UPSC Prelims 2021 Analysis
Subject-Wise MCQ Distribution
- Environment & Ecology (18 questions): Consistently a major component due to its relevance in both the Civil Services Examination (CSE) and the Indian Forest Service (IFoS) prelims. Several questions required maps for identifying key environmental regions.
- Indian Polity (18 questions): A high-weightage subject with several assertion-based and conceptual questions.
- Economy (14 questions): Covered major economic policies, fiscal measures, and budget-related aspects.
- Science & Technology (13 questions): Focused on innovations, emerging technologies, and applications in real-world scenarios.
- History (24 questions total):
- Ancient History: 3 questions
- Medieval History: 4 questions
- Modern History: 7 questions
- Art & Culture: 10 questions, including match the following-based formats.
- Geography (9 questions total):
- Indian Geography: 5 questions
- Physical Geography: 2 questions
- World Geography: 2 questions
- Social Issues & Schemes (2 questions): Covered important government initiatives and their societal impact.
- International Relations (2 questions): Focused on international organizations and global events, underlining the importance of reading newspapers and NCERT basics.

Difficulty Analysis
- Easy (35 questions): Required fundamental NCERT knowledge and factual recall.
- Medium (38 questions): Needed deeper analytical abilities and elimination techniques.
- Hard (27 questions): Demanded conceptual clarity, particularly in assertion-reasoning and interdisciplinary topics.

Variations in Question Framing
- Multi-Statement Based Questions: A large portion of the paper tested analytical abilities by requiring candidates to determine the correctness of multiple statements.
- Direct Questions: Some questions were fact-based, relying on static knowledge from textbooks and previous UPSC question papers.
- Application-Based Questions: Many questions in Economy and Science & Technology assessed real-world applications of concepts.
- Match the Following: Commonly seen in Art & Culture, Geography, and Environment sections.

Static vs Current Affairs Distribution
- Static Content: Dominated the paper with key subjects like History, Polity, Geography, and Economy forming the foundation.
- Current Affairs (22 questions): Focused on recent government policies, budget highlights, and global events influencing India.
Key Learnings for Future Preparation
- Master Static & Current Affairs: A blend of both is necessary, especially for high-weightage subjects like Polity, Economy, and Environment.
- Strengthen Analytical Abilities: Many questions required assertion-reasoning, elimination techniques, and multi-statement evaluation.
- Focus on Budget & Economic Policies: Economy and budget-related topics remain crucial for UPSC preparation.
- Practice Match the Following & Statement-Based MCQs: These were heavily featured in Geography, History, and Environment sections.
- Utilize Maps for Geography & Environment: Many UPSC last year question papers have included map-based questions, making this an essential skill.
Subject-Wise Answer Key
QUESTION 1
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2021
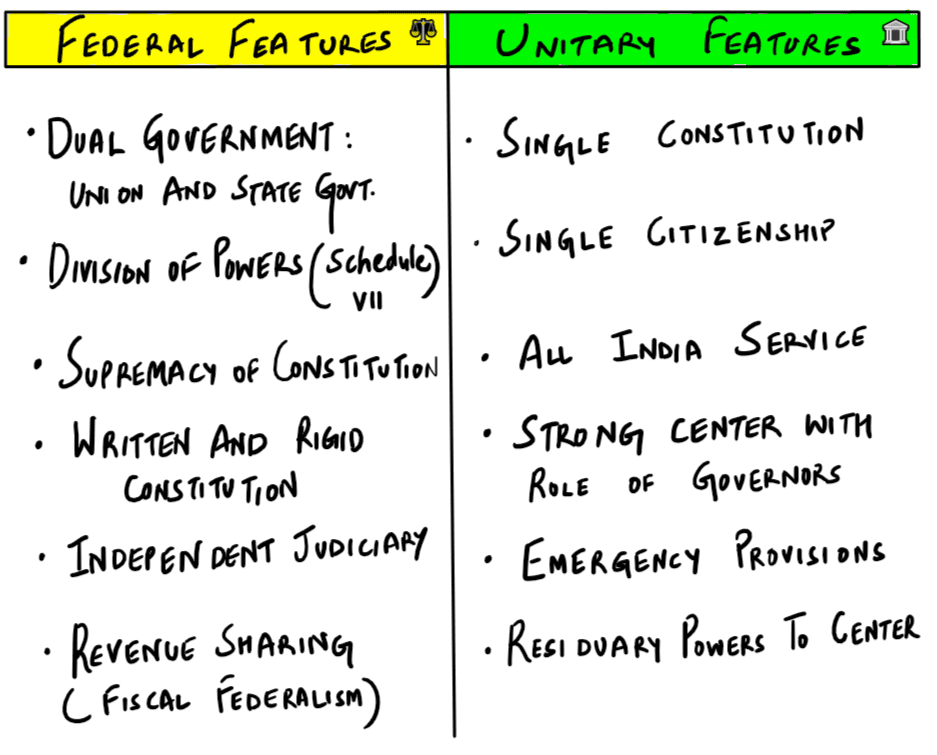
Which one of the following in Indian polity is an essential feature that indicates that it is federal in character?
