UPSC Prelims 2018 Analysis
Subject wise MCQ distribution
- Economy (20 Questions): The highest weightage in the paper, covering macroeconomic indicators, policies, and economic development themes. Analytical abilities were essential to interpret trends.
- Environment & Ecology (15 Questions): A significant presence, likely reflecting UPSC’s increasing focus on climate change, biodiversity, and sustainable development. Maps were useful in location-based questions.
- Indian Polity (15 Questions): A core subject, testing governance, constitutional provisions, and landmark judgments. Many questions followed an assertion-reasoning pattern.
- Modern History (13 Questions): A relatively high emphasis on the freedom struggle, key personalities, and movements.
- Science & Technology (12 Questions): Covered advancements in AI, biotechnology, and space technology, requiring both static and current knowledge.
- Art & Culture (7 Questions): More weightage than in some later years, indicating an expectation for deeper knowledge of cultural heritage.
- International Relations (7 Questions): Focused on global organizations, treaties, and India's foreign policy.
- Medieval History (1 Question): Minimal representation, following the usual trend of fewer medieval history questions.
- Geography (Indian Geography: 4, Physical Geography: 2, World Geography: 0): The focus was on Indian geography, with limited physical geography and no direct world geography questions.

Difficulty analysis
- Medium Difficulty (50 Questions): The largest segment, requiring a balance of factual knowledge and application skills.
- Hard Questions (29 Questions): A significant portion of the paper, making elimination techniques and conceptual clarity essential.
- Easy Questions (21 Questions): Fewer than in later years, indicating a relatively tougher paper.
The 2018 Prelims had tougher questions than before, which made them hard to solve. This is reflected in the final cut-off, which was only 98 marks.

Variations in Question framing
Multi-Statement Questions (58%):
- The most common type, requiring elimination techniques and conceptual clarity.
- Particularly prevalent in Polity, Economy, and Environment sections.
- Many followed match the following and assertion-reasoning formats.
Direct Questions (42%):
- Straightforward factual questions, especially in History and Geography.
- Easier to score but required precise knowledge.

Current Affairs vs. Static Questions
- Current Affairs-Based (44 Questions): UPSC maintained a strong current affairs focus, particularly in Economy, Science & Technology, and International Relations.
- Static (56 Questions): A balanced approach, with a considerable portion testing foundational knowledge, often derived from NCERT books.
Key learning for Future Preparation
- Strengthen Economy and Polity: These subjects consistently hold high weightage and require an in-depth understanding of fundamental concepts.
- Master Multi-Statement Questions: Since a majority of questions require elimination skills, practice structured reasoning techniques.
- Balance Static and Current Affairs: While static knowledge remains crucial, integrating dynamic current developments is essential for scoring well.
- Prepare for Moderate to Hard Questions: The paper had a higher proportion of challenging questions, so aspirants should refine their approach to conceptual application and strategic guessing.
- History and Culture Awareness: Despite variations in different years, Art & Culture and Modern History continue to hold importance, making them key focus areas.
