UPSC Prelims 2020 Analysis
Subject-Wise MCQ Distribution
The UPSC Prelims 2020 maintained its dynamic nature, demanding strong analytical abilities across subjects.
- Environment & Ecology: 19 questions, emphasizing its crucial role in both the Civil Services Examination (CSE) and Indian Forest Service (Ifos) prelims.
- Economy: Emerged as the dominant subject with 21 questions, underscoring its foundational significance.
- Indian Polity: 15 questions, reinforcing its position as one of the most essential areas for aspirants.
- History: A well-distributed section with 3 questions from Ancient History, 2 from Medieval History, 9 from Modern History, and 5 from Art & Culture.
- Geography: 6 questions on Indian Geography, 1 on Physical Geography, and 1 on World Geography. Some questions required maps-based knowledge.
- Science & Technology: 13 questions, highlighting its increasing significance in the exam.
- International Relations: 3 questions, marking a decline from previous years but still requiring awareness of global affairs and India's foreign policy.
- Social Issues & Schemes: 2 questions, demonstrating the need for understanding government programs and their societal impact.

Difficulty Analysis
- Easy: 30 questions, requiring fundamental knowledge.
- Medium: 43 questions, designed to test deeper understanding and application.
- Hard: 27 questions, focusing on conceptual depth and critical thinking.

Variations in Question Framing
- Multi-Statement Based: 63 questions, testing analytical abilities through comparisons and logical deductions.
- Direct Questions: 37 questions, yielding approximately 74 marks.
- Assertion & Reasoning: Notably, no assertion and reason-based questions were asked this year.
- Match the Following: Several match the following type questions were present, assessing conceptual clarity across subjects.

Static vs Current Affairs Distribution
- Static Questions: 75% of the paper, reflecting the importance of mastering NCERT fundamentals.
- Current Affairs: 25 questions, many of which blended static concepts with contemporary relevance. Economics and Science & Technology, in particular, were influenced by recent developments, making it difficult to separate static from dynamic content.
Key Learnings for Future Preparation
The UPSC Prelims 2020 presented several challenges due to its unique question patterns and focus areas:
The exam was challenging and unconventional, requiring strong analytical abilities.
Heavy focus on Science & Technology, Environment, and Agriculture.
Topics like eco-friendly farming, biochar, and MSP were particularly tricky.
While current affairs played a role, most questions were static and application-driven, demanding a strong conceptual foundation.
Underrepresented areas included:
Key government schemes
COVID-19-related policies
International organizations
The unpredictability of the exam reaffirmed the need for:
Well-rounded preparation
NCERT-based conceptual clarity
Interdisciplinary approach was crucial, integrating multiple subjects effectively.
Subject-Wise Answer Key
QUESTION 1
Hard
Economy
Prelims 2020
With reference to chemical fertilizers in India, consider the following statements:
- At present, the retail price of chemical fertilizers is market-driven and not administered by the Government.
- Ammonia, which is an input of urea, is produced from natural gas.
- Sulphur, which is a raw material for phosphoric acid fertilizer, is a by-product of oil refineries.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 2 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 2
Easy
Economy
Prelims 2020
Consider the following statements:
- In the case of all cereals, pulses and oil-seeds, the procurement at Minimum Support Price (MSP) is unlimited in any State/UT of India.
