UPSC Prelims 2018 Analysis
Subject wise MCQ distribution
- Economy (20 Questions): The highest weightage in the paper, covering macroeconomic indicators, policies, and economic development themes. Analytical abilities were essential to interpret trends.
- Environment & Ecology (15 Questions): A significant presence, likely reflecting UPSC’s increasing focus on climate change, biodiversity, and sustainable development. Maps were useful in location-based questions.
- Indian Polity (15 Questions): A core subject, testing governance, constitutional provisions, and landmark judgments. Many questions followed an assertion-reasoning pattern.
- Modern History (13 Questions): A relatively high emphasis on the freedom struggle, key personalities, and movements.
- Science & Technology (12 Questions): Covered advancements in AI, biotechnology, and space technology, requiring both static and current knowledge.
- Art & Culture (7 Questions): More weightage than in some later years, indicating an expectation for deeper knowledge of cultural heritage.
- International Relations (7 Questions): Focused on global organizations, treaties, and India's foreign policy.
- Medieval History (1 Question): Minimal representation, following the usual trend of fewer medieval history questions.
- Geography (Indian Geography: 4, Physical Geography: 2, World Geography: 0): The focus was on Indian geography, with limited physical geography and no direct world geography questions.

Difficulty analysis
- Medium Difficulty (50 Questions): The largest segment, requiring a balance of factual knowledge and application skills.
- Hard Questions (29 Questions): A significant portion of the paper, making elimination techniques and conceptual clarity essential.
- Easy Questions (21 Questions): Fewer than in later years, indicating a relatively tougher paper.
The 2018 Prelims had tougher questions than before, which made them hard to solve. This is reflected in the final cut-off, which was only 98 marks.

Variations in Question framing
Multi-Statement Questions (58%):
- The most common type, requiring elimination techniques and conceptual clarity.
- Particularly prevalent in Polity, Economy, and Environment sections.
- Many followed match the following and assertion-reasoning formats.
Direct Questions (42%):
- Straightforward factual questions, especially in History and Geography.
- Easier to score but required precise knowledge.

Current Affairs vs. Static Questions
- Current Affairs-Based (44 Questions): UPSC maintained a strong current affairs focus, particularly in Economy, Science & Technology, and International Relations.
- Static (56 Questions): A balanced approach, with a considerable portion testing foundational knowledge, often derived from NCERT books.
Key learning for Future Preparation
- Strengthen Economy and Polity: These subjects consistently hold high weightage and require an in-depth understanding of fundamental concepts.
- Master Multi-Statement Questions: Since a majority of questions require elimination skills, practice structured reasoning techniques.
- Balance Static and Current Affairs: While static knowledge remains crucial, integrating dynamic current developments is essential for scoring well.
- Prepare for Moderate to Hard Questions: The paper had a higher proportion of challenging questions, so aspirants should refine their approach to conceptual application and strategic guessing.
- History and Culture Awareness: Despite variations in different years, Art & Culture and Modern History continue to hold importance, making them key focus areas.
Subject-Wise Answer Key
QUESTION 1
Hard
Economy
Prelims 2018
Consider the following events:
- The first democratically elected communist party government formed in a State in India.
- India's then largest bank, 'Imperial Bank of India', was renamed 'State Bank of India'.
- Air India was nationalised and became the national carrier.
- Goa became a part of independent India.
Which of the following is the correct chronological sequence of the above events?
A. 4 - 1 - 2 - 3
B. 3 - 2 - 1 - 4
C. 4 - 2 - 1 - 3
D. 3 - 1 -2 - 4
QUESTION 2
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2018
With reference to the provisions made under the National Food Security Act, 2013 consider the following statements:
- The families coming under the category of 'below poverty line (BPL)' only are eligible to receive subsidised grains.
- The eldest woman in a household, of age 18 years or above, shall be the head of the household for the purpose of issuance of a ration card.
- Pregnant women and lactating mothers are entitled to a take-home ration' of 1600 calories per day during pregnancy and for six months thereafter.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2
B. 2 only
C. 1 and 3
D. 3 only
QUESTION 3
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2018
Consider the following items:
- Cereal grains hulled
- Chicken eggs cooked
- Fish processed and canned
- Newspapers containing advertising material
Which of the above items is/are exempted under GST (Goods and Services Tax)?