Subject-Wise Answer Key
QUESTION 1
Hard
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2018
"Momentum for Change: Climate Neutral Now" is an initiative launched by
A. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
B. The UNEP Secretariat
C. The UNFCCC Secretariat
D. The World Meteorological Organisation
QUESTION 2
Hard
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2018
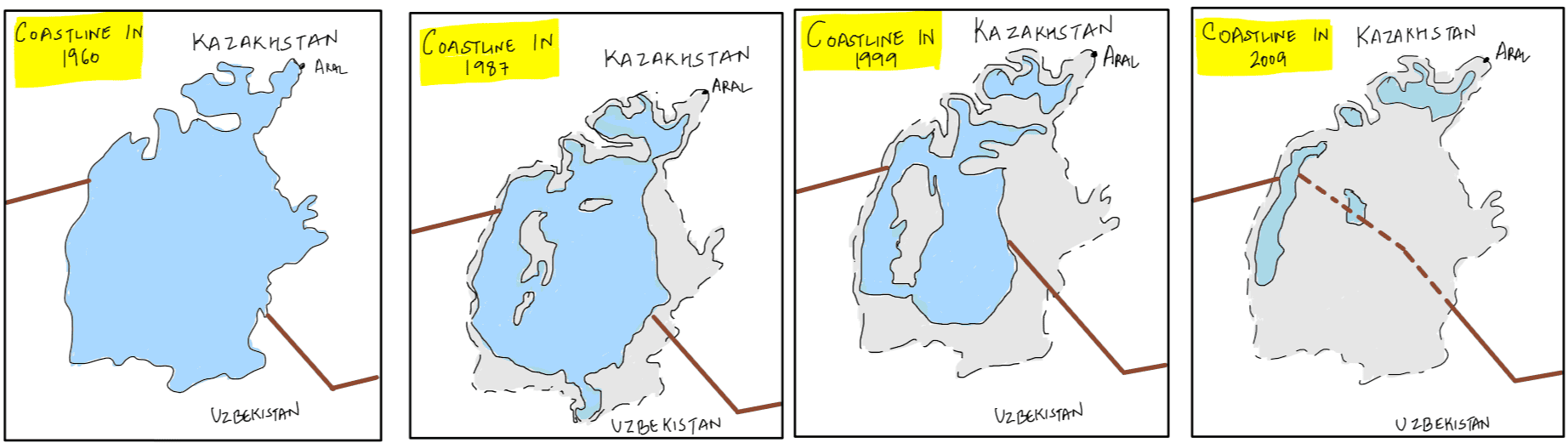
Which of the following has/have shrunk immensely/dried up in the recent past due to human activities?
- Aral Sea
- Black Sea
- Lake Baikal
A. 1 and 3
B. 2 and 3
C. 2 only
D. 1 only
QUESTION 3
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2018
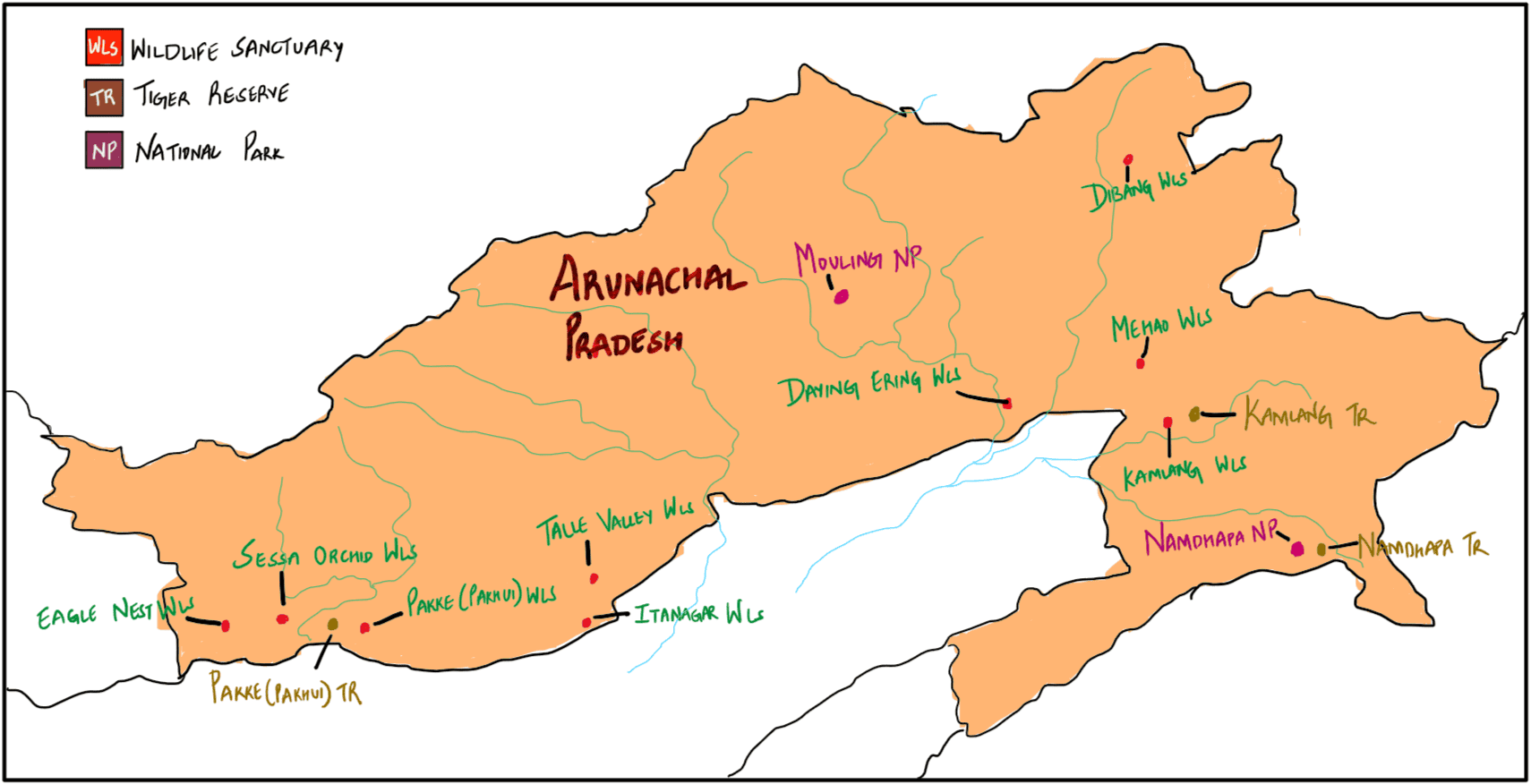
In which one of the following States is Pakhui Wildlife Sanctuary located?
A. Arunachal Pradesh
B. Manipur
C. Meghalaya
D. Nagaland
QUESTION 4
Easy
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2018
The term "sixth mass extinction/sixth extinction" is often mentioned in the news in the context of the discussion of
A. Widespread monoculture practices in agriculture and large-scale commercial farming with indiscriminate use of chemicals in many parts of the world that may result in the loss of good native ecosystems.
B. Fears of a possible collision of a meteorite with the Earth in the near future in the manner it happened 65 million years ago that caused the mass extinction of many species including those of dinosaurs.
C. Large scale cultivation of genetically modified crops in many parts of the world and promoting their cultivation in other parts of the world which may cause the disappearance of good native crop plants and the loss of food biodiversity.
D. Mankind's over-exploitation/misuse of natural resources, fragmentation/loss of natural habitats, destruction of ecosystems, pollution and global climate change.
QUESTION 5
Hard
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2018
With reference to solar power production in India, consider the following statements:
- India is the third largest in the world in the manufacture of silicon wafers used in photovoltaic units.
- The solar power tariffs are determined by the Solar Energy Corporation of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 6
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2018
How is the National Green Tribunal (NGT) different from the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB)?
- The NGT has been established by an Act whereas the CPCB has been created by executive order of the Government.
- The NGT provides environmental justice and helps reduce the burden of litigation in the higher courts whereas the CPCB promotes cleanliness of streams and wells, and aims to improve the quality of air in the country.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. 1 and 2
D. None of the above
QUESTION 7
Easy
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2018
Why is a plant called Prosopis juliflora often mentioned in the news?
A. Its extract is widely used in cosmetics.
B. It tends to reduce the biodiversity in the area in which it grows.
C. Its extract is used in the synthesis of pesticides.
D. None of the above
QUESTION 8
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2018
With reference to agricultural soils, consider the following statements :
- The high content of organic matter in soil drastically reduces its water holding capacity.
- Soil does not play any role in the sulphur cycle.
