UPSC Prelims 2013 Analysis
Subject-Wise MCQ Distribution
- Economy (16 Questions): A significant portion covered monetary policies, banking, economic indicators, and core concepts such as inflation and the balance of payments. Many questions followed the assertion-reasoning format, testing both conceptual clarity and practical application.
- Environment & Ecology (19 Questions): Focused on biodiversity, national parks, environmental pollution, and fundamental ecology concepts. Several questions required an interdisciplinary approach, linking topics to geography, governance, and climate policies.
- Indian Polity (15 Questions): Included constitutional provisions, policy frameworks, and governmental bodies. The paper tested static knowledge while integrating current affairs-based reasoning, making analytical abilities crucial.
- Science & Technology (16 Questions): Emphasized fundamental concepts and emerging technologies from biotechnology, space, and AI. Instead of direct current affairs-based questions, many were current affairs-inspired, requiring an understanding of recent developments and their applications.
- Art & Culture (9 Questions): Had a notable weightage, with a focus on Buddhism & Jainism, the Bhakti movement, architecture, and performing arts. Many questions followed the match the following format, requiring factual knowledge and conceptual linkages.
- History (8 Questions): Covered Ancient History (2) and Modern History (6), with no Medieval History questions. Modern History questions were relatively easy to medium in difficulty, making them scoring opportunities for well-prepared candidates.
- Geography (13 Questions): Included Physical Geography (5), Indian Geography (5), and World Geography (3). A strong emphasis was placed on conceptual understanding, with several questions integrating maps and geophysical phenomena.
- Social Issues & Government Schemes (4 Questions): Covered welfare schemes, social development programs, and demographic trends. Many were elimination-based, requiring a clear understanding of policy frameworks.
- International Relations (0 Questions): Unlike previous years, there were no direct questions on India’s foreign policy or global affairs, marking a deviation in trends.

Difficulty Analysis
- Easy Questions (39 Questions): Tested foundational knowledge, making them accessible to well-prepared aspirants.
- Medium Questions (39 Questions): Required analytical skills and an ability to link static concepts with real-world applications, especially in Economy and Science & Technology.
- Hard Questions (22 Questions): Demanded deep conceptual clarity and critical thinking, particularly in subjects like Economy and Environment.

Variations in Question Framing
- Multi-Statement Questions (56%) – A significant portion required critical analysis, logical deduction, and elimination strategies. These were common in Polity, Economy, and Environment, with many questions following the assertion-reasoning format.
- Direct Questions (44%) – Focused on factual recall, particularly in Science & Technology and History. These were relatively easier for candidates with strong static knowledge.