- In the case of cereals and pulses, the MSP is fixed in any State/UT at a level to which the market price will never rise.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 3
Easy
Economy
Prelims 2020
Consider the following statements:
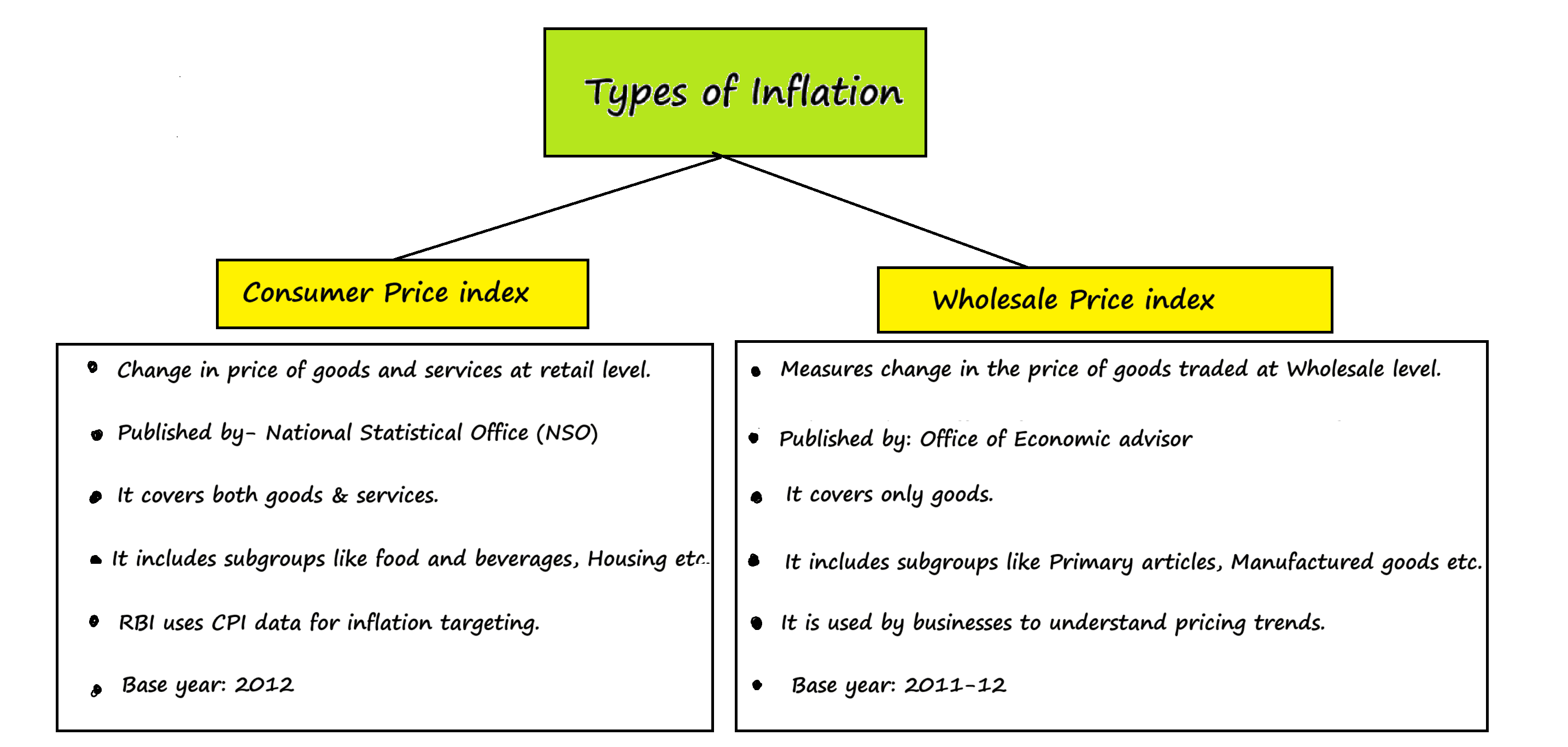
- The weightage of food in Consumer Price Index (CPI) is higher than that in Wholesale Price Index (WPI).
- The WPI does not capture changes in the prices of services, which CPI does.
- Reserve Bank of India has now adopted WPI as its key measure of inflation and to decide on changing the key policy rates.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 only
C. 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 4
Easy
Economy
Prelims 2020
If the RBI decides to adopt an expansionist monetary policy, which of the following would it not do?
- Cut and optimize the Statutory Liquidity Ratio
- Increase the Marginal Standing Facility Rate
- Cut the Bank Rate and Repo Rate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 5
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2020
In the context of the Indian economy, non-financial debt includes which of the following?