- Irrigation over a period of time can contribute to the salinization of some agricultural lands.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 9
Hard
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2018
With reference to the 'Global Alliance for Climate-Smart Agriculture (GACSA)', which of the following statements is/are correct.
- GACSA is an outcome of the Climate Summit held in Paris in 2015.
- Membership of GACSA does not create any binding obligations.
- India was instrumental in the creation of GACSA.
Select the correct answer using the code given
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 10
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2018
Which of the following is/are the possible consequence/s of heavy sand mining in riverbeds?
- Decreased salinity in the river
- Pollution of groundwater
- Lowering of the water-table
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 11
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2018
The Partnership for Action on Green Economy (PAGE), a UN mechanism to assist countries transition towards greener and more inclusive economies, emerged at
A. The Earth Summit on Sustainable Development 2002, Johannesburg
B. The United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development 2012, Rio de Janeiro
C. The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change 2015, Paris
D. The World Sustainable Development Summit 2016, New Delhi
QUESTION 12
Easy
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2018
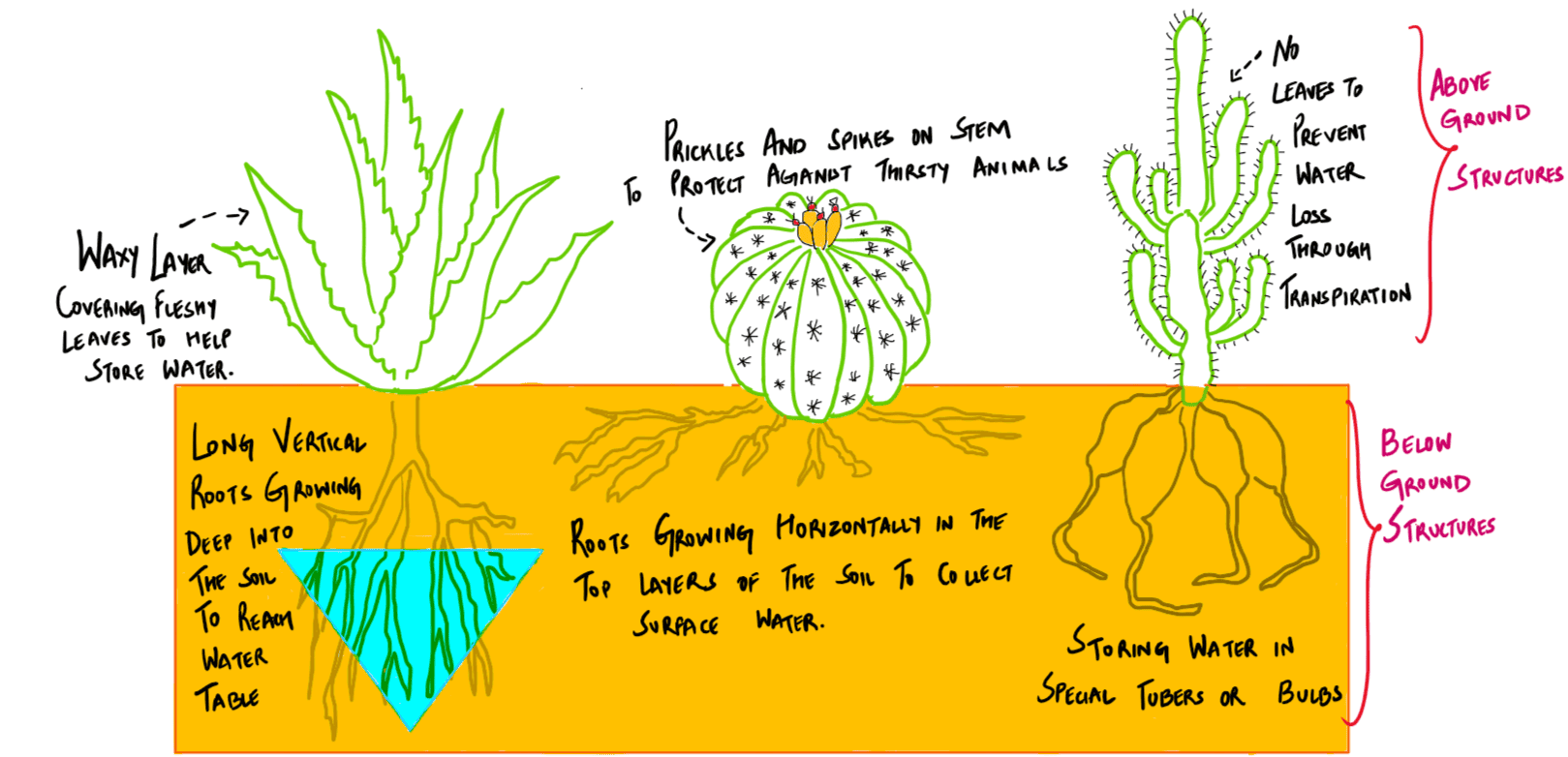
Which of the following leaf modifications occur(s) in the desert areas to inhibit water loss?
