UPSC Prelims 2016 Analysis
Subject wise MCQ distribution
- Environment & Ecology (22 Questions): The most dominant subject, covering biodiversity, climate change, conservation efforts, and environmental legislation. Many questions incorporated maps for better understanding.
Economy (17 Questions): Included monetary policies, fiscal policy, banking, government schemes, and international economic developments. This section was heavily inclined towards current affairs and required strong analytical abilities for elimination-based questions.
Science & Technology (13 Questions): Focused on emerging technologies, biotechnology, AI, space research, and their recent developments. Many questions followed an assertion-reasoning format to test conceptual understanding.
International Relations (11 Questions): Heavy emphasis on India’s foreign policy, international organizations like the New Development Bank and International Monetary and Financial Committee. Some questions required match the following format.
Social Issues & Schemes (11 Questions): Included government schemes & initiatives like MUDRA Yojana and Stand Up India Scheme along with policies related to education, health, and nutrition. Many questions were framed using the elimination technique.
Indian Polity (5 Questions): A relatively low count, marking a departure from UPSC’s usual trend of high-weightage in this section. However, the questions that appeared tested deep constitutional concepts and analytical abilities.
History (10 Questions Combined): Ancient (1), Medieval (3), and Modern (6), with a focus on factual recall rather than analytical aspects. Many were match the following or multi-statement-based, requiring careful reading.
Geography (Indian Geography: 4, World & Physical Geography: 0): Minimal representation, making it one of the least emphasized subjects in this year’s paper. Questions required strong NCERT-based conceptual clarity, especially in maps and location-based understanding.

Difficulty analysis
- Medium Difficulty (57 Questions): The largest portion, demanding conceptual clarity and critical thinking.
Hard Questions (29 Questions): A significant number, testing advanced knowledge and deeper analytical skills.
Easy Questions (14 Questions): A relatively small proportion, offering limited direct scoring opportunities.

Variations in Question framing
- Multi-Statement Questions (57%) – The most common type, requiring analytical skills and elimination strategies. These appeared more frequently in Polity and Environment.
Direct Questions (43%) – Straightforward factual recall, mainly seen in History and Science & Technology.

Current Affairs vs. Static Questions
- Current Affairs-Based (60 Questions): The paper marked a shift from the trend observed over the past four years. UPSC has increasingly focused on current affairs, making it crucial for aspirants to stay updated.
Static-Based (40 Questions): Still significant but much lower compared to previous years, highlighting UPSC’s shift towards contemporary relevance.
Key learning for Future Preparation
- Prioritize Current Affairs: Given that 60% of the questions were current-based, aspirants should regularly follow newspapers, government reports, and international developments.
- Strengthen Environment & Ecology Preparation: The dominance of this section indicates that topics like climate change, environmental policies, and sustainability should be high-priority study areas.
- Develop Multi-Statement Question Solving Techniques: Since more than half the paper consisted of multi-statement questions, mastering elimination techniques is essential.
- Balance Conceptual & Factual Knowledge: Subjects like Economy and Science & Technology require both static understanding and awareness of recent developments.
- Focus on Analytical Thinking: The difficulty level and multi-statement nature of the paper suggest that rote memorization alone is insufficient—conceptual clarity is key.
Subject-Wise Answer Key
QUESTION 1
Recently, which of the following States has explored the possibility of constructing an artificial inland port to be connected to the sea by a long navigational channel?
