UPSC Prelims 2015 Analysis
Subject wise MCQ distribution
- Environment & Ecology (18 Questions): Covered biodiversity, climate change, environmental governance, and sustainability. Questions on international conservation initiatives like BioCarbon Fund and Green Climate Fund were prominent. Several questions were maps-based, requiring conceptual clarity and an ability to link static concepts with current affairs.
- Economy (16 Questions): Topics included monetary policies, banking sector trends, post-1991 reforms, and international economic developments. Many questions required analytical abilities and an elimination-based approach. A mix of conceptual and factual questions, with a significant focus on current affairs.
- Indian Polity (14 Questions): Focused on constitutional provisions, governance structures, and recent legislative changes. Several questions followed the assertion-reasoning format. Required a strong grasp of NCERT-based themes and core governance concepts.
- International Relations (10 Questions): Covered global organizations, India’s foreign policy, and international treaties. This section was heavily inclined towards current affairs, testing awareness of recent geopolitical developments. Some questions followed the match the following pattern.
- Science & Technology (10 Questions): Focused on space technology, biotechnology, AI, and emerging technologies. Many questions required linking current affairs with static concepts, reflecting the increasing importance of interdisciplinary knowledge.
- History (Ancient: 1, Medieval: 3, Modern: 8, Art & Culture: 4): Modern History had the highest representation, emphasizing national movements, colonial policies, and governance structures. Many questions followed the multi-statement and match the following formats, requiring both factual recall and analytical thinking.
- Geography (Indian: 8, Physical: 4, World: 2): Had a moderate presence, with emphasis on physical features, climate patterns, and resource distribution. Several questions were maps-based, testing location awareness and conceptual clarity.
- Social Issues & Schemes (2 Questions): A minor section, covering key government schemes & initiatives related to education, health, and welfare programs. Some questions were designed for elimination-based problem-solving.

Difficulty analysis
- Medium Difficulty (54 Questions): Formed the largest portion, requiring a blend of conceptual clarity and critical thinking.
- Easy Questions (29 Questions): Nearly one-third of the paper consisted of relatively simple questions, providing scoring opportunities for well-prepared candidates.
- Hard Questions (17 Questions): A limited but significant number of challenging questions, demanding deeper analytical skills and application-oriented thinking.

Variations in Question framing
- Multi-Statement Questions (46%) – Required critical thinking, analytical abilities, and elimination strategies. Frequently seen in Polity, Economy, and Environment.
- Direct Questions (54%) – More straightforward, favoring factual recall, particularly in Geography, History, and Science & Technology.

Current Affairs vs. Static Questions
- Static-Based (60 Questions): The majority of the paper was based on NCERTs, standard textbooks, and foundational knowledge from traditional sources.
- Current Affairs-Based (40 Questions): The paper deviated from the past four years' trend. While some topics required inference-based reasoning, many current affairs questions were direct. The focus was more on factual details rather than integrating concepts with dynamic events.
Key learning for Future Preparation
- Strengthen Static Fundamentals: Given that 60% of questions were from static topics, aspirants should focus on NCERTs, standard textbooks, and government reports.
- Prioritize Environment & Ecology: The increasing weightage highlights the need to cover conservation initiatives, biodiversity, and environmental policies comprehensively.
- Master Indian Economy Concepts: This section remains crucial, requiring conceptual understanding of financial policies, economic trends, GST, Monetary Policy Committee, and government initiatives.
- Enhance Multi-Statement Question Solving Techniques: With nearly half the paper in this format, mastering elimination techniques and analytical reasoning is essential.
- Maintain a Strong Balance Between Static and Dynamic Knowledge: The 40% share of current affairs reinforces the need to integrate contemporary events into static concepts.
Subject-Wise Answer Key
QUESTION 1
GS
Medium
Indian Geography
Prelims 2015
Which one of the following regions of India has a combination of mangrove forest, evergreen forest and deciduous forest?
