UPSC Prelims 2019 Analysis
Subject wise MCQ distribution
- Economy had the highest number of questions (21), with a special focus on the banking sector, making it the most important subject.
- Environment & Ecology followed with 18 questions, highlighting its significance due to the Forest Service prelims merging with the Civil Services Prelims.
- Science & Technology was another key area, contributing 15 questions, with a major focus on biotechnology and related current affairs.
- Indian Polity remained crucial, featuring 13 questions.
- Modern History had a relatively lower weightage, with only 6 questions.

Difficulty analysis
- Medium Questions (45) formed the largest portion, requiring a blend of static and current knowledge with strong analytical abilities.
- Hard Questions (31) were conceptually tricky and usually lowered the cutoff. A strategic approach involved eliminating high-risk questions and attempting only those with certainty.
- Easy Questions (24) were straightforward and should have been attempted with maximum accuracy to gain easy marks.

Variations in Question framing
- The paper was evenly split between multi-statement and direct questions.
- Multi-statement questions held a slight majority, making the paper lengthy and increasing the risk of errors, as each statement had to be analyzed carefully.
- However, multi-statement questions also allowed for option elimination, enabling candidates to answer with limited information.

Key learning for Future Preparation
- Prioritize Key Subjects: Allocate more time to Polity, Economy, and Environment, as they consistently have higher weightage.
- Integrate Current Affairs: Link recent developments with syllabus topics for better retention.
- Develop Analytical Thinking: Focus on the why behind policies, events, and phenomena, rather than just memorizing facts.
- Revise Regularly: Reinforce concepts through periodic revisions and multiple mock tests.
- Master Multi-Statement Questions: Practice elimination techniques to improve accuracy in multi-statement questions.
- Practice PYQs: Understand important areas from the examiner’s perspective and familiarize yourself with option elimination techniques.
Subject-Wise Answer Key
QUESTION 1
GS
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2019
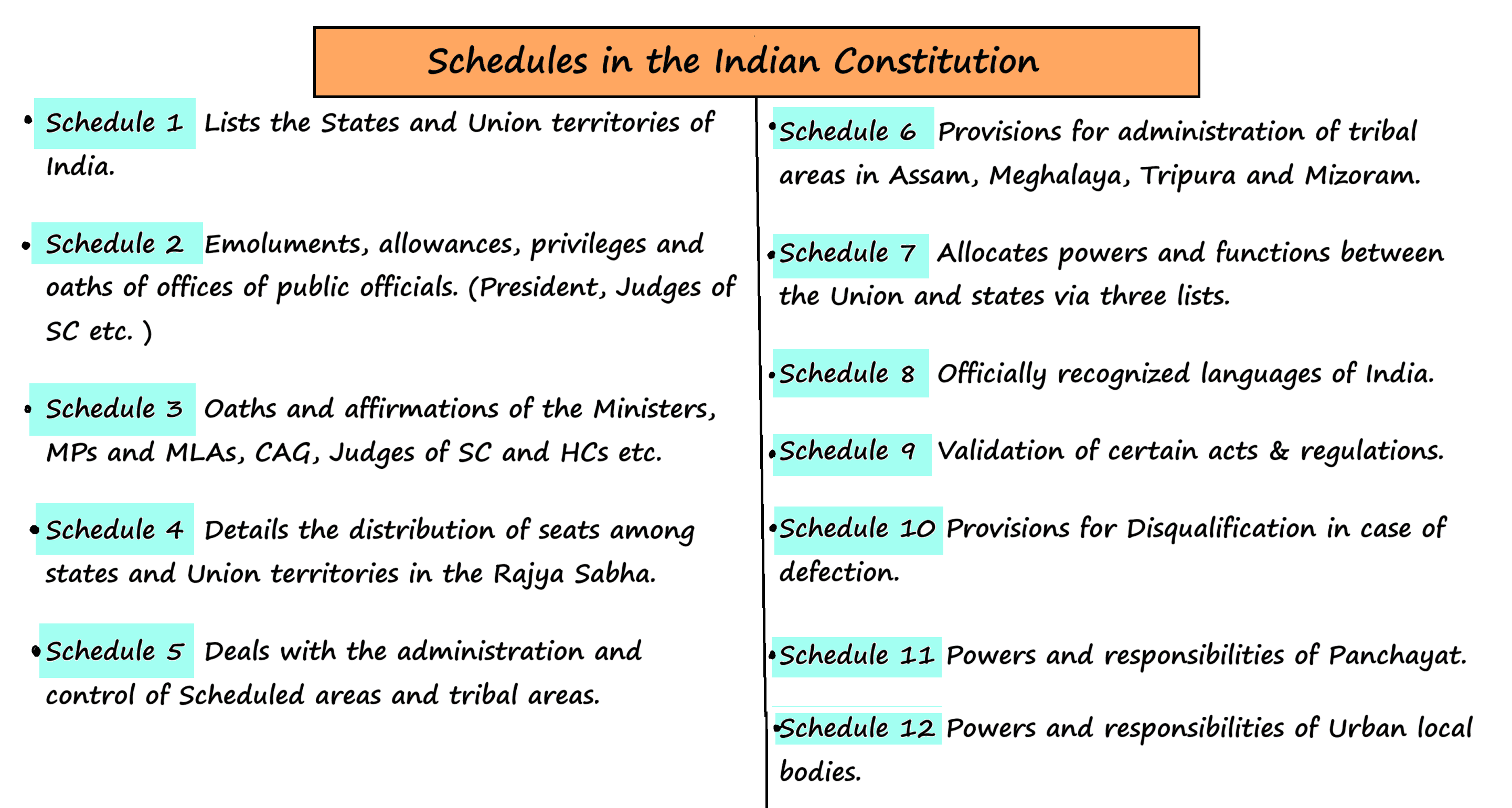
Under which Schedule of the Constitution of India can the transfer of tribal land to private parties for mining be declared null and void?
A. Third Schedule
B. Fifth Schedule
C. Ninth Schedule
D. Twelfth Schedule
QUESTION 2
GS
Medium
Indian Polity
Prelims 2019
Consider the following statements :
- The motion to impeach a Judge of the Supreme Court of India cannot be rejected by the Speaker of the Lok Sabha as per the Judges (Inquiry) Act, 1968.
- The Constitution of India defines and gives details of what constitutes ‘incapacity and proved misbehaviour’ of the Judges of the Supreme Court of India.
- The details of the process of impeachment of the Judges of the Supreme Court of India are given in the Judges (Inquiry) Act, 1968.
- If the motion for the impeachment of a Judge is taken up for voting, the law requires the motion to be backed by each House of the Parliament and supported by a majority of the total membership of that House and by not less than two-thirds of total members of that House present and voting.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2
B. 3 only
C. 3 and 4 only
D. 1, 3 and 4
QUESTION 3
GS
Hard
Indian Polity
Prelims 2019
With reference to the management of minor minerals in India consider the following statements:
- Sand is a ‘minor mineral’ according to the prevailing law in the country.
- State Governments have the power to grant mining leases of minor minerals, but the powers regarding the formation of rules related to the grant of minor minerals lie with the Central Government.
- State Governments have the power to frame rules to prevent illegal mining of minor minerals.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 4
GS
Medium
Indian Polity
Prelims 2019