A. The independence of judiciary is safeguarded.
B. The Union Legislature has elected representatives from constituent units.
C. The Union Cabinet can have elected representatives from regional parties.
D. The Fundamental Rights are enforceable by Courts of Law.
QUESTION 2
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2021
What is the position of the Right to Property in India?
A. Legal right available to citizens only
B. Legal right available to any person
C. Fundamental Right available to citizens only
D. Neither Fundamental Right nor legal right
QUESTION 3
Hard
Indian Polity
Prelims 2021
With reference to the Union Government, consider the following statements:
- N. Gopalaswamy Iyengar Committee suggested that a minister and a secretary be designated solely for pursuing the subject of administrative reform and promoting it.
- In 1970, the Department of Personnel was constituted on the recommendation of the Administrative Reforms Commission, 1966, and this was placed under the Prime Minister’s charge.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 Only
B. 2 Only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 4
Hard
Indian Polity
Prelims 2021
Consider the following statements:
- ‘Right to the City’ is an agreed human right and the UN-Habitat monitors the commitments made by each country in this regard.
- ‘Right to the City’ gives every occupant of the city the right to reclaim public spaces and public participation in the city.
- ‘Right to the City’ means that the State cannot deny any public service or facility to the unauthorized colonies in the city.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct:
A. 1 only
B. 3 only
C. 1 and 2
D. 2 and 3
QUESTION 5
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2021
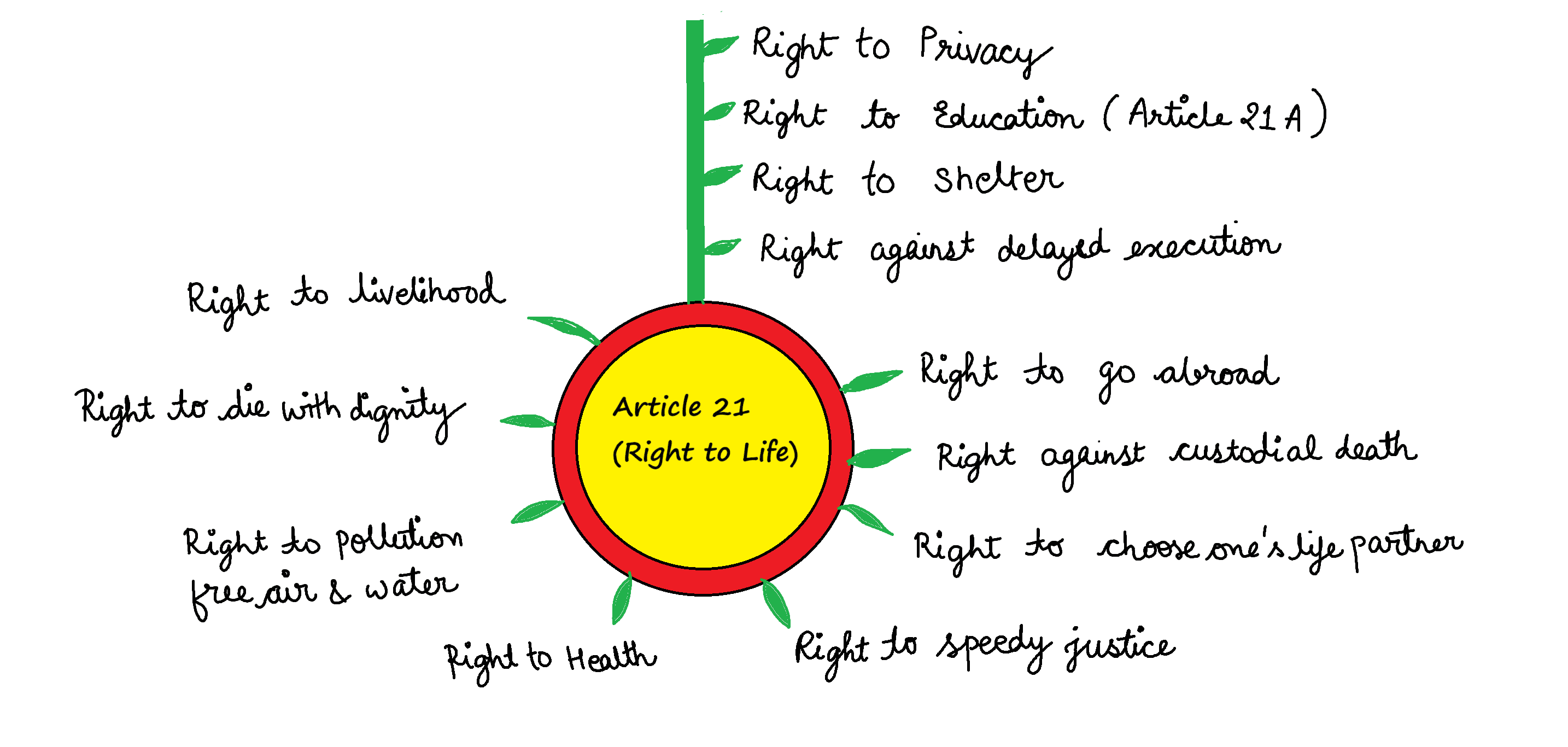
‘Right to privacy’ is protected under which Article of the Constitution of India?
A. Article 15
B. Article 19
C. Article 21
D. Article 29
QUESTION 6
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2021
Which one of the following best defines the term ‘State’?
A. A community of persons permanently occupying a definite territory independent of external control and possessing an organized government.