- Housing loans owed by households
- Amounts outstanding on credit cards
- Treasury bills
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 6
Hard
Economy
Prelims 2020
In India, under cyber insurance for individuals, which of the following benefits are generally covered, in addition to payment for the funds and other benefits?
- Cost of restoration of the computer system in case of malware disrupting access to one's computer
- Cost of a new computer if some miscreant wilfully damages it, if proved so
- Cost of hiring a specialized consultant to minimize the loss in case of cyber extortion.
- Cost of defence in the Court of Law if any third party files a suit
A. 1, 2 and 4 only
B. 1, 3 and 4 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
QUESTION 7
Easy
Economy
Prelims 2020
Along with the Budget, the Finance Minister also places other documents before the Parliament which include “The Macro Economic Framework Statement”. The aforesaid document is presented because this is mandated by
A. Long standing parliamentary convention
B. Article 112 and Article 1101 of the Constitution of India
C. Article 113 of the Constitution of India
D. Provisions of the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act, 2003
QUESTION 8
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2020
If another global financial crisis happens in the near future, which of the following actions/policies are most likely to give some immunity to India?
- Not depending on short-term foreign borrowings
- Opening up to more foreign banks
- Maintaining full capital account convertibility
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 9
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2020
Under the Kisan Credit Card scheme, short-term credit support is given to farmers for which of the following purposes?
- Working capital for maintenance of farm assets
- Purchase of combine harvesters, tractors and mini trucks.
- Consumption requirements of farm households
- Post-harvest expense
- Construction of family house and setting up of village cold storage facility.
Select the correct answer
A. 1, 2 and 5 only
B. 1, 3 and 4 only
