UPSC Prelims 2020 Analysis
Subject-Wise MCQ Distribution
The UPSC Prelims 2020 maintained its dynamic nature, demanding strong analytical abilities across subjects.
- Environment & Ecology: 19 questions, emphasizing its crucial role in both the Civil Services Examination (CSE) and Indian Forest Service (Ifos) prelims.
- Economy: Emerged as the dominant subject with 21 questions, underscoring its foundational significance.
- Indian Polity: 15 questions, reinforcing its position as one of the most essential areas for aspirants.
- History: A well-distributed section with 3 questions from Ancient History, 2 from Medieval History, 9 from Modern History, and 5 from Art & Culture.
- Geography: 6 questions on Indian Geography, 1 on Physical Geography, and 1 on World Geography. Some questions required maps-based knowledge.
- Science & Technology: 13 questions, highlighting its increasing significance in the exam.
- International Relations: 3 questions, marking a decline from previous years but still requiring awareness of global affairs and India's foreign policy.
- Social Issues & Schemes: 2 questions, demonstrating the need for understanding government programs and their societal impact.

Difficulty Analysis
- Easy: 30 questions, requiring fundamental knowledge.
- Medium: 43 questions, designed to test deeper understanding and application.
- Hard: 27 questions, focusing on conceptual depth and critical thinking.

Variations in Question Framing
- Multi-Statement Based: 63 questions, testing analytical abilities through comparisons and logical deductions.
- Direct Questions: 37 questions, yielding approximately 74 marks.
- Assertion & Reasoning: Notably, no assertion and reason-based questions were asked this year.
- Match the Following: Several match the following type questions were present, assessing conceptual clarity across subjects.

Static vs Current Affairs Distribution
- Static Questions: 75% of the paper, reflecting the importance of mastering NCERT fundamentals.
- Current Affairs: 25 questions, many of which blended static concepts with contemporary relevance. Economics and Science & Technology, in particular, were influenced by recent developments, making it difficult to separate static from dynamic content.
Key Learnings for Future Preparation
The UPSC Prelims 2020 presented several challenges due to its unique question patterns and focus areas:
The exam was challenging and unconventional, requiring strong analytical abilities.
Heavy focus on Science & Technology, Environment, and Agriculture.
Topics like eco-friendly farming, biochar, and MSP were particularly tricky.
While current affairs played a role, most questions were static and application-driven, demanding a strong conceptual foundation.
Underrepresented areas included:
Key government schemes
COVID-19-related policies
International organizations
The unpredictability of the exam reaffirmed the need for:
Well-rounded preparation
NCERT-based conceptual clarity
Interdisciplinary approach was crucial, integrating multiple subjects effectively.
Subject-Wise Answer Key
QUESTION 1
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2020
Which one of the following statements best describes the term ‘Social Cost of Carbon’?
A. Long-term damage done by a tonne of CO2 emissions in a given year.
B. Requirement of fossil fuels for a country to provide goods and services to its citizens, based on the burning of those fuels.
C. Efforts put in by a climate refugee to adapt to live in a new place.
D. Contribution of an individual person to the carbon footprint on the planet Earth.
QUESTION 2
Hard
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2020
Which of the following Protected Areas are located in Cauvery basin?
