manipuri
- Nepali
- Maithili
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1, 2 and 3
B. 1, 2 and 4
C. 1, 3 and 4
D. 2, 3 and 4
QUESTION 4
GS
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2024
As per Article 368 of the Constitution of India, the Parliament may amend any provision of the Constitution by way of:
- Addition
- Variation
- Repeal
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 5
GS
Medium
Indian Polity
Prelims 2024
Consider the following statements:
- It is the Governor of the State who recognizes and declares any community of that State as a Scheduled Tribe.
- A community declared as a Scheduled Tribe in a State need not be so in another State.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 6
GS
Medium
Indian Polity
Prelims 2024
The North Eastern Council (NEC) was established by the North Eastern Council Act, 1971. Subsequent to the amendment of NEC Act in 2002, the Council comprises which of the following members?
- Governor of the Constituent State
- Chief Minister of the Constituent State
- Three Members to be nominated by the President of India
- The Home Minister of India
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
A. 1, 2 and 3 only
B. 1, 3 and 4 only
C. 2 and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
QUESTION 7
GS
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2024
Consider the following statements regarding 'Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam':
- Provisions will come into effect from the 18th Lok Sabha.
- This will be in force for 15 years after becoming an Act.
- There are provisions for the reservation of seats for Scheduled Castes Women within the quota reserved for the Scheduled Castes.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
A. 1, 2 and 3
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1 and 3 only
QUESTION 8
GS
Hard
Indian Polity
Prelims 2024
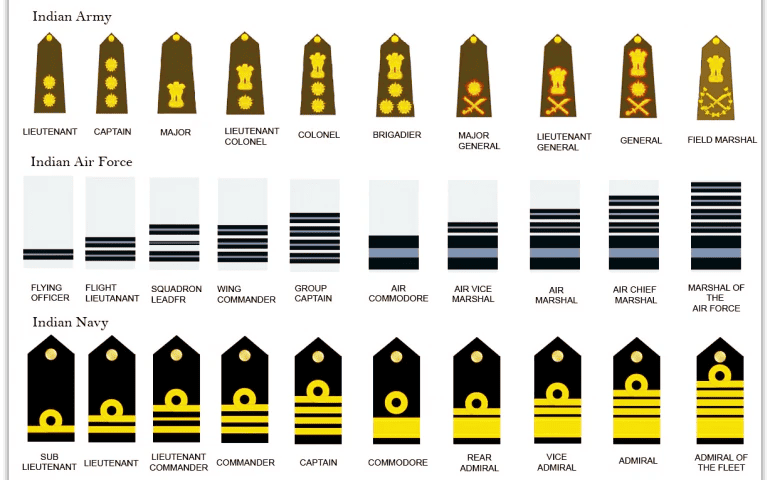
Which of the following is/are correctly matched in terms of equivalent rank in the three services of Indian Defence forces?
| Army | Airforce | Navy |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Brigadier | Air Commodore | Commander |
| 2. Major General | Air Vice Marshal | Vice Admiral |
| 3. Major | Squadron Leader | Lieutenant Commander |
| 4. Lieutenant Colonel | Group Captain | Captain |
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 4
B. 1 and 3
C. 2, 3 and 4
D. 3 only
QUESTION 9
GS
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2024
Under which of the following Articles of the Constitution of India, has the Supreme Court of India placed the Right to Privacy?
A. Article 15
B. Article 16
C. Article 19
D. Article 21
QUESTION 10
GS
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2024
With reference to the Parliament of India, consider the following statements :
- Prorogation of a House by the President of India does not require the advice of the Council of Ministers.
- Prorogation of a House is generally done after the House is adjourned sine die but there is no bar to the President of India prorogating the House which is in session.
- Dissolution of the Lok Sabha is done by the President of India who, save in exceptional circumstances, does so on the advice of the Council of Ministers.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2
C. 2 and 3
D. 3 only
QUESTION 11
GS
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2024
With reference to the Speaker of the Lok Sabha, consider the following statements :
While any resolution for the removal of the Speaker of the Lok Sabha is under consideration
- He/She shall not preside.
- He/She shall not have the right to speak.
- He/She shall not be entitled to vote on the resolution in the first instance.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 12
GS
Medium
Indian Polity
Prelims 2024
Which of the following statements are correct about the Constitution of India?
- Powers of the Municipalities are given in Part IX A of the Constitution.
- Emergency provisions are given in Part XVIII of the Constitution.
- Provisions related to the amendment of the Constitution are given in Part XX of the Constitutions
Select the answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 13
GS
Medium
Indian Polity
Prelims 2024
What are the duties of the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) as Head of the Department of Military Affairs?
- Permanent Chairman of Chiefs of Staff Committee
- Exercise military command over the three Service Chiefs
- Principal Military Advisor to Defence Minister on all tri-service matters
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1, 2 and 3
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1 and 3 only
QUESTION 14
GS
Medium
Indian Polity
Prelims 2024
Which of the following statements about the Ethics Committee in the Lok Sabha are correct?