A. Andhra Pradesh
B. Chhattisgarh
C. Karnataka
D. Rajasthan
QUESTION 2
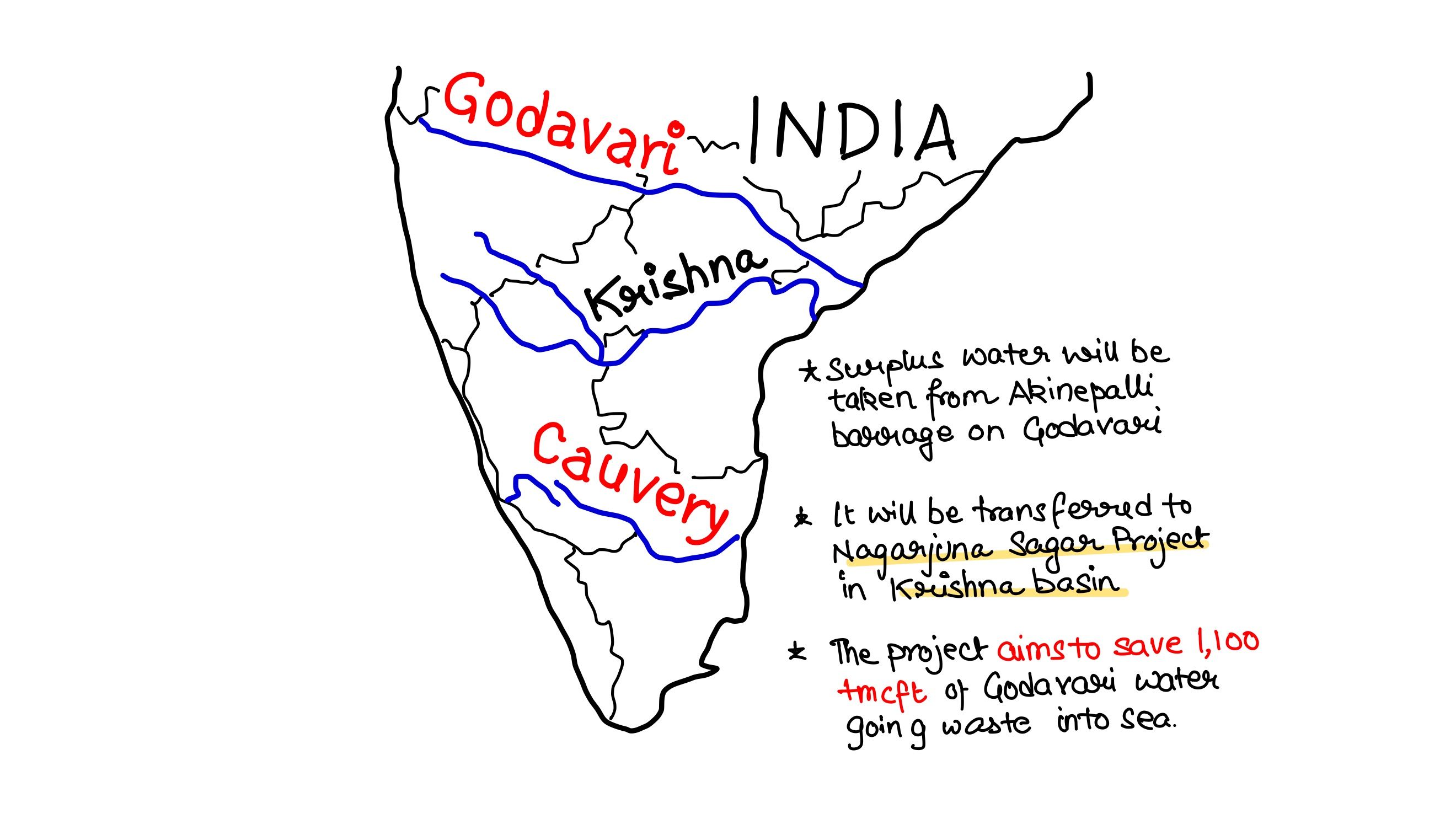
Recently, linking of which of the following rivers was undertaking?
