UPSC Prelims 2021 Analysis
Subject-Wise MCQ Distribution
- Environment & Ecology (18 questions): Consistently a major component due to its relevance in both the Civil Services Examination (CSE) and the Indian Forest Service (IFoS) prelims. Several questions required maps for identifying key environmental regions.
- Indian Polity (18 questions): A high-weightage subject with several assertion-based and conceptual questions.
- Economy (14 questions): Covered major economic policies, fiscal measures, and budget-related aspects.
- Science & Technology (13 questions): Focused on innovations, emerging technologies, and applications in real-world scenarios.
- History (24 questions total):
- Ancient History: 3 questions
- Medieval History: 4 questions
- Modern History: 7 questions
- Art & Culture: 10 questions, including match the following-based formats.
- Geography (9 questions total):
- Indian Geography: 5 questions
- Physical Geography: 2 questions
- World Geography: 2 questions
- Social Issues & Schemes (2 questions): Covered important government initiatives and their societal impact.
- International Relations (2 questions): Focused on international organizations and global events, underlining the importance of reading newspapers and NCERT basics.

Difficulty Analysis
- Easy (35 questions): Required fundamental NCERT knowledge and factual recall.
- Medium (38 questions): Needed deeper analytical abilities and elimination techniques.
- Hard (27 questions): Demanded conceptual clarity, particularly in assertion-reasoning and interdisciplinary topics.

Variations in Question Framing
- Multi-Statement Based Questions: A large portion of the paper tested analytical abilities by requiring candidates to determine the correctness of multiple statements.
- Direct Questions: Some questions were fact-based, relying on static knowledge from textbooks and previous UPSC question papers.
- Application-Based Questions: Many questions in Economy and Science & Technology assessed real-world applications of concepts.
- Match the Following: Commonly seen in Art & Culture, Geography, and Environment sections.

Static vs Current Affairs Distribution
- Static Content: Dominated the paper with key subjects like History, Polity, Geography, and Economy forming the foundation.
- Current Affairs (22 questions): Focused on recent government policies, budget highlights, and global events influencing India.
Key Learnings for Future Preparation
- Master Static & Current Affairs: A blend of both is necessary, especially for high-weightage subjects like Polity, Economy, and Environment.
- Strengthen Analytical Abilities: Many questions required assertion-reasoning, elimination techniques, and multi-statement evaluation.
- Focus on Budget & Economic Policies: Economy and budget-related topics remain crucial for UPSC preparation.
- Practice Match the Following & Statement-Based MCQs: These were heavily featured in Geography, History, and Environment sections.
- Utilize Maps for Geography & Environment: Many UPSC last year question papers have included map-based questions, making this an essential skill.
Subject-Wise Answer Key
QUESTION 1
Hard
Modern History
Prelims 2021
With reference to Madanapalle of Andhra Pradesh, which one of the following statements is correct?
A. Pingali Venkayya designed the tricolour Indian National Flag here.
B. Pattabhi Sitaramaiah led the Quit India Movement of Andhra region from here.
C. Rabindranath Tagore translated the National Anthem from Bengali to English here.
D. Madame Blavastsky and Colonel Olcott set up headquarters of Theosophical Society first here.
QUESTION 2
Medium
Modern History
Prelims 2021
Consider the following statements:
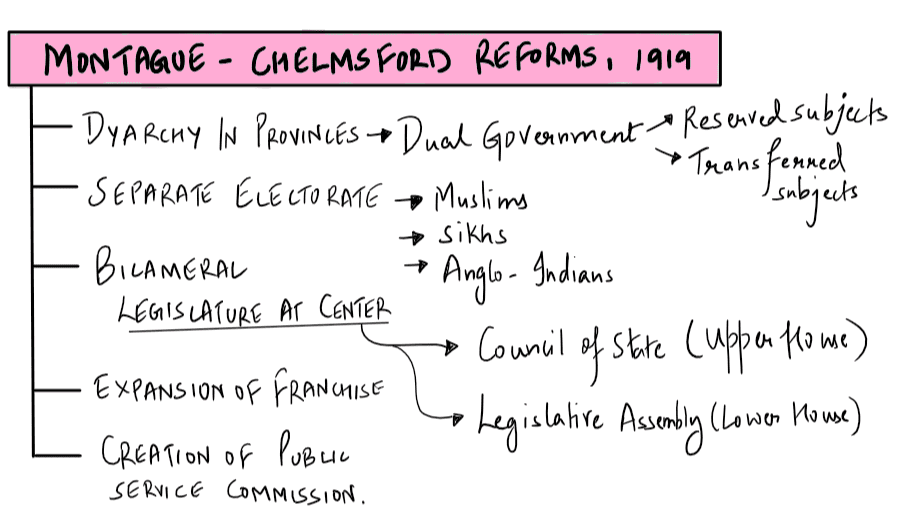
- The Montagu-Chelmsford Reforms of 1919 recommended granting voting rights to all the women above the age 21.