- Initially it was an ad-hoc Committee.
- Only a Member of the Lok Sabha can make a complaint relating to unethical conduct of a member of the Lok Sabha.
- This Committee cannot take up any matter which is sub-judice.
Select the answer using the code given below :
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 15
GS
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2024
With reference to Union Budget, consider the following statements :
- The Union Finance Minister on behalf of the Prime Minister lays the Annual Financial Statement before both the Houses of Parliament.
- At the Union level, no demand for a grant can be made except on the recommendation of the President of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 16
GS
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2024
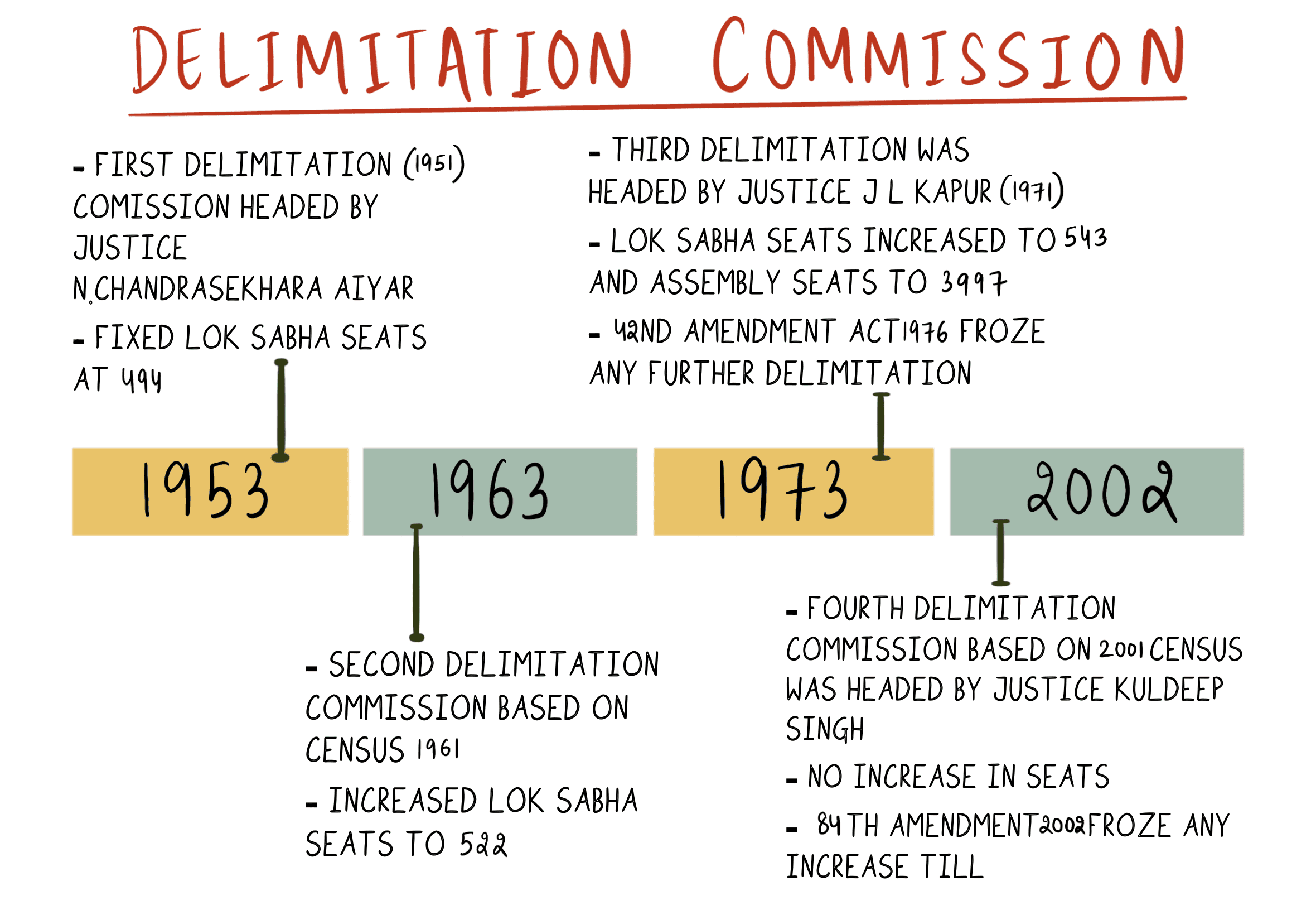
How many Delimitation Commissions have been constituted by the Government of India till December 2023?