B. A politically organized people of a definite territory and possessing an authority to govern them, maintain law and order, protect their natural rights and safeguard their means of sustenance.
C. A number of persons who have been living in a definite territory for a very long time with their own culture, tradition, and government.
D. A society permanently living in a definite territory with a central authority, an executive responsible to the central authority, and an independent judiciary.
QUESTION 7
Hard
Indian Polity
Prelims 2021
With reference to India, consider the following statements:
- When a prisoner makes out a sufficient case, parole cannot be denied to such prisoner because it becomes a matter of his/her right.
- State Governments have their own Prisoners Release on Parole Rules.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 Only
B. 2 Only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 8
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2021
At the national level, which ministry is the nodal agency to ensure effective implementation of the Scheduled Tribes and other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006?
A. Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change
B. Ministry of Panchayati Raj
C. Ministry of Rural Development
D. Ministry of Tribal Affairs
QUESTION 9
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2021
A legislation which confers on the executive or administrative authority an unguided and uncontrolled discretionary power in the matter of application of law violates which one of the following Articles of the Constitution of India?
A. Article 14
B. Article 28
C. Article 32
D. Article 44
QUESTION 10
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2021
Constitutional government means
A. a representative government of a nation with federal structure.
B. a government whose Head enjoys nominal powers.
C. a government whose Head enjoys real power.
D. a government limited by the terms of the constitution
QUESTION 11
Hard
Indian Polity
Prelims 2021
With reference to India, consider the following statements:
- Judicial custody means an accused is in the custody of the concerned magistrate and such accused is locked up in police station, not in Jail.