C. 2, 3, 4 and 5 only
D. 1, 2, 3 4 and 5
QUESTION 10
Easy
Economy
Prelims 2020
The term 'West Texas Intermediate', sometimes found in news, refers to a grade of
A. Crude oil
B. Bullion
C. Rare earth elements
D. Uranium
QUESTION 11
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2020
Consider the following statements:
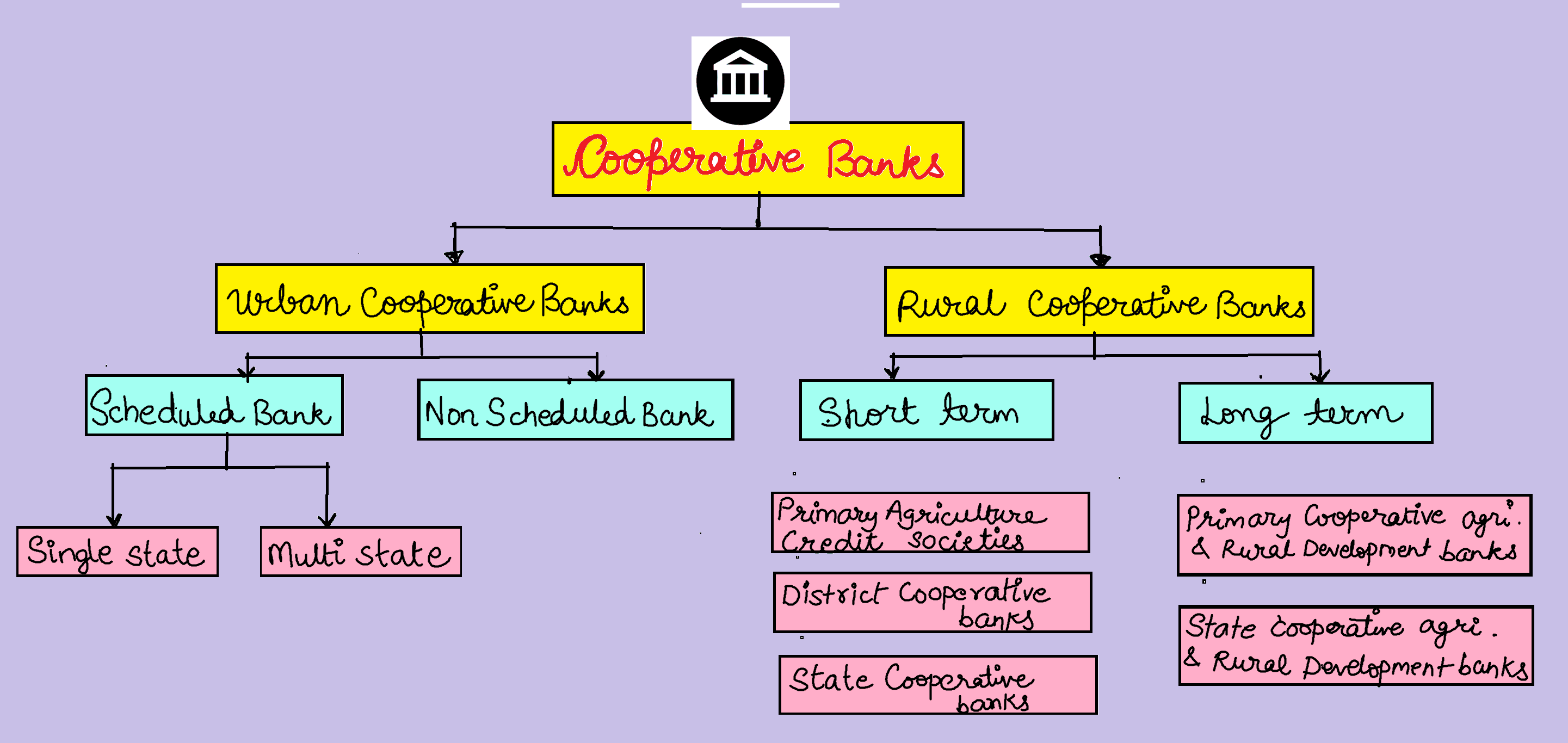
- In terms of short-term credit delivery to the agriculture sector, District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs) deliver more credit in comparison of Scheduled Commercial Banks are Regional Rural Banks
- One of the most important functions of DCCBs is to provide funds to the Primary Agricultural Credit Societies.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 12
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2020
Which of the following factors/policies were affecting the price of rice in India in the recent past?
- Minimum Support Price
- Government’s trading
- Government’s stockpiling
- Consumer subsidies
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1, 2 and 4 only
B. 1, 3 and 4 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
QUESTION 13
Hard
Economy
Prelims 2020
With reference of the Indian economy after the 1991 economic liberalization, consider the following statements:
- Worker productivity (per worker at 2004-05 prices) increased in urban areas while it decreased in rural areas.
- The percentage share of rural areas in the workforce steadily increased.
- In rural areas, the growth in non-farm economy increased.
- The growth rate in rural employment decreased.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 and 4 only
C. 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 4 only
QUESTION 14
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2020
With reference to the international trade of India at present, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- India’s merchandise exports are less than its merchandise imports.
- India’s imports of iron and steel, chemicals, fertilisers and machinery have decreased in recent years.
- India’s exports of services are more than its imports of services.