- Hard and waxy leaves
- Tiny leaves
- Thorns instead of leaves
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 2 and 3 only
B. 2 only
C. 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 13
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2018
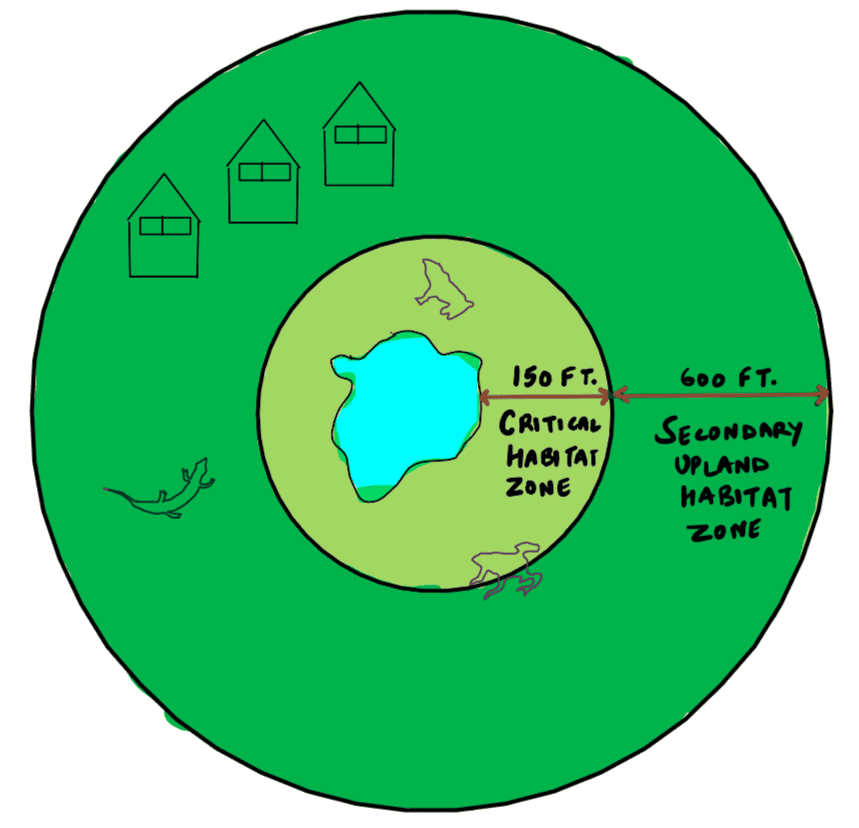
Consider the following statements:
- The definition of "Critical Wildlife Habitat" is incorporated in the Forest Rights Act, 2006.
- For the first time in India, Baigas have been given Habitat Rights.
- Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change officially decides and declares Habitat Rights for Primitive and Vulnerable Tribal Groups in any part of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct ?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 14
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2018
Which of the following statements best describes "carbon fertilization"?
