UPSC Prelims 2013 Analysis
Subject-Wise MCQ Distribution
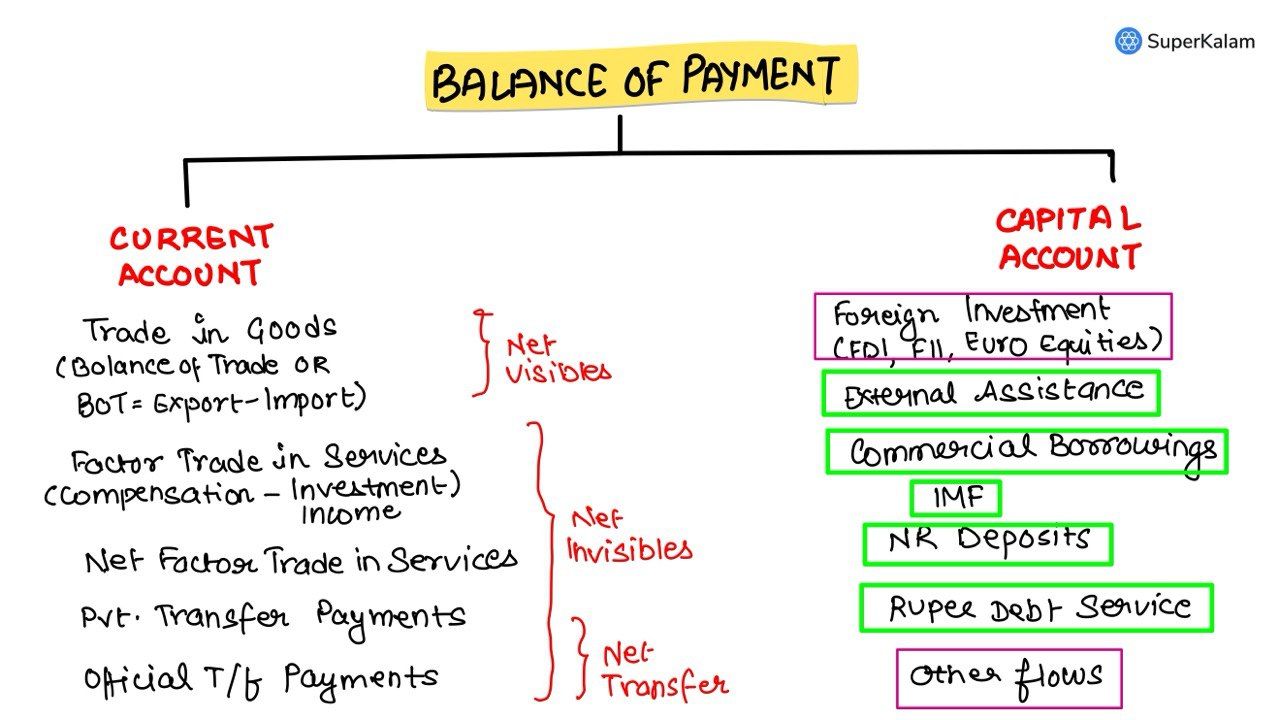
- Economy (16 Questions): A significant portion covered monetary policies, banking, economic indicators, and core concepts such as inflation and the balance of payments. Many questions followed the assertion-reasoning format, testing both conceptual clarity and practical application.
- Environment & Ecology (19 Questions): Focused on biodiversity, national parks, environmental pollution, and fundamental ecology concepts. Several questions required an interdisciplinary approach, linking topics to geography, governance, and climate policies.
- Indian Polity (15 Questions): Included constitutional provisions, policy frameworks, and governmental bodies. The paper tested static knowledge while integrating current affairs-based reasoning, making analytical abilities crucial.
- Science & Technology (16 Questions): Emphasized fundamental concepts and emerging technologies from biotechnology, space, and AI. Instead of direct current affairs-based questions, many were current affairs-inspired, requiring an understanding of recent developments and their applications.
- Art & Culture (9 Questions): Had a notable weightage, with a focus on Buddhism & Jainism, the Bhakti movement, architecture, and performing arts. Many questions followed the match the following format, requiring factual knowledge and conceptual linkages.
- History (8 Questions): Covered Ancient History (2) and Modern History (6), with no Medieval History questions. Modern History questions were relatively easy to medium in difficulty, making them scoring opportunities for well-prepared candidates.
- Geography (13 Questions): Included Physical Geography (5), Indian Geography (5), and World Geography (3). A strong emphasis was placed on conceptual understanding, with several questions integrating maps and geophysical phenomena.
- Social Issues & Government Schemes (4 Questions): Covered welfare schemes, social development programs, and demographic trends. Many were elimination-based, requiring a clear understanding of policy frameworks.
- International Relations (0 Questions): Unlike previous years, there were no direct questions on India’s foreign policy or global affairs, marking a deviation in trends.

Difficulty Analysis
- Easy Questions (39 Questions): Tested foundational knowledge, making them accessible to well-prepared aspirants.
- Medium Questions (39 Questions): Required analytical skills and an ability to link static concepts with real-world applications, especially in Economy and Science & Technology.
- Hard Questions (22 Questions): Demanded deep conceptual clarity and critical thinking, particularly in subjects like Economy and Environment.