- India suffers from an overall trade/current account deficit.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 4 only
C. 3 only
D. 1, 3 and 4 only
QUESTION 15
Easy
Economy
Prelims 2020
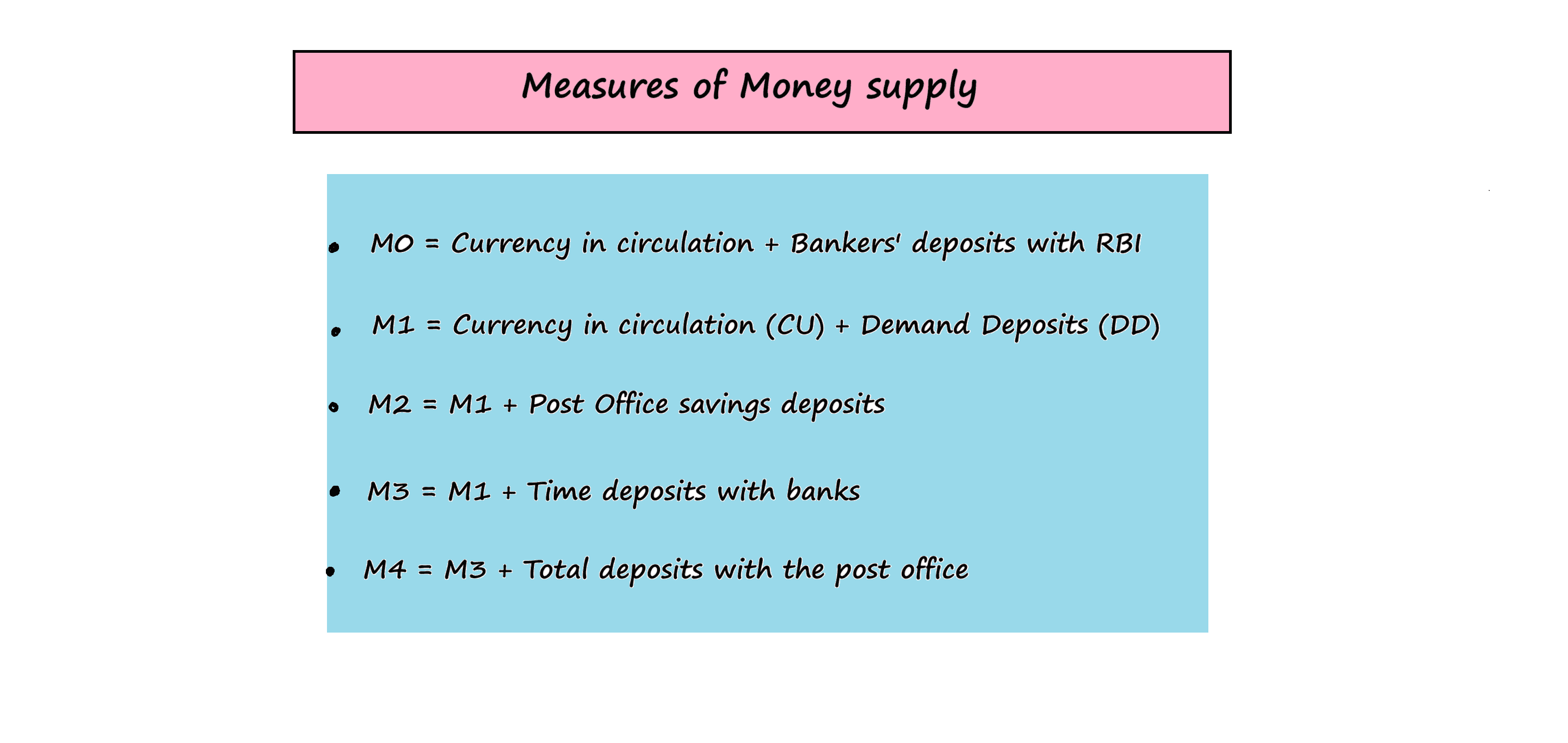
If you withdraw Rs. 1,00,000 in cash from your Demand Deposit Account at your bank, the immediate effect on aggregate money supply in the economy will be
A. to reduce it by Rs 1,00,000
B. to increase it by Rs 1,00,000
C. to increase it by more than Rs 1,00,000
D. to leave it unchanged
QUESTION 16
Easy
Economy
Prelims 2020
“Gold Tranche” (Reserve Tranche) refers to
A. a loan system of the World Bank
B. one of the operations of a Central Bank
C. a credit system granted by WTO to its members
D. a credit system granted by IMF to its members
QUESTION 17
Hard
Economy
Prelims 2020
What is the importance of the term “Interest Coverage Ratio” of a firm in India?
- It help in understanding the present risk of a firm that a bank is going to give loan to.
- It helps in evaluating the emerging risk of a firm that a bank is going to give loan to.