A. Cauvery and Tungabhadra
B. Godavari and Krishna
C. Mahanadi and Son
D. Narmada and Tapti
QUESTION 3
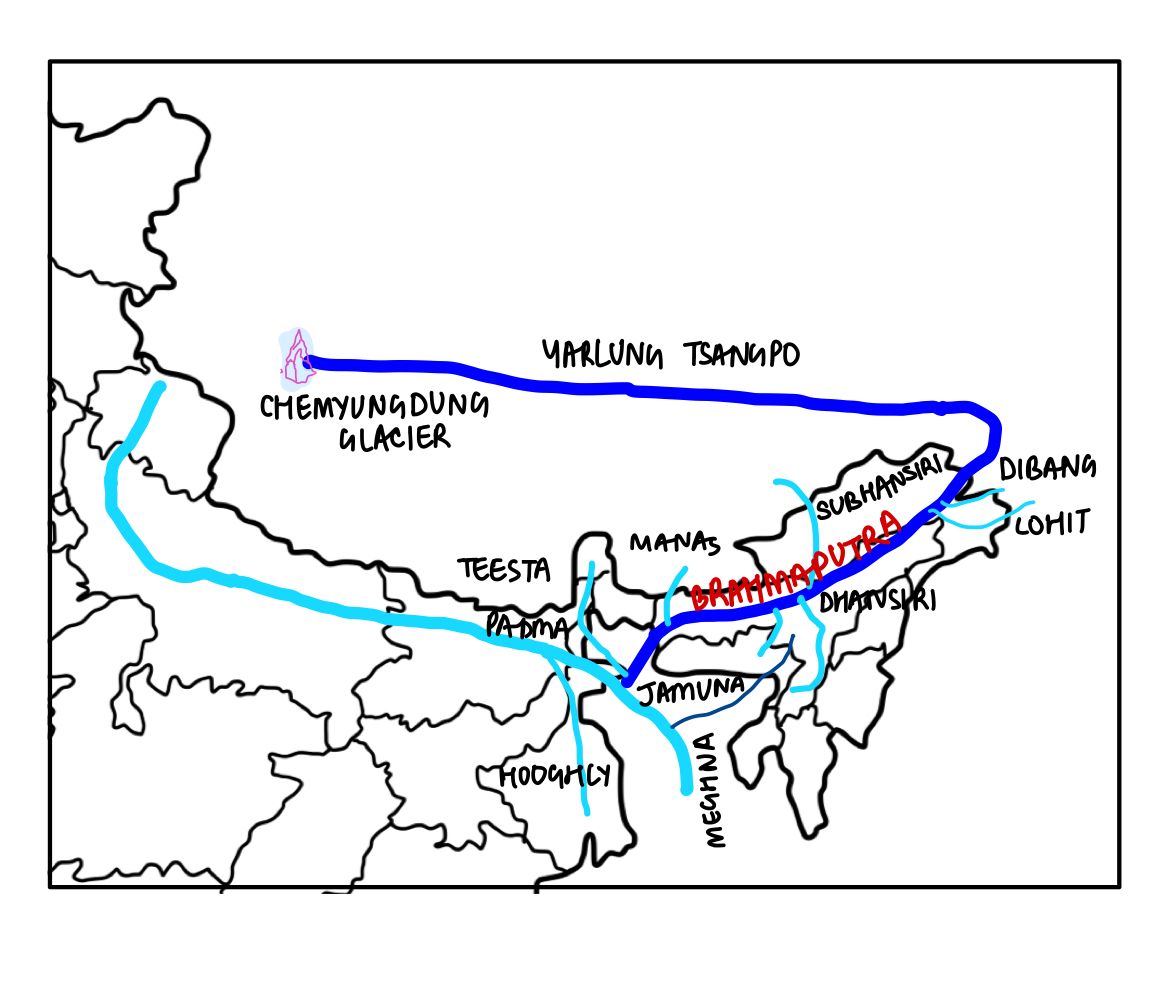
Which of the following is/are tributary/tributaries of Brahmaputra?