- During judicial custody, the police officer in charge of the case is not allowed to interrogate the suspect without the approval of the court.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct:
A. 1 Only
B. 2 Only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 12
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2021
We adopted parliamentary democracy based on the British model, but how does our model differ from that model?
- As regards legislation, the British Parliament is supreme or sovereign but in India, the power of the Parliament to legislate is limited.
- In India, matters related to the constitutionality of the Amendment of an Act of the Parliament are referred to the Constitution Bench by the Supreme Court
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
A. 1 Only
B. 2 Only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 13
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2021
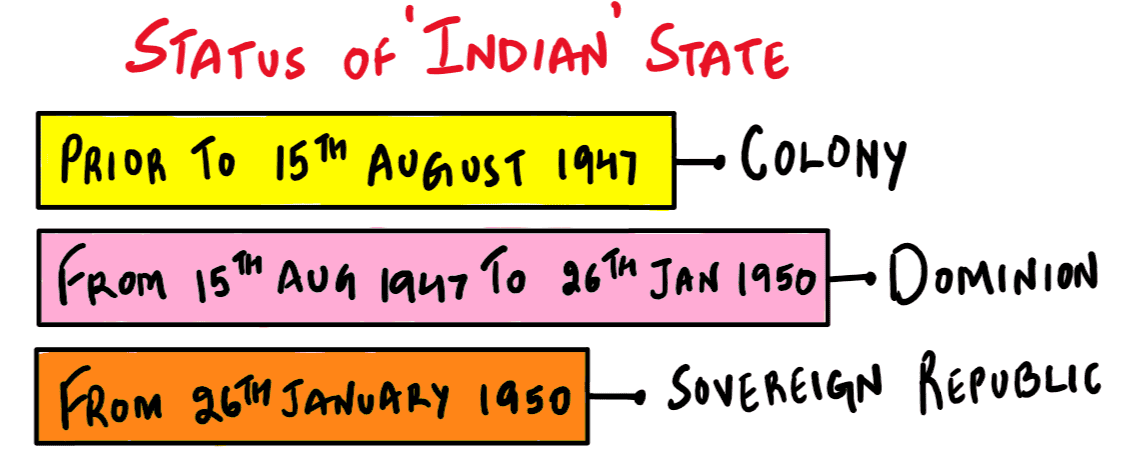
What was the exact constitutional status of India on 26th January 1950?
A. A Democratic Republic
B. A Sovereign Democratic Republic
C. Sovereign Secular Democratic Republic
D. A Sovereign Socialist Secular Democratic Republic
QUESTION 14
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2021
With reference to India, consider the following statements:
- There is only one citizenship and one domicile.
- A citizen by birth only can become the Head of State.
- A foreigner once granted the citizenship cannot be deprived of it under any circumstances.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 Only
B. 2 Only
C. 1 and 3
D. 2 and 3
QUESTION 15
Medium
Indian Polity
Prelims 2021
Which one of the following factors constitutes the best safeguard of liberty in a liberal democracy?
A. A committed judiciary
B. Centralization of powers
C. Elected government
D. Separation of powers
QUESTION 16
Hard
Indian Polity
Prelims 2021
Consider the following statements:
- In India, there is no law restricting the candidates from contesting in one Lok Sabha election from three constituencies.
- In 1991, Lok Sabha Election, Shri Devi Lal contested from three Lok Sabha constituencies
- As per the existing rules, if a candidate contests in one Lok Sabha election from many constituencies, his/her party should bear the cost of bye-elections to the constituencies vacated by him/her in the event of him/her winning in all the constituencies.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 Only
B. 2 Only
C. 1 and 3
D. 2 and 3
QUESTION 17
Medium
Indian Polity
Prelims 2021
With reference to Indian Judiciary, consider the following statements:
- Any retired judge of the Supreme Court of India can be called back to sit and act as a Supreme Court judge by the Chief Justice of India with prior permission of the President of India.
- A High Court in India has the power to review its own judgement as the Supreme Court does.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 Only
B. 2 Only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 18
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2021
Under the Indian Constitution, the concentration of wealth violates:
A. The Right to Equality
B. The Directive Principles of State Policy
C. The Right to Freedom
D. The Concept of Welfare