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1, 2, 3 and 4
D. 1, 2 and 4 only
QUESTION 4
Easy
Economy
Prelims 2018
In spite of being a high saving economy, capital formation may not result in a significant increase in output due to -
A. weak administrative machinery
B. illiteracy
C. high population density
D. high capital-output ratio
QUESTION 5
Hard
Economy
Prelims 2018
Consider the following statements: Human capital formation as a concept is better explained in terms of a process, which enables
- individuals of a country to accumulate more capital.
- increasing the knowledge, skill levels and capacities of the people of the country.
- accumulation of tangible wealth.
- accumulation of intangible wealth.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2
B. 2 and 4 only
C. 2 only
D. 1, 3 and 4
QUESTION 6
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2018
Which one of the following links all the ATMs in India?
A. Indian banks' Association
B. National Securities Depository Limited
C. National Payments Corporation of India
D. Reserve Bank of India
QUESTION 7
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2018
Consider the following:
- Areca nut
- Barley
- Coffee
- Finger millet
- Groundnut
- Sesamum
- Turmeric
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affair, has announced the Minimum Support Price for which of the above?
A. 1, 2, 3 and 7 only
B. 2, 4, 5 and 6 only
C. 1, 3, 4, 5 and 6 only
D. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7
QUESTION 8
Easy
Economy
Prelims 2018
Consider the following statements:
- Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) is the amount that banks have to maintain in the form of their own funds to offset any loss that banks incur if the account-holders fail to repay dues.
- CAR is decided by each individual bank.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 9
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2018
Consider the following statements
- The quantity of imported edible oils is more than the domestic production of edible oils in the last five years.
- The Government does not impose any customs duty on all the imported edible oils as a special case.
Which of the two statements given above is/are correct
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 10
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2018
With reference to digital payments, consider the following statements:
- BHIM app allows the user to transfer money to anyone with a UPI-enabled bank account.
- While a chip-pin debit card has four factors of authentication, BHIM app has only two factors of authentication.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 11
Hard
Economy
Prelims 2018
Consider the following statements
- The Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Review Committee Report has recommended a debt to GDP ratio of 60% for the general (combined) government by 2023, comprising 40% for the Central Government and 20% for the State Governments.
- The Central Government has domestic liabilities of 21% of GDP as compared to 49% of GDP of the State Governments.
- As per the Constitution of India, it is mandatory for a State to take the Central Government’s consent for raising any loan if the former owes any outstanding liabilities to the latter.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 12
Easy
Economy
Prelims 2018
India enacted the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 in order to comply with the obligations to
A. ILO
B. IMF
C. UNCTAD
D. WTO
QUESTION 13
Hard
Economy
Prelims 2018
If a commodity is provided free to the public by the Government, then
A. the opportunity cost is zero.
B. the opportunity cost is ignored.
C. the opportunity cost is transferred from the consumers of the product to the Government.
D. the opportunity cost is transferred from the consumers of the product to the tax-paying public.
QUESTION 14
Easy
Economy
Prelims 2018
Which one of the following statements correctly describes the meaning of legal tender money?
A. The money which is tendered in courts of law to defray the fee of legal cases
B. The money which a creditor is under compulsion to accept in settlement of his claims
C. The bank money in the form of cheques, drafts, bills of exchange, etc.
D. The metallic money in circulation in a country
QUESTION 15
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2018
With reference to the governance of public sector banking in India, consider the following statements
- Capital infusion into public sector banks by the Government of India has steadily increased in the last decade.
- To put the public sector banks in order, the merger of associate banks with the parent State Bank of India has been affected.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2
C. 2 only
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 16
Hard
Economy
Prelims 2018
With reference to India's decision to levy an equalization tax of 6% on online advertisement services offered by non-resident entities, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- It is introduced as a part of the Income Tax Act.
- Non-resident entities that offer advertisement services in India can claim a tax credit in their home country under the "Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements".
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. None
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. 1 only
QUESTION 17
Hard
Economy
Prelims 2018
With reference to organic farming in India, consider the following statements:
- The National Programme for Organic Production' (NPOP) is operated under the guidelines and directions of the Union Ministry of Rural Development.