- Dibang
- Kameng
- Lohit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 4
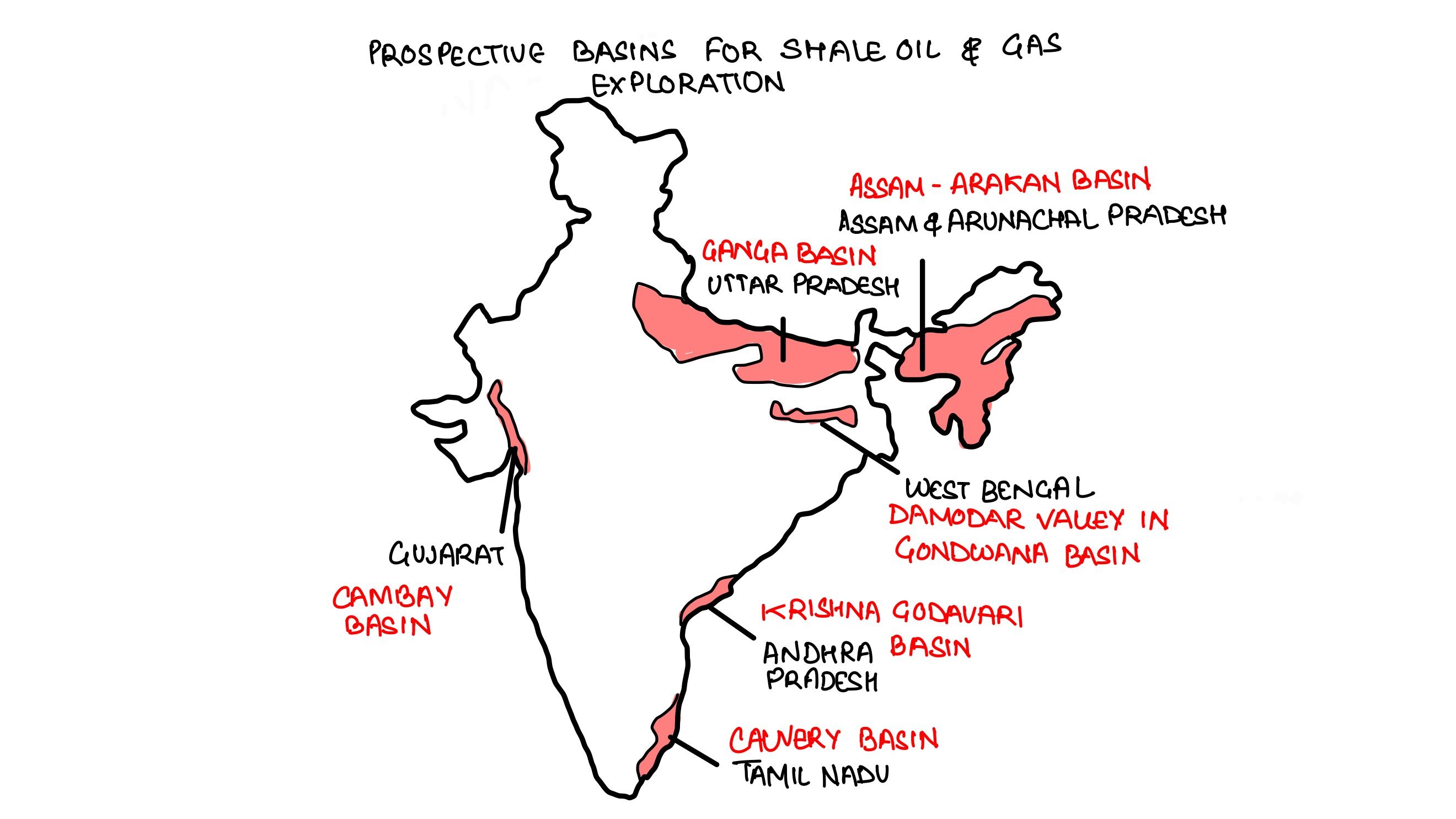
In which of the following regions of India are shale gas resources found?
- Cambay Basin
- Cauvery basin
- Krishna-Godavari Basin
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3