- Nagarhole National Park
- Papikonda National Park
- Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve
- Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 and 4 only
C. 1, 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
QUESTION 3
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2020
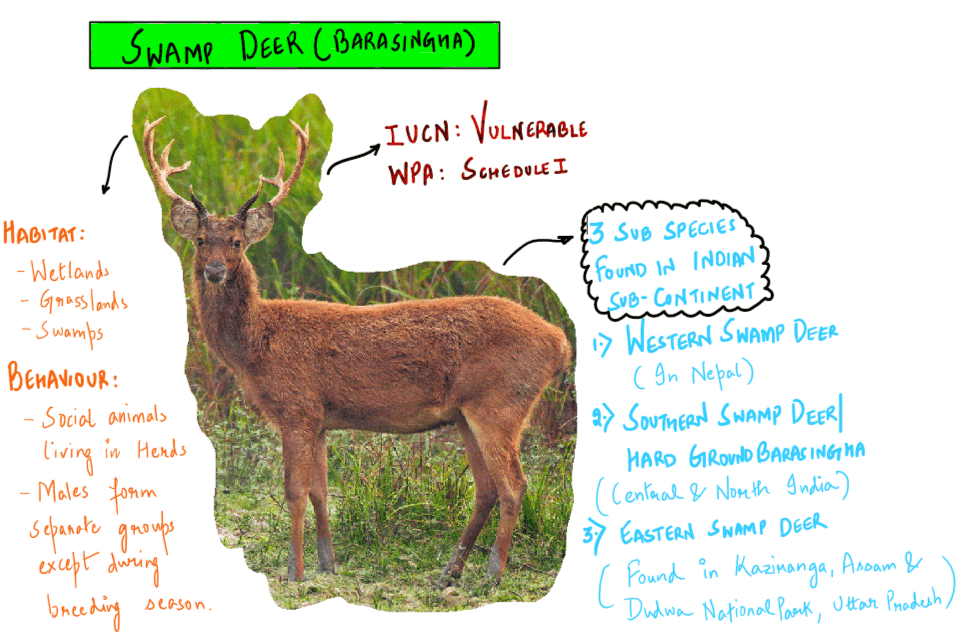
Which one of the following protected areas is well-known for the conservation of a sub-species of the Indian swamp deer (Barasingha) that thrives well on hard ground and is exclusively graminivorous?
A. Kanha National Park
B. Manas National Park
C. Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary
D. Tal Chhaper Wildlife Sanctuary
QUESTION 4
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2020
Which of the following are the reasons/factors for exposure to benzene pollution?
- Automobile exhaust
- Tobacco smoke
- Wood burning
- Using varnished wooden furniture
- Using products made of polyurethane
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1, 2 and 3 only
B. 2 and 4 only
C. 1, 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
QUESTION 5
Hard
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2020
What is the use of biochar in farming?
- Biochar can be used as a part of the growing medium in vertical farming.
- When biochar is a part of the growing medium, it promotes the growth of nitrogen-fixing microorganisms.
- When biochar is a part of the growing medium, it enables the growing medium to retain water for longer time.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 6
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2020
In the context of India, which of the following is/are considered to be practice(s) of eco-friendly agriculture?
- Crop diversification
- Legume intensification
- Tensiometer use
- Vertical farming
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1, 2 and 3 only
B. 3 only
C. 4 only
D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
QUESTION 7
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2020
What are the advantages of fertigation in agriculture?
- Controlling the alkalinity of irrigation water is possible.
- Efficient application of Rock Phosphate and all other phosphatic fertilizers is possible.
- Increased availability of nutrients to plants is possible.
- Reduction in the leaching of chemical nutrients is possible.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1, 2 and 3 only
B. 1, 2 and 4 only
C. 1, 3 and 4 only
D. 2, 3 and 4 only
QUESTION 8
Easy
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2020
With reference to India’s biodiversity, Ceylon frogmouth, Coppersmith barbet, Gray-chinned minivet and White-throated redstart are
A. Birds
B. Primates
C. Reptiles
D. Amphibians
QUESTION 9
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2020
With reference to India’s Desert National Park, which of the following statements are correct?
- It is spread over two districts.
- There is no human habitation inside the Park.
- It is one of the natural habitats of Great Indian Bustard.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 10
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2020
Consider the following statements:
- Coal ash contains arsenic, lead and mercury.
- Coal-fired power plants release Sulphur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen into the environment.
- High ash content is observed in Indian coal.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 11
Hard
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2020
In rural road construction, the use of which of the following is preferred for ensuring environmental sustainability or to reduce carbon footprint?
- Copper slag
- Cold mix asphalt technology
- Geotextiles
- Hot mix asphalt technology
- Portlant cement
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1, 2 and 3 only
B. 2, 3 and 4 only
C. 4 and 5 only
D. 1 and 5 only
QUESTION 12
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2020
Consider the following statements:
- 36% of India’s districts are classified as “overexploited” or critical” by the Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA).
- CGWAwas formed under the Environment (Protection) Act.
- India has the largest area under groundwater irrigation in the world.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 2 only
D. 1 and 3 only
QUESTION 13
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2020
Among the following Tiger Reserves, which one has the largest area under “Critical Tiger Habitat”?
