UPSC Prelims 2016 Analysis
Subject wise MCQ distribution
- Environment & Ecology (22 Questions): The most dominant subject, covering biodiversity, climate change, conservation efforts, and environmental legislation. Many questions incorporated maps for better understanding.
Economy (17 Questions): Included monetary policies, fiscal policy, banking, government schemes, and international economic developments. This section was heavily inclined towards current affairs and required strong analytical abilities for elimination-based questions.
Science & Technology (13 Questions): Focused on emerging technologies, biotechnology, AI, space research, and their recent developments. Many questions followed an assertion-reasoning format to test conceptual understanding.
International Relations (11 Questions): Heavy emphasis on India’s foreign policy, international organizations like the New Development Bank and International Monetary and Financial Committee. Some questions required match the following format.
Social Issues & Schemes (11 Questions): Included government schemes & initiatives like MUDRA Yojana and Stand Up India Scheme along with policies related to education, health, and nutrition. Many questions were framed using the elimination technique.
Indian Polity (5 Questions): A relatively low count, marking a departure from UPSC’s usual trend of high-weightage in this section. However, the questions that appeared tested deep constitutional concepts and analytical abilities.
History (10 Questions Combined): Ancient (1), Medieval (3), and Modern (6), with a focus on factual recall rather than analytical aspects. Many were match the following or multi-statement-based, requiring careful reading.
Geography (Indian Geography: 4, World & Physical Geography: 0): Minimal representation, making it one of the least emphasized subjects in this year’s paper. Questions required strong NCERT-based conceptual clarity, especially in maps and location-based understanding.

Difficulty analysis
- Medium Difficulty (57 Questions): The largest portion, demanding conceptual clarity and critical thinking.
Hard Questions (29 Questions): A significant number, testing advanced knowledge and deeper analytical skills.
Easy Questions (14 Questions): A relatively small proportion, offering limited direct scoring opportunities.

Variations in Question framing
- Multi-Statement Questions (57%) – The most common type, requiring analytical skills and elimination strategies. These appeared more frequently in Polity and Environment.
Direct Questions (43%) – Straightforward factual recall, mainly seen in History and Science & Technology.

Current Affairs vs. Static Questions
- Current Affairs-Based (60 Questions): The paper marked a shift from the trend observed over the past four years. UPSC has increasingly focused on current affairs, making it crucial for aspirants to stay updated.
Static-Based (40 Questions): Still significant but much lower compared to previous years, highlighting UPSC’s shift towards contemporary relevance.
Key learning for Future Preparation
- Prioritize Current Affairs: Given that 60% of the questions were current-based, aspirants should regularly follow newspapers, government reports, and international developments.
- Strengthen Environment & Ecology Preparation: The dominance of this section indicates that topics like climate change, environmental policies, and sustainability should be high-priority study areas.
- Develop Multi-Statement Question Solving Techniques: Since more than half the paper consisted of multi-statement questions, mastering elimination techniques is essential.
- Balance Conceptual & Factual Knowledge: Subjects like Economy and Science & Technology require both static understanding and awareness of recent developments.
- Focus on Analytical Thinking: The difficulty level and multi-statement nature of the paper suggest that rote memorization alone is insufficient—conceptual clarity is key.