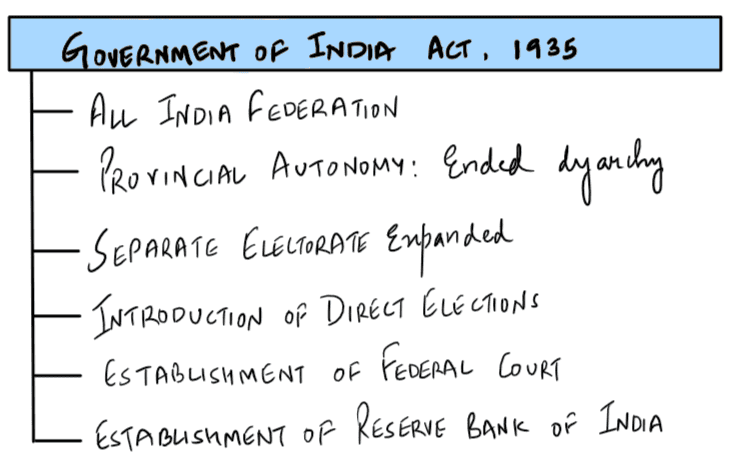
- The Government of India Act of 1935 gave women reserved seats in legislature.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 3
Easy
Modern History
Prelims 2021
In the context of Colonial India, Shah Nawaz Khan, Prem Kumar Sehgal, and Gurbaksh Singh Dhillon are remembered as
A. Leaders of Swadeshi and Boycott Movement.
B. Members of the Interim Government in 1946.
C. Members of the Drafting Committee in the Constituent Assembly.
D. Officers of the Indian National Army
QUESTION 4
Medium
Modern History
Prelims 2021
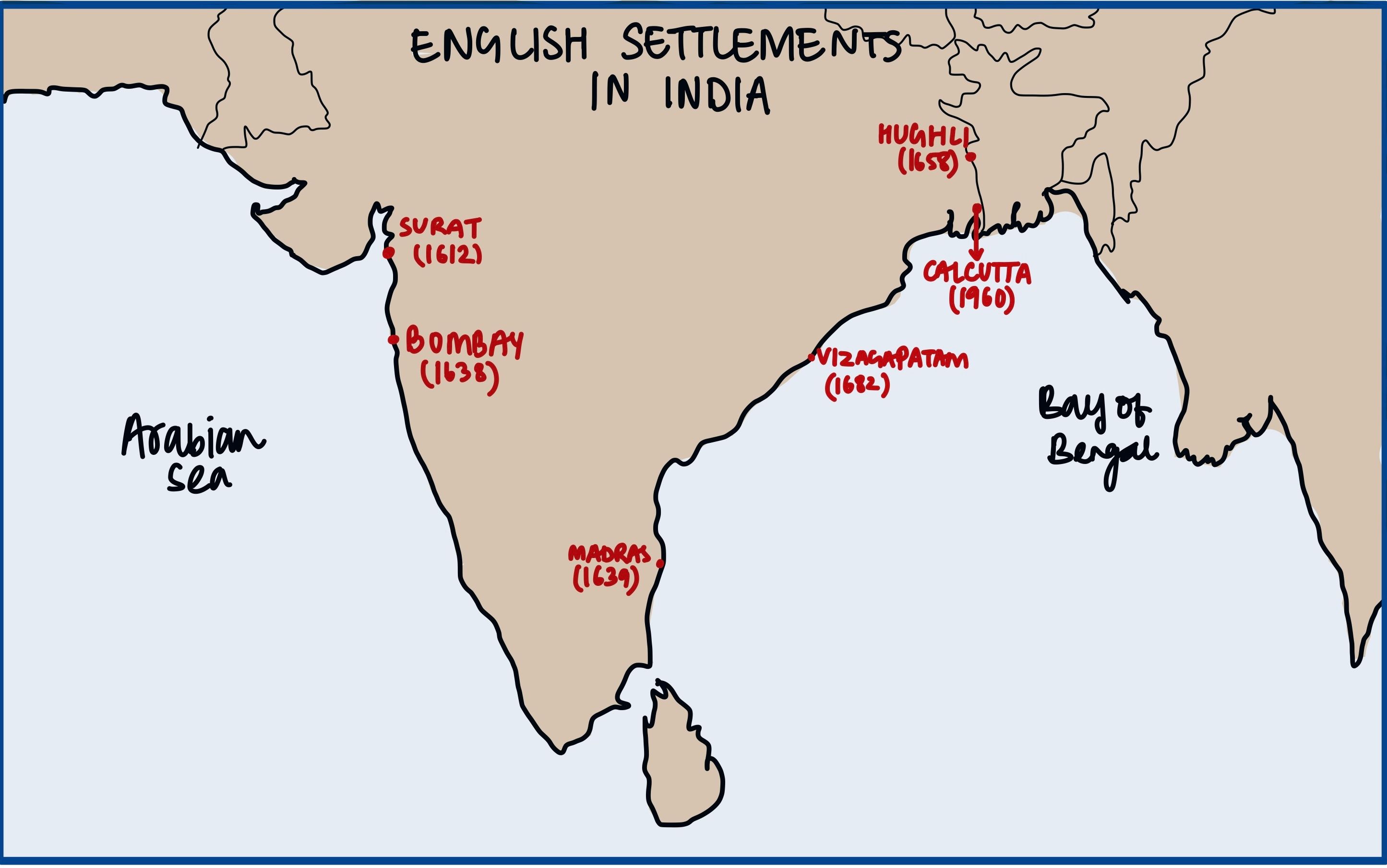
In the first quarter of the seventeenth century, in which of the following was/were the factory/factories of the English East India Company located?