A. North Coastal Andhra Pradesh
B. South-West Bengal
C. Southern Saurashtra
D. Andaman and Nicobar Islands
QUESTION 2
GS
Medium
Indian Geography
Prelims 2015
In a particular region in India, the local people train the roots of the living trees into robust bridges across the streams. As time passes these bridges become stronger. These unique ‘Living Root Bridges’ are found in -
A. Meghalaya
B. Himachal Pradesh
C. Jharkhand
D. Tamil Nadu
QUESTION 3
GS
Medium
Indian Geography
Prelims 2015
In India the steel production industry requires the import of
A. saltpetre
B. rock phosphate
C. coking coal
D. All of the above
QUESTION 4
GS
Medium
Physical Geography
Prelims 2015
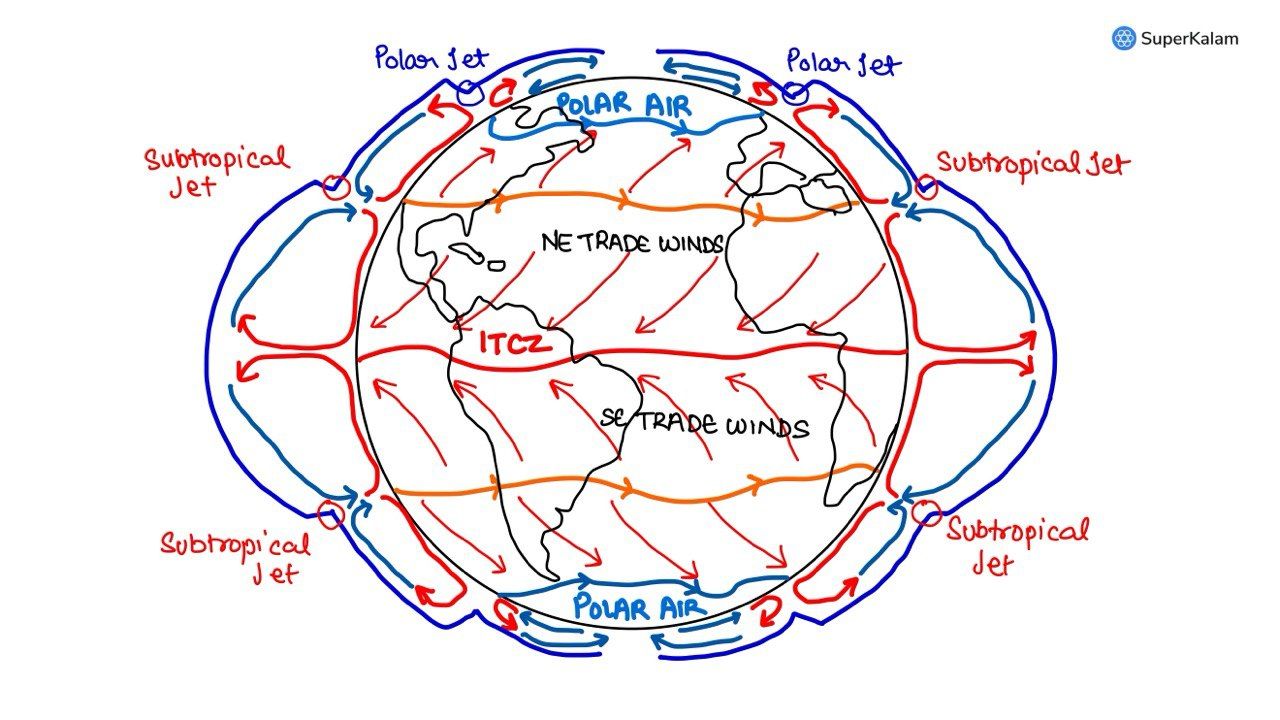
Consider the following statements:
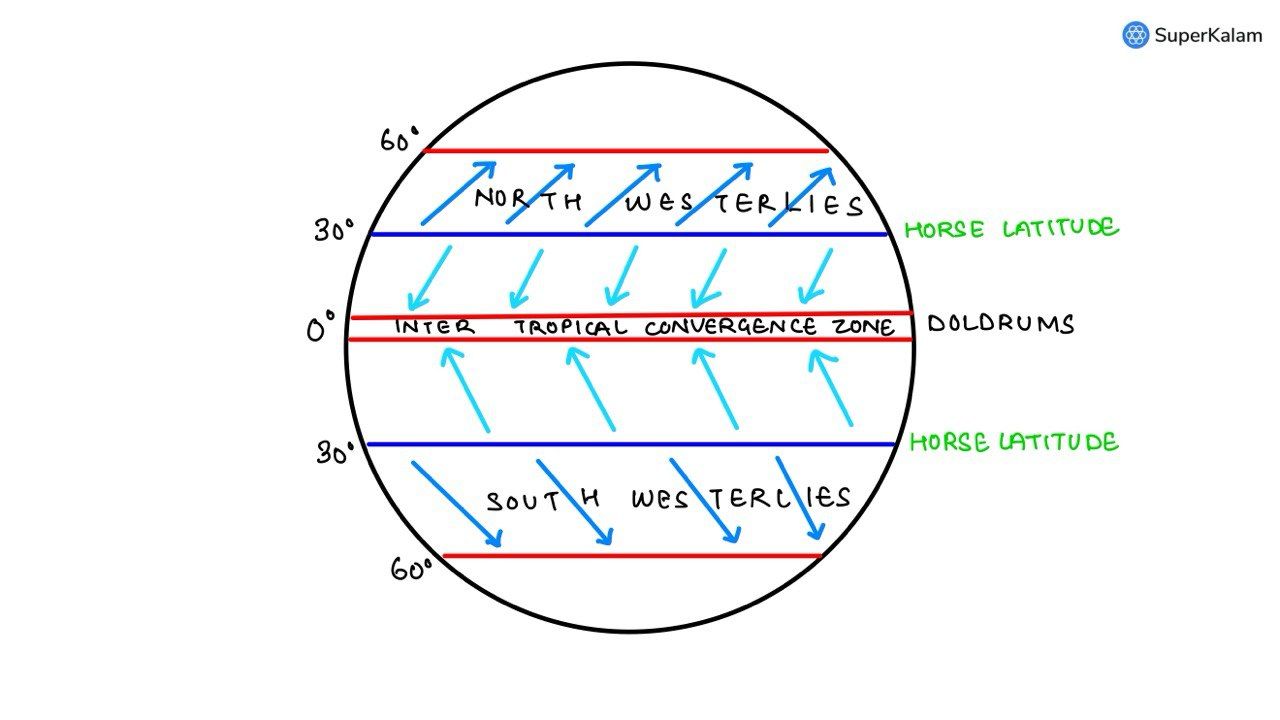
- The winds that blow between 30 degrees N and 60 degrees S latitudes throughout the year are known as westerlies.