- The Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority' (APEDA) functions as the Secretariat for the implementation of NPOP.
- Sikkim has become India's first fully organic State.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 18
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2018
Increase in absolute and per capita real GNP do not connote a higher level of economic development, if -
A. industrial output fails to keep pace with agricultural output.
B. agricultural output fails to keep pace with industrial output.
C. poverty and unemployment increase.
D. imports grow faster than exports.
QUESTION 19
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2018
Consider the following statements:
- The Reserve Bank of India manages and services Government of India Securities but not any State Government Securities.
- Treasury bills are issued by the Government of India and there are no treasury bills issued by the State Governments.
- Treasury bills offer are issued at a discount from the par value.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 Only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 20
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2018
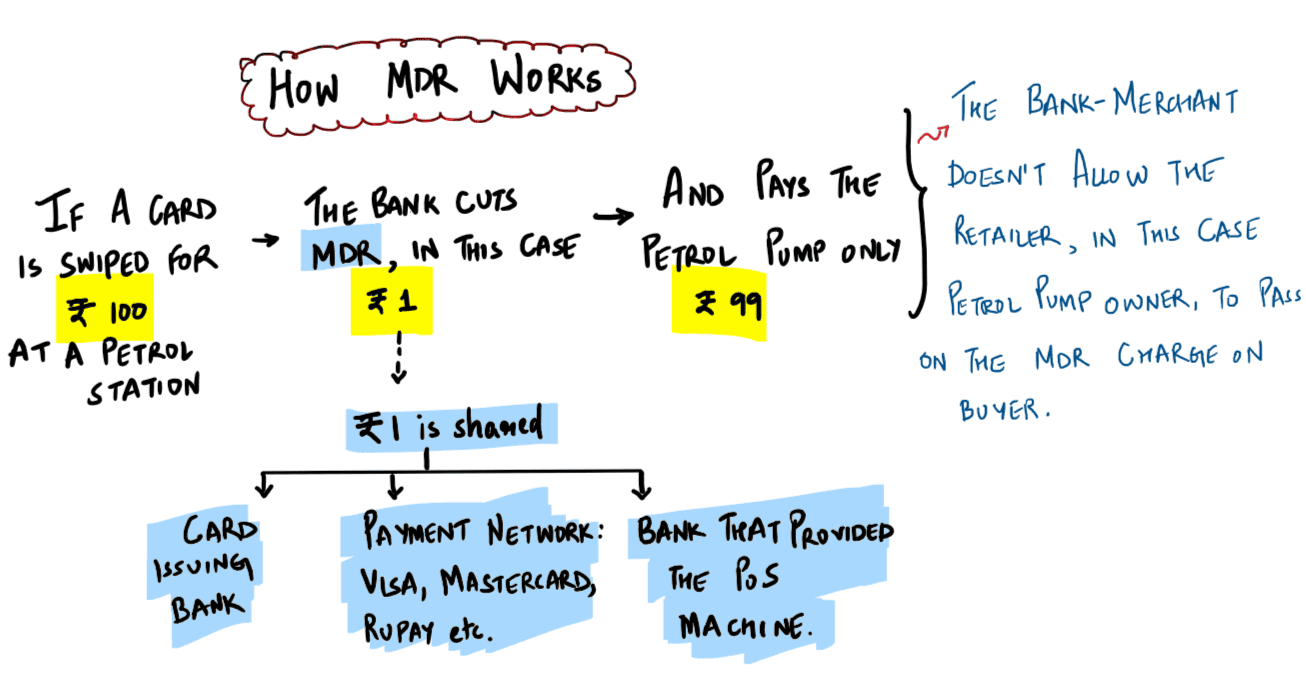
Which one of the following best describes the term "Merchant Discount Rate" sometimes seen in the news?
A. The incentive is given by a bank to a merchant for accepting payments through debit cards pertaining to that bank.
B. The amount paid back by banks to their customers when they use debit cards for financial transactions for purchasing goods or services.
C. The charge to a merchant by a bank for accepting payments from his customers through the bank's debit cards.
D. The incentive given by the Government, to merchants for promoting digital payments by their customers through Point of Sale PoS machines and debit cards.