- Broach
- Chicacole
- Trichinopoly
Select the correct answer using the codes given below
A. 1 Only
B. 1 and 2
C. 3 only
D. 2 and 3
QUESTION 5
Hard
Modern History
Prelims 2021
Who among the following is associated with ‘Songs from Prison’, a translation of ancient Indian religious lyrics in English?
A. Bal Gangadhar Tilak
B. Jawaharlal Nehru
C. Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi
D. Sarojini Naidu
QUESTION 6
Easy
Modern History
Prelims 2021
Who among the following was associated as Secretary with Hindu Female School which later came to be known as Bethune Female School?
A. Annie Besant
B. Debendranath Tagore
C. Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar
D. Sarojini Naidu
QUESTION 7
Easy
Modern History
Prelims 2021
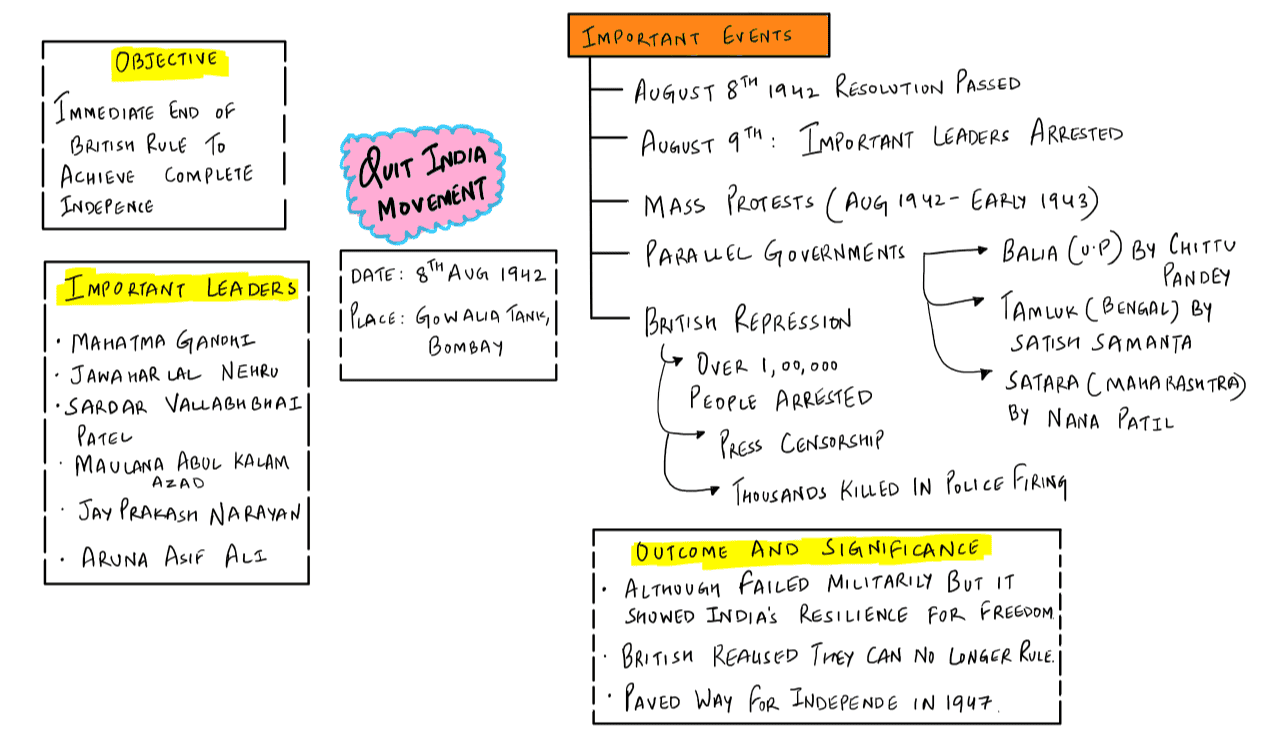
With reference to 8th August 1942 in Indian history, which one of the following statements is correct?
A. The Quit India Resolution was adopted by the AICC.
B. The Viceroy’s Executive council was expanded to include more Indians.
C. The Congress ministries resigned in seven provinces.
D. Cripps proposed an Indian Union with full Dominion Status once the Second World War was over.