Subject-Wise Answer Key
QUESTION 1
Easy
Social Issues & Schemes
Prelims 2016
Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana is aimed at -
A. Bringing the small entrepreneurs into the formal financial system
B. Providing loans to poor farmers for cultivating particular crops
C. Providing pensions to old and destitute persons
D. Funding the voluntary organization involved in the promotion of skill development and employment generation
QUESTION 2
Medium
Social Issues & Schemes
Prelims 2016
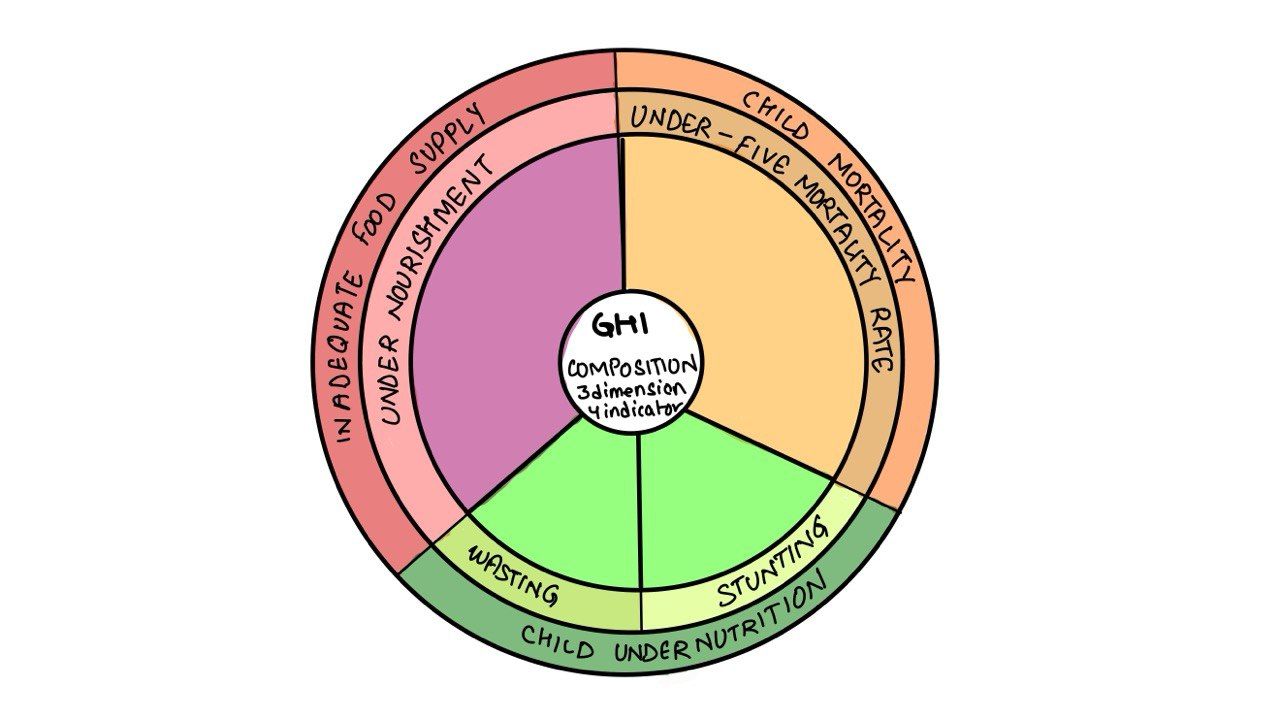
Which of the following is/are the indicator/indicators used by IFPRI to compute the Global Hunger Index Report?
- Undernourishment
- Child stunting
- Child mortality
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1, 2 and 3
D. 1 and 3 only
QUESTION 3
Medium
Social Issues & Schemes
Prelims 2016
What is/are the purpose of ‘District Mineral Foundations” in India?
- Promoting mineral explorative activities in mineral-rich districts
- Protecting the interests of the persons affected by mining operations
- Authorizing State Governments to issue licenses for mineral exploration
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 4
Hard
Social Issues & Schemes
Prelims 2016
With reference to ‘Initiative for Nutritional Security through Intensive Millets Promotion’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- This initiative aims to demonstrate the improved production and post-harvest technologies and to demonstrate value addition techniques, in an integrated manner, with a cluster approach.
- Poor, small, marginal and tribal farmers have a larger stake in this scheme.
- An important objective of the scheme is to encourage farmers of commercial crops to shift to millet cultivation by offering them free kits of critical inputs of nutrients and micro-irrigation equipment.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 2 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 5
Medium
Social Issues & Schemes
Prelims 2016
‘Rashtriya Garima Abhiyaan’ is a national campaign to -
A. rehabilitate the homeless and destitute persons and provide them with suitable sources of livelihood
B. release the sex workers from the practice and provide them with alternative sources of livelihood
C. eradicate the practice of manual scavenging and rehabilitate the manual scavenger
D. release the bonded labourers free their bondage and rehabilitate them
QUESTION 6
Medium
Social Issues & Schemes
Prelims 2016
With reference to ‘Stand Up India Scheme’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- Its purpose is to promote entrepreneurship among SC/ST and women entrepreneurs.