A. Corbett
B. Ranthambore
C. Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam
D. Sunderbans
QUESTION 14
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2020
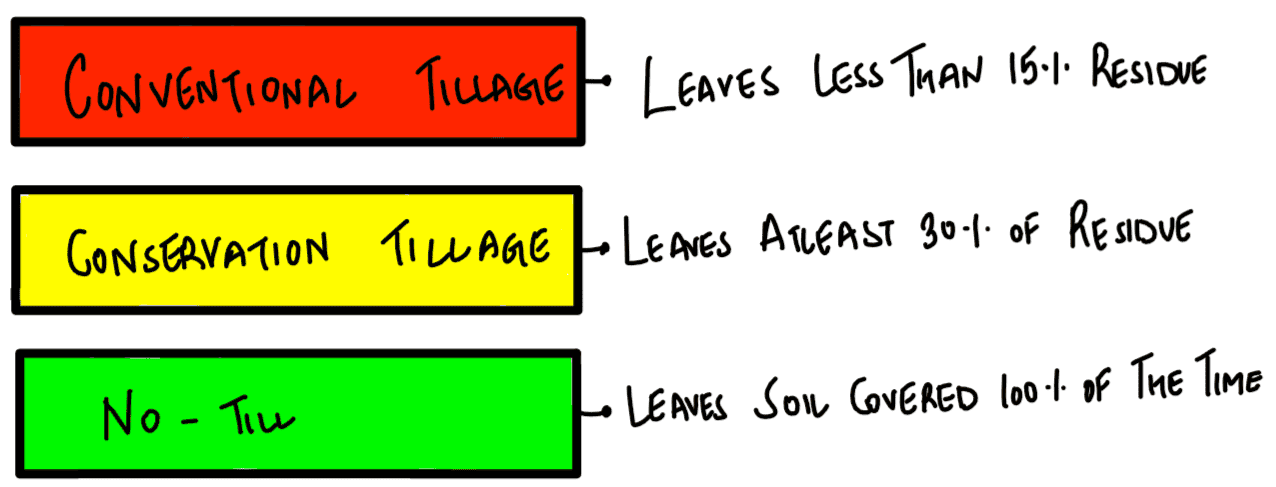
What is/are the advantage/advantages of zero tillage in agriculture?
- Sowing of wheat is possible without burning the residue of previous crop.
- Without the need for nursery of rice saplings, direct planting of paddy seeds in the wet soil is possible.
- Carbon sequestration in the soil is possible.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 15
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2020
Which of the following are the most likely places to find the musk deer in its natural habitat?
- Askot Wildlife Sanctuary
- Gangotri National Park
- Kishanpur Wildlife Sanctuary
- Manas National Park
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 3 and 4 only
D. 1 and 4 only
QUESTION 16
Hard
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2020
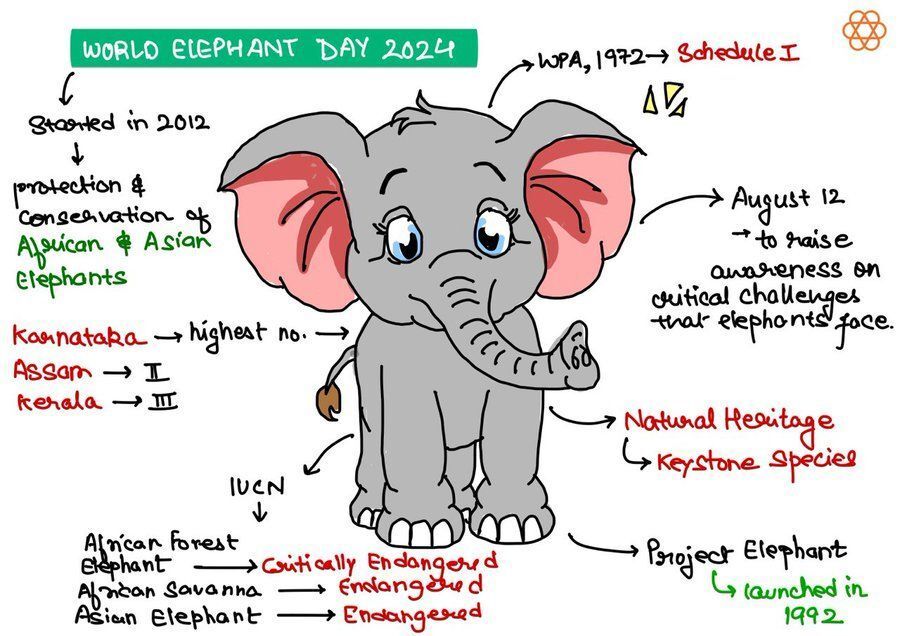
With reference to Indian elephants, consider the following statements:
- The leader of an elephant group is a female.