- The higher a borrowing firm’s level of Interest Coverage Ratio, the worse is its ability to service its debt.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 18
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2020
In India, which of the following can be considered as public investment in agriculture?
- Fixing Minimum Support Price for agricultural produce of all crops
- Computerization of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies
- Social Capital development
- Free electricity supply to farmers
- Waiver of agricultural loans by the banking system
- Setting up of cold storage facilities by the governments
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1, 2 and 5 only
B. 1, 3, and 4 and 5 only
C. 2, 3 and 6 only
D. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
QUESTION 19
Easy
Economy
Prelims 2020
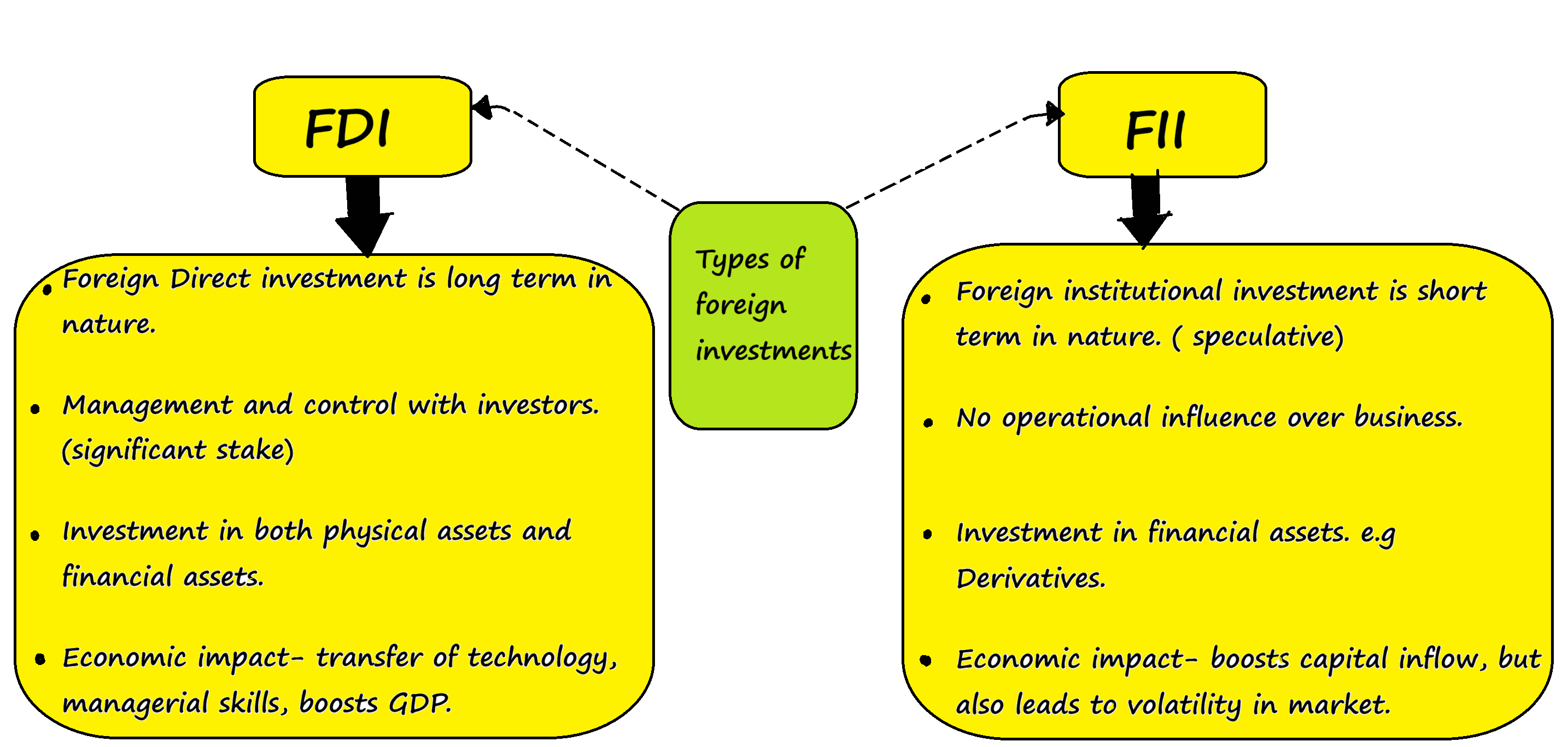
With reference to Foreign Direct Investment in India, which one of the following is considered its major characteristic?