With reference to the Constitution of India, prohibitions or limitations or provisions contained in ordinary laws cannot act as prohibitions or limitations on the constitutional powers under Article 142. It could mean which one of the following?
A. The decisions taken by the Election Commission of India while discharging its duties cannot be challenged in any court of law.
B. The Supreme Court of India is not constrained in the exercise of its powers by laws made by the Parliament.
C. In the event of grave financial crisis in the country, the President of India can declare Financial Emergency without the counsel from the Cabinet.
D. State legislatures cannot make laws on certain matters without the concurrence of Union Legislature.
QUESTION 5
GS
Medium
Indian Polity
Prelims 2019
In India, which of the following review the independent regulators in sectors like telecommunications, insurance, electricity, etc.?
- Ad Hoc Committees set up by the Parliament
- Parliamentary Department Related Standing Committees
- Finance Commission
- Financial Sector Legislative Reforms Commission
- NITI Aayog
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A. 1 and 2
B. 1, 3 and 4
C. 3, 4 and 5
D. 2 and 5
QUESTION 6
GS
Medium
Indian Polity
Prelims 2019
Consider the following statements :
- The 44th Amendment to the Constitution of India introduced an Article placing the election of the Prime Minister beyond judicial review.
- The Supreme Court of India struck down the 99th Amendment to the Constitution of India as being violative of the independence of the judiciary.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct ?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 7
GS
Medium
Indian Polity
Prelims 2019
Consider the following statements:
- The Parliament (Prevention of Disqualification) Act, 1959 exempts several posts from disqualification on the grounds of ‘Office of Profit’.
- The above-mentioned Act was amended five times.
- The term ‘Office of Profit’ is well- defined in the Constitution of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 8
GS
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2019
Which Article of the Constitution of India safeguards one’s right to marry the person of one’s choice?
A. Article 19
B. Article 21
C. Article 25
D. Article 29
QUESTION 9
GS
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2019
The Ninth Schedule was introduced in the Constitution of India during the prime ministership of
A. Jawaharlal Nehru
B. Lal Bahadur Shastri
C. Indira Gandhi
D. Morarji Desai
QUESTION 10
GS
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2019
Which one of the following suggested that the Governor should be an eminent person from outside the State and should be a detached figure without intense political links or should not have taken part in politics in the recent past?
A. First Administrative Reforms Commission 1966
B. Rajamannar Committee 1969
C. Sarkaria Commission 1983
D. National Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution 2000
QUESTION 11
GS
Hard
Indian Polity
Prelims 2019
With reference to the Legislative Assembly of a State in India, consider the following statements:
- The governor makes a customary address to members of the house at the commencement of the first session of the year.
- When a State Legislature does not have a rule on a particular matter, it follows the Lok Sabha rule on that matter.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 12
GS
Easy
Indian Polity
Prelims 2019
With reference to the Constitution of India, consider the following statements:
- No High Court shall have the jurisdiction to declare any central law to be constitutionally invalid.
- An amendment to the Constitution of India cannot be called into question by the Supreme Court of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. None of the above
QUESTION 13
GS
Medium
Indian Polity
Prelims 2019
In the context of polity, which one of the following would you accept as the most appropriate definition of liberty?
A. Protection against the tyranny of political rulers
B. Absence of restraint
C. Opportunity to do whatever one likes
D. Opportunity to develop oneself fully