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. Four
QUESTION 17
GS
Medium
Indian Polity
Prelims 2024
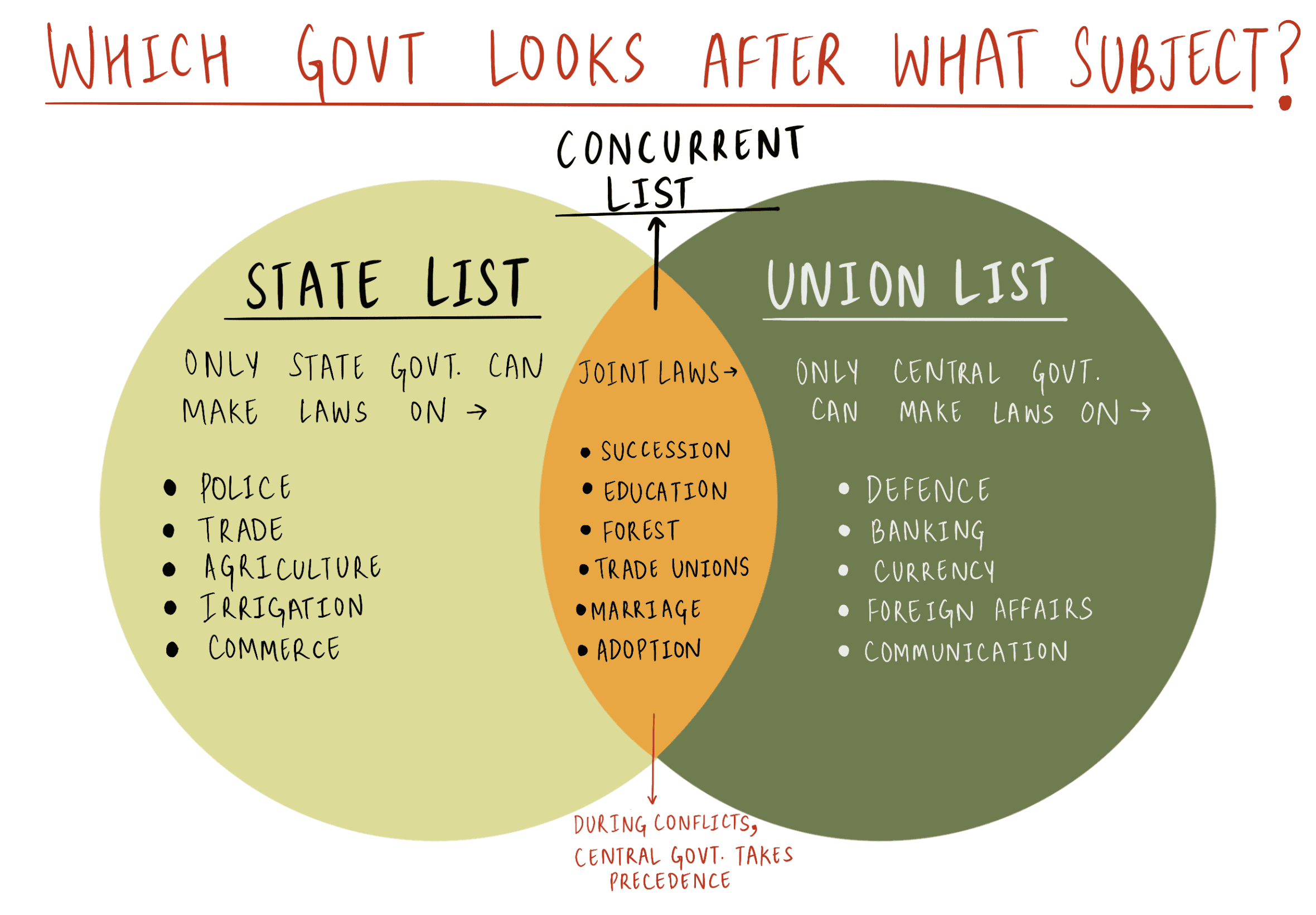
Which one of the following statements is correct as per the Constitution of India?
A. Inter-State trade and commerce is a State subject under the State List.
B. Inter-State migration is a State subject under the State List.
C. Inter-State quarantine is a Union subject under the Union List.
D. Corporation tax is a State subject under the State List.
QUESTION 18
GS
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2024
Which of the following statements are correct in respect of a Money Bill in the Parliament?
- Article 109 mentions special procedure in respect of Money Bills.
- A Money Bill shall not be introduced in the Council of States.
- The Rajya Sabha can either approve the Bill or suggest changes but cannot reject it.
- Amendments to a Money Bill suggested by the Rajya Sabha have to be accepted by the Lok Sabha.
Select the answer using the code given below :
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1, 2 and 3
D. 1, 3 and 4
QUESTION 19
GS
Medium
Indian Polity
Prelims 2024
With reference to the Indian Parliament, consider the following statements:
- A bill pending in the Lok Sabha lapses on its dissolution.
- A bill passed by the Lok Sabha and pending in the Rajya Sabha lapses on the dissolution of the Lok Sabha.
- A bill in regard to which the President of India notified his/her intention to summon the Houses to a joint sitting lapses on the dissolution of the Lok Sabha.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2
C. 2 and 3
D. 3 only