- The moist air masses that cause winter rains in the North-Western region of India are part of westerlies.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 5
GS
Easy
Indian Geography
Prelims 2015
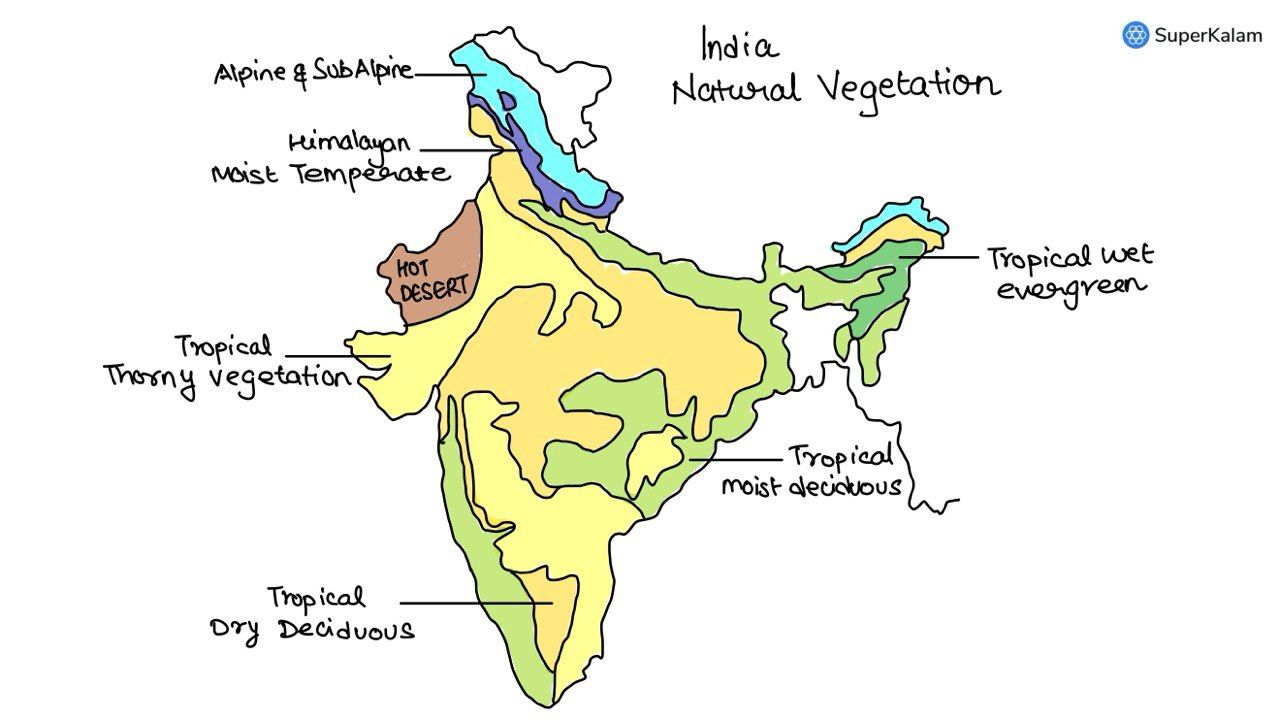
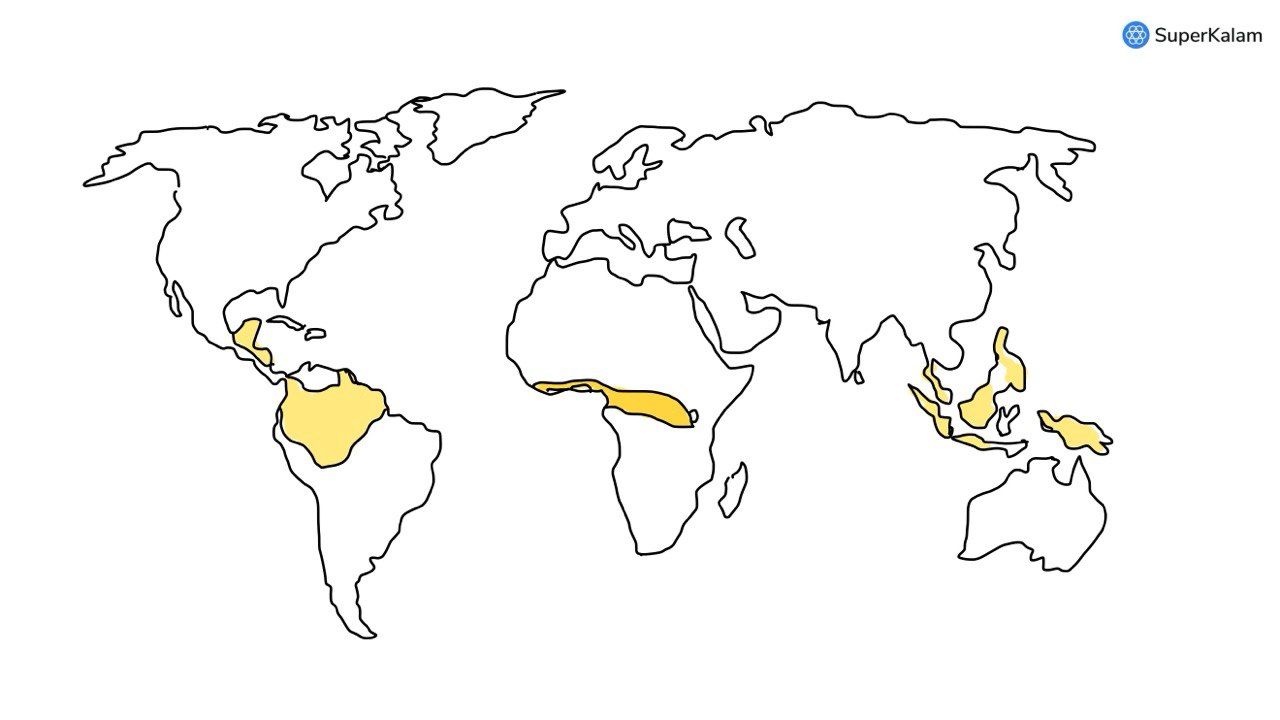
In India, in which one of the following types of forests is teak a dominant tree species?