- It provides for refinancing through SIDBI.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 7
Medium
Social Issues & Schemes
Prelims 2016
‘SWAYAM’, an initative of the Government of India, aims at
A. Promoting Self Help Groups in rural areas
B. Providing financial and technical assistance to young start-up entrepreneurs
C. Promoting the education and health of adolescent girls
D. Providing affordable and quality education to the citizens for free
QUESTION 8
Medium
Social Issues & Schemes
Prelims 2016
Regarding ‘Atal Pension Yojana’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- It is a minimum guaranteed pension scheme mainly targeted at unorganized sector workers
- Only one member of a family can join the scheme
- Some amount of pension is guaranteed for the spouse for life after the subscriber’s death.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 9
Medium
Social Issues & Schemes
Prelims 2016
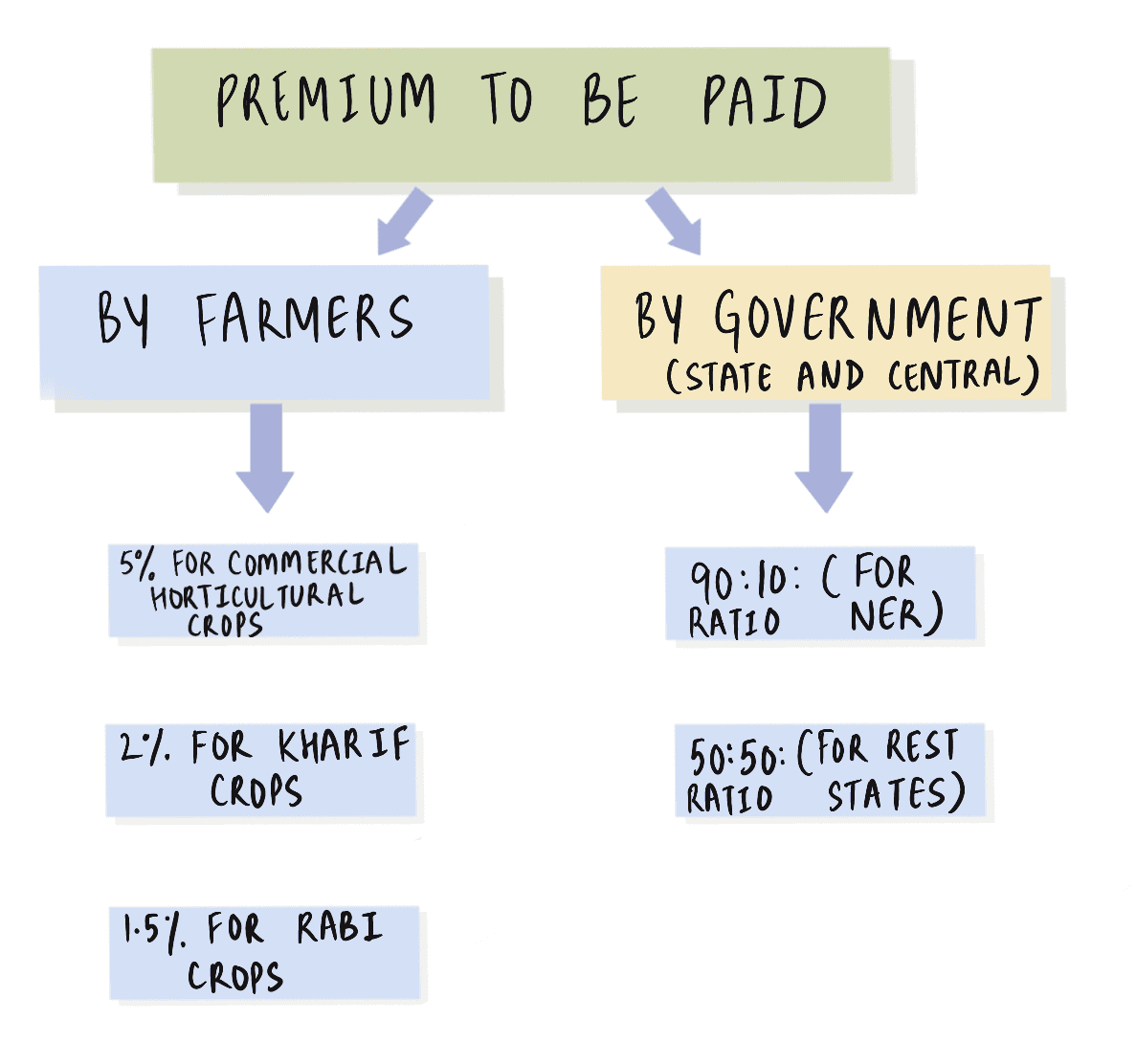
With reference to ‘Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana’, consider the following statements:
- Under this scheme, farmers will have to pay a uniform premium of two per cent for any crop they cultivate in any season of the year.
- This scheme covers post-harvest losses arising out of cyclones and unseasonal rains.
Which of the statements given about is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 10
Easy
Social Issues & Schemes
Prelims 2016
‘Mission Indradhanush’ launched by the Government of India pertains to -
A. Immunization of children and pregnant women
B. Construction of smart cities across the country
C. India’ own search for Earth-like planets in outer space
D. New Educational policy