Variations in Question Framing
- Multi-Statement Questions (56%) – A significant portion required critical analysis, logical deduction, and elimination strategies. These were common in Polity, Economy, and Environment, with many questions following the assertion-reasoning format.
- Direct Questions (44%) – Focused on factual recall, particularly in Science & Technology and History. These were relatively easier for candidates with strong static knowledge.

Current Affairs vs. Static Questions
- Current Affairs-Based Questions (14%) – While fewer in number, many static questions were inspired by current events, requiring candidates to apply their knowledge in real-world contexts.
- Static Knowledge-Based Questions (86%) – The majority of the paper focused on core subjects, reaffirming the importance of NCERT-based themes, standard books, and foundational concepts.
Key Learnings for Future Preparation
- Prioritize Static Subjects: Since 86% of the questions were static, aspirants must focus on NCERTs, standard reference books, and core concepts.
- Master Multi-Statement Questions: Developing skills to break down statements, eliminate incorrect options, and infer logical conclusions is crucial for improving accuracy.
- Emphasize Environment & Science & Technology: These subjects had a significant presence, requiring conceptual clarity over rote learning.
- Strengthen Art & Culture Preparation: With 9 questions, this subject played an important role, emphasizing cultural history and heritage.
- Approach Current Affairs Selectively: Although current affairs questions were fewer, many were inspired by contemporary issues, highlighting the need for smart, selective preparation instead of exhaustive memorization.
Subject-Wise Answer Key
QUESTION 1
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2013
Consider the following liquid assets:
- Demand deposits with the banks
- Time deposits with the banks
- Savings deposits with the banks
- Currency
The correct sequence of these decreasing order of Liquidity is
A. 1-4-3-2
B. 4-3-2-1
C. 2-3-1-4
D. 4-1-3-2
QUESTION 2
Easy
Economy
Prelims 2013
In India, deficit financing is used for raising resources for
A. Economic development
B. Redemption of public debt
C. Adjusting the balance of payments
D. Reducing foreign debt
QUESTION 3
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2013
The Reserve Bank of India regulates the commercial banks in matters of -
- Liquidity of assets
- Branch expansion
- Merger of banks
- Winding-up of banks
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
A. 1 and 4 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2, 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
QUESTION 4
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2013
Which of the following constitute Capital Account?
- Foreign Loans
- Foreign Direct Investment
- Private Remittances
- Portfolio Investment
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
A. 1, 2 and 3 only
B. 1, 2 and 4 only
C. 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 5
Easy
Economy
Prelims 2013
Disguised unemployment generally means
A. A Large number of people remain unemployed
B. Alternative employment is not available
C. Marginal productivity of labour is zero
D. Productivity of workers is low
QUESTION 6
Easy
Economy
Prelims 2013
In the context of Indian economy, Open Market Operations’ refers to:
A. Borrowing by scheduled banks from the RBI
B. Lending by commercial banks to industry and trade
C. Purchase and sale of government securities by the RBI
D. None of the above
QUESTION 7
Easy
Economy
Prelims 2013
Supply of money remaining the same when there is an increase in demand for money, there will be:
A. a fall in the level of prices
B. an increase in the rate of interest
C. a decrease in the rate of interest
D. an increase in the level of income and employment
QUESTION 8
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2013
The National income of a country for a given period is equal to the:
A. The total value of goods and services produced by the nationals
B. Sum of total consumption and investment expenditure
C. Sum of personal income of all individuals
D. Money value of final goods and services produced
QUESTION 9
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2013
Economic growth in country X will necessarily have to occur if
A. there is technical progress in the world economy
B. there is population growth in X
C. there is a capital formation in X
D. the volume of trade grows in the world economy
QUESTION 10
Easy
Economy
Prelims 2013
Which one of the following is likely to be the most inflationary in its effect?
A. Repayment of public debt
B. Borrowing from the public to finance a budget deficit
C. Borrowing from banks to finance a budget deficit
D. Creating new money to finance a budget deficit
QUESTION 11
Easy
Economy
Prelims 2013
Which one of the following groups of items are included in India’s foreign-exchange reserves?
A. Foreign-currency assets, Special Drawing Rights SDRs and loans from foreign countries
B. Foreign-currency assets, gold holdings of the RBI and SDRs
C. Foreign-currency assets, loans from the World Bank and SDRs
D. Foreign-currency assets, gold holdings of the RBI and loans from the World Bank
QUESTION 12
Easy
Economy
Prelims 2013
The balance of payments of a country is a systematic record of
A. all import and export transactions of a country during a given period of time, normally a year
B. goods exported from a country during a year
C. the economic transaction between the government of one country to another
D. capital movements from one country to another
QUESTION 13
Easy
Economy
Prelims 2013
A rise in the general level of prices may be caused by:
- an increase in the money supply
- a decrease in the aggregate level of output
- an increase in the effective demand
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 14
Easy
Economy
Prelims 2013
An increase in the Bank Rate generally indicates that the:
A. market rate of interest is likely to fall
B. Central Bank is no longer making loans to commercial banks
C. Central Bank is following an easy money policy
D. Central Bank is following a tight money policy
QUESTION 15
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2013
Consider the following statements :
- Inflation benefits the debtors.
- Inflation benefits the bondholders.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 16
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2013
Which of the following grants/ grant direct credit assistance to rural households?
- Regional Rural Banks
- National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development
- Land Development Banks
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3