A. Tropical moist deciduous forest
B. Tropical RainForest
C. Tropical thorn scrub forest
D. Temperate forest with grasslands
QUESTION 6
GS
Easy
Physical Geography
Prelims 2015
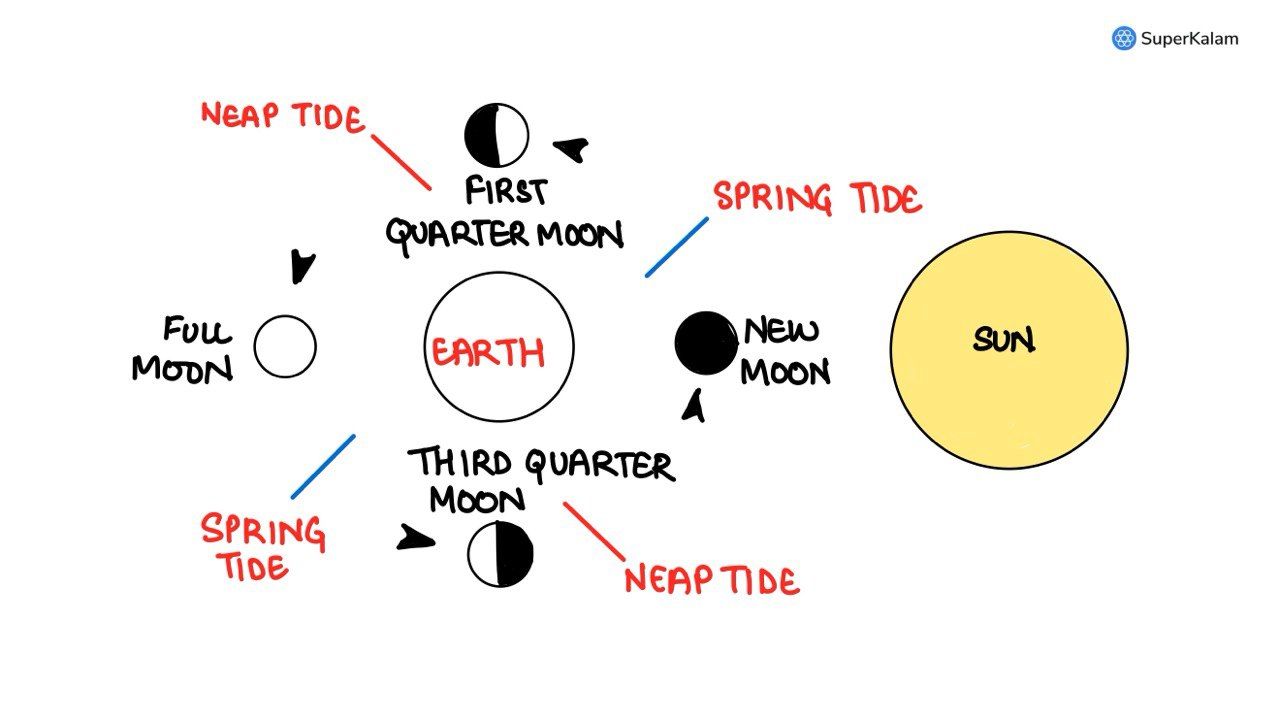
Tides occur in oceans and seas due to which among the following?