- The maximum gestation period can be 22 months.
- An elephant can normally go on calving till the age of 40 years only.
- Among the States in India, the highest elephant population is in Kerala.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 4 only
C. 3 only
D. 1, 3 and 4 only
QUESTION 17
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2020
According to India’s National Policy on Biofuels, which of the following can be used as raw materials for the production of biofuels?
- Cassava
- Damaged wheat grains
- Groundnut seeds
- Horse gram
- Rotten potatoes
- Sugar beet
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1, 2, 5 and 6 only
B. 1, 3, 4 and 6 only
C. 2, 3, 4 and 5 only
D. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
QUESTION 18
Medium
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2020
With reference to solar water pumps, consider the following statements:
- Solar power can be used for running surface pumps and not for submersible pumps.
- Solar power can be used for running centrifugal pumps and not the ones with piston.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 19
Easy
Environment & Ecology
Prelims 2020
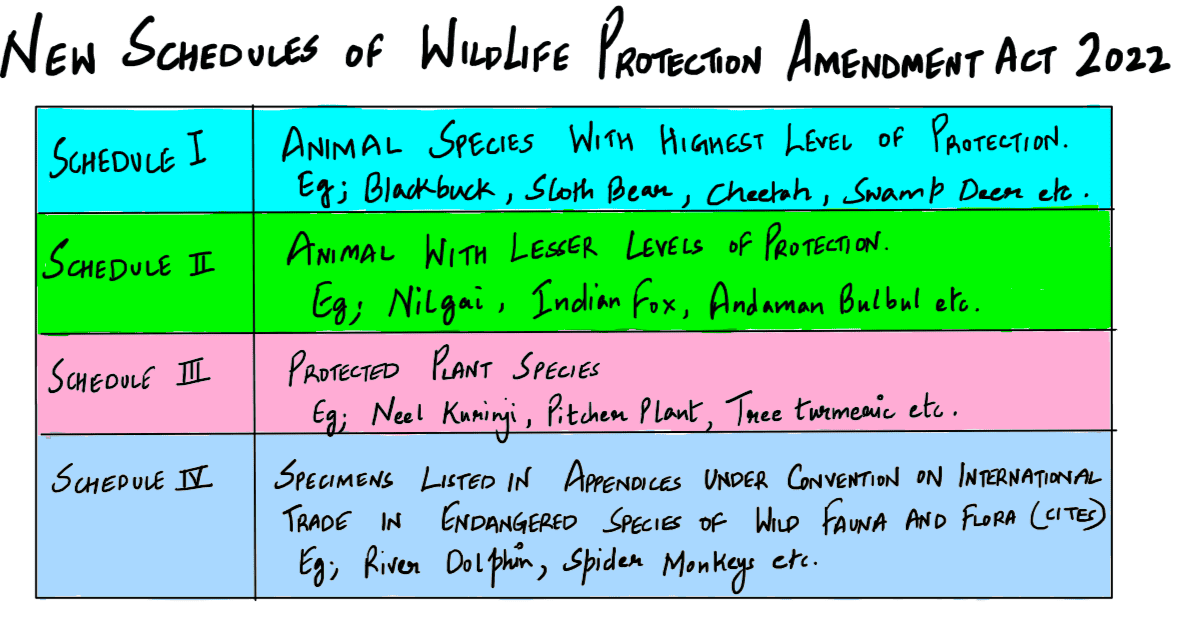
If a particular plant species is placed under Schedule VI of The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, what is the implication?
A. A licence is required to cultivate that plant.
B. Such a plant cannot be cultivated under any circumstances.
C. It is a Genetically Modified crop plant.
D. Such a plant is invasive and harmful to the ecosystem.