A. Increased plant growth due to increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
B. Increased temperature of Earth due to increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
C. Increased acidity of oceans as a result of increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
D. Adaptation of all living beings on Earth to the climate change brought about hr the increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
QUESTION 15
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2018
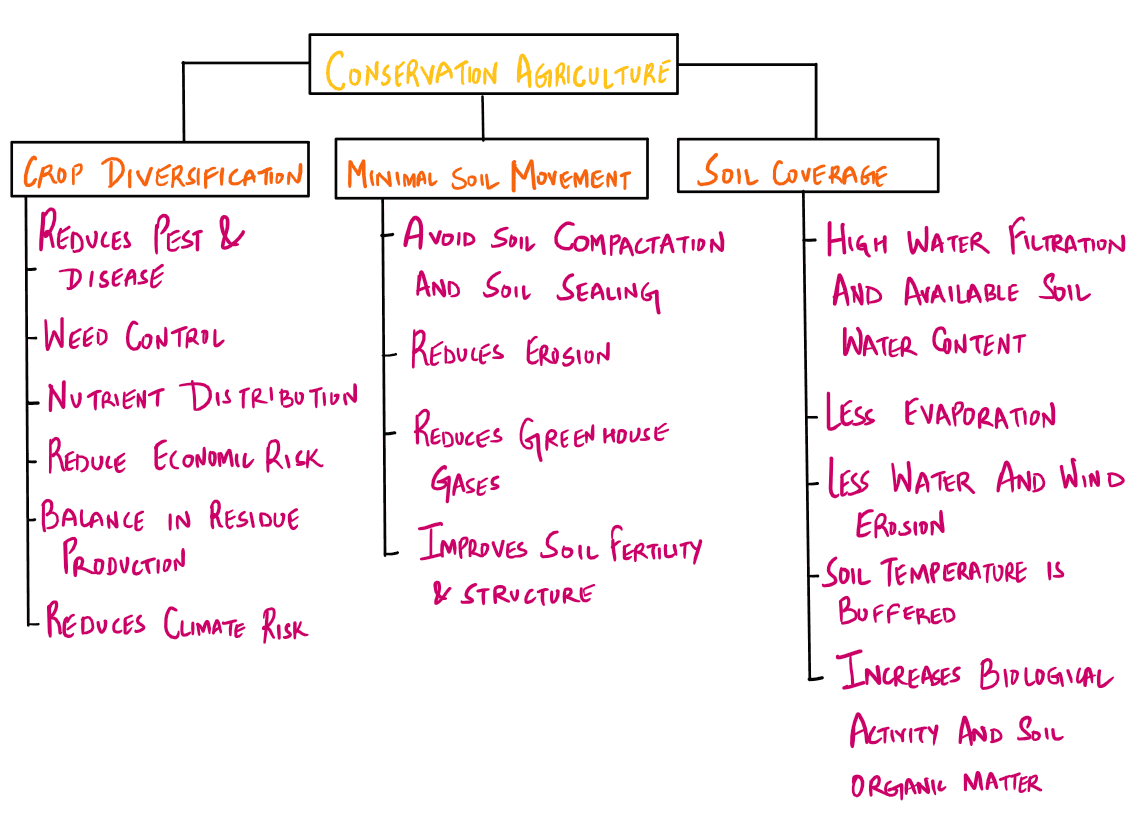
With reference to the circumstances in Indian agriculture, the concept of "Conservation Agriculture" assumes significance. Which of the following fall under the Conservation Agriculture?
- Avoiding monoculture practices
- Adopting minimum tillage
- Avoiding the cultivation of plantation crops
- Using crop residues to cover the soil surface
- Adopting spatial and temporal crop sequencing/crop rotations
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1, 3 and 4
B. 2, 3, 4 and 5
C. 1, 2, 3 and 5
D. 2, 4 and 5