Current Affairs vs. Static Questions
- Current Affairs-Based Questions (14%) – While fewer in number, many static questions were inspired by current events, requiring candidates to apply their knowledge in real-world contexts.
- Static Knowledge-Based Questions (86%) – The majority of the paper focused on core subjects, reaffirming the importance of NCERT-based themes, standard books, and foundational concepts.
Key Learnings for Future Preparation
- Prioritize Static Subjects: Since 86% of the questions were static, aspirants must focus on NCERTs, standard reference books, and core concepts.
- Master Multi-Statement Questions: Developing skills to break down statements, eliminate incorrect options, and infer logical conclusions is crucial for improving accuracy.
- Emphasize Environment & Science & Technology: These subjects had a significant presence, requiring conceptual clarity over rote learning.
- Strengthen Art & Culture Preparation: With 9 questions, this subject played an important role, emphasizing cultural history and heritage.
- Approach Current Affairs Selectively: Although current affairs questions were fewer, many were inspired by contemporary issues, highlighting the need for smart, selective preparation instead of exhaustive memorization.
Subject-Wise Answer Key
QUESTION 1
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2013
With reference to the food chains in ecosystems, which of the following kinds of an organism is/are known as decomposer organism/organisms?
- Virus
- Fungi
- Bacteria
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 2
Hard
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2013
Which one among the following industries is the maximum consumer of water in India?
A. Engineering
B. Paper and pulp
C. Textiles
D. Thermal power
QUESTION 3
Hard
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2013
Which of the following can be found as pollutants in the drinking water in some parts of India?
- Arsenic
- Sorbitol
- Fluoride
- Formaldehyde
- Uranium
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 2, 4 and 5 only
C. 1, 3 and 5 only
D. 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
QUESTION 4
Hard
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2013
Consider the following
- Star tortoise
- Monitor lizard
- Pygmy Hog
- Spider monkey
Which of the above found in India?
A. 1, 2 and 3 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 4 only
D. 1, 2,3 and 4
QUESTION 5
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2013
Which of the following leaf modifications occurs/occur in desert areas to inhibit water loss?
- Hard and waxy leaves
- Tiny leaves or no leaves
- Thorns instead of leaves
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 6
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2013
Which of the following adds/add nitrogen to the soil?
- Excretion of urea by animals
- Burning of coal by man
- Death of vegetation
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 7
Easy
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2013
Acid rain is caused by the pollution of the environment by -
A. Carbon dioxide and nitrogen
B. Carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide
C. Ozone and carbon dioxide
D. Nitrous oxide and sulphur dioxide
QUESTION 8
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2013
Due to improper/indiscriminate disposal of old and used computers or their parts, which of the following are released into the environment as e-waste?
- Beryllium
- Cadmium
- Chromium
- Heptachlor
- Mercury
- Lead
- Plutonium
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
A. 1, 3, 4, 6 and 7 only
B. 1, 2, 3, 5 and 6 only
C. 2, 4, 5 and 7 only
D. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7
QUESTION 9
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2013
In which of the following States is lion-tailed macaque found in its natural habitat?
- Tamil Nadu
- Kerala
- Karnataka
- Andhra Pradesh
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
A. 1, 2 and 3 only
B. 2 only
C. 1, 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
QUESTION 10
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2013
Consider the following fauna of India:
- Gharial
- Leatherback turtle
- Swamp deer
Which of the above is/are endangered?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 1, 2 and 3 only
D. None
QUESTION 11
Easy
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2013
In the grasslands, trees do not replace the grasses as a part of an ecological succession because of
A. Insects and fungi
B. Limited sunlight and the paucity of nutrients
C. Water limits and fire
D. None of the above
QUESTION 12
Easy
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2013
Which one of the following terms describes not only the physical space occupied by an organism but also its functional role in the community of organisms?
A. Ecotone
B. Ecological niche
C. Habitat
D. Home range
QUESTION 13
Easy
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2013
With reference to food chains in ecosystems, consider the following statements :
- A food chain illustrates the order in which a chain of organisms feeds upon each other.
- Food chains are found within the populations of a species.
- A food chain illustrates the numbers of each organism which are eaten by others.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 1, 2 and 3
D. None
QUESTION 14
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2013
Consider the following pairs about parks and rivers passing through them:
- Corbett National Park: Ganga
- Kaziranga National Park: Manas
- Silent Valley National Park: Kaveri
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. None
QUESTION 15
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2013
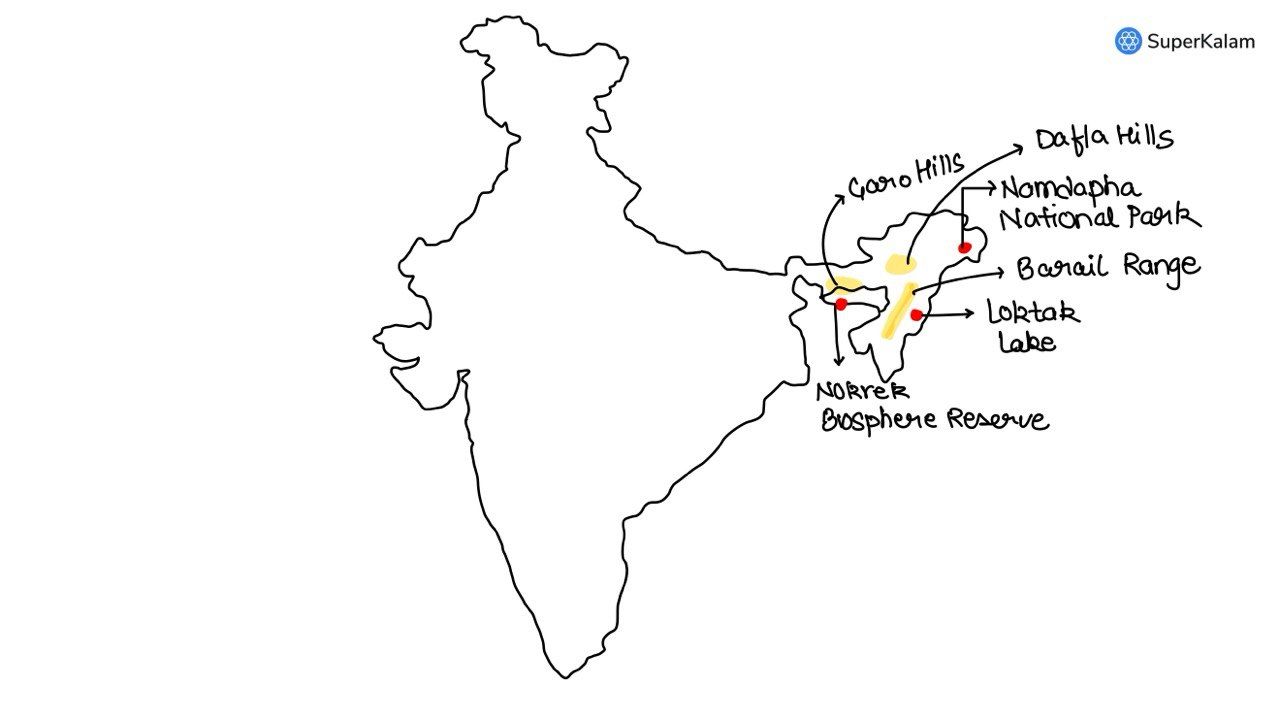
Consider the following pairs:
| Protected areas | Region |
|---|---|
| 1. Nokrek Biosphere Reserve | Garo Hills |
| 2. Logtak (Loktak) Lake | Barail Range |
| 3. Namdapha National Park | Dafla Hills |
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
A. None
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1,2 and 3 only
D. 1 only
QUESTION 16
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2013
Which one of the following is the correct sequence of ecosystems in the order of decreasing productivity?
A. Oceans, lakes, grasslands, mangroves
B. Mangroves, oceans, grasslands, lakes
C. Mangroves, grasslands, lakes, oceans
D. Oceans, mangroves, lakes, grasslands
QUESTION 17
Hard
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2013
Consider the following organisms:
- Agaricus
- Nostoc
- Spirogyra
Which of the above is/are used as biofertilizer/biofertilizers?
A. 1 and 2
B. 2 only
C. 2 and 3
D. 3 only
QUESTION 18
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2013
Photochemical smog is a resultant of the reaction among -
A. NO2, O3 and peroxyacetyl nitrate in the presence of sunlight
B. CO, O2 and peroxyacetyl nitrate in the presence of sunlight
C. CO, CO2 and NO2 at low temperature
D. High concentration of NO2, O3 and CO in the evening
QUESTION 19
Easy
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2013
Contour bunding is a method of soil conservation used in
A. Desert margins, liable to strong wind action
B. Low flat plains, close to stream courses, liable to flooding
C. Scrublands, liable to spread of weed growth
D. None of the above