A. It is the investment through capital instruments essentially in a listed company.
B. It is a largely non-debt creating capital flow.
C. It is the investment which involves debt-servicing.
D. It is the investment made by foreign institutional investors in the Government securities.
QUESTION 20
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2020
With reference of the Indian economy, consider the following statements:
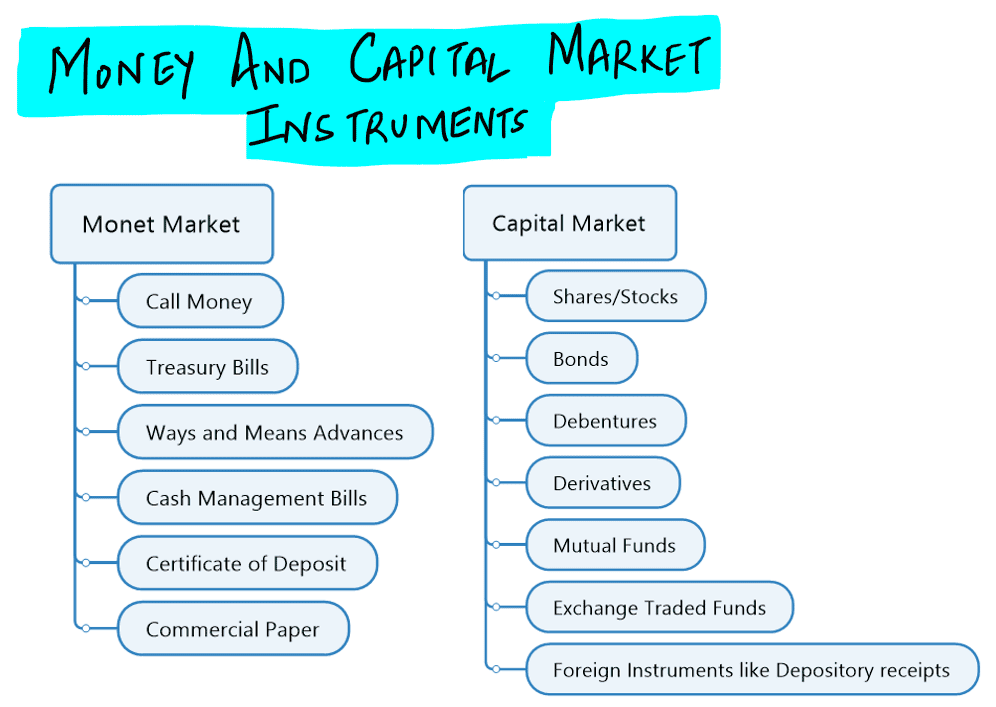
- ‘Commercial Paper’ is a short-term unsecured promissory note.
- ‘Certificate of Deposit’ is a long-term instrument issued by the Reserve Bank of India to a corporation.
- ‘Call Money’ is a short-term finance used for interbank transitions.
- ‘Zero-Coupon Bonds’ are the interest bearing short-term bonds issued by the Scheduled Commercial Banks to corporations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 4 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 2, 3 and 4 only
QUESTION 21
Medium
Economy
Prelims 2020
With reference to the Trade-Related Investment Measures (TRIMS), which of the following statements is/are correct?
- Quantitative restrictions on imports by foreign investors are prohibited.
- They apply to investment measures related to trade in both goods and services.
- They are not concerned with the regulation of foreign investments.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3 only