- Gravitational Force of the Sun
- Gravitational Force of the Moon
- Centrifugal force of the Earth
Select the correct answer using the code given below
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, and 3
QUESTION 7
GS
Medium
Indian Geography
Prelims 2015
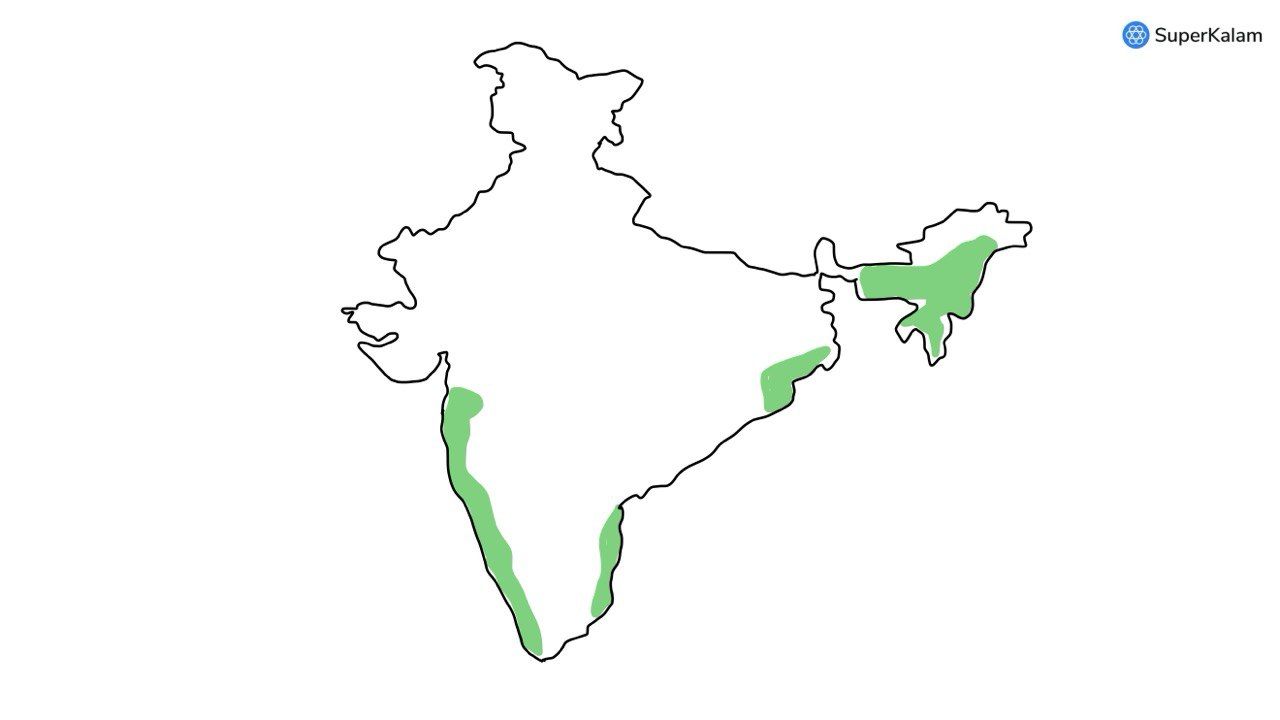
Consider the following States:
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Himachal Pradesh
- Mizoram
In which of the following states do ‘Tropical Wet Evergreen Forests’ occur?
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 8
GS
Hard
Physical Geography
Prelims 2015
In the South Atlantic and South Eastern Pacific regions in tropical latitudes, cyclone does not originate. What is the reason?
A. Sea Surface temperature are low
B. Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone seldom occurs
C. Coriolis force is too weak
D. The absence of land in those regions
QUESTION 9
GS
Medium
World Geography
Prelims 2015
“Each day is more or less the same, the morning is clear and bright with a sea breeze; as the sun climbs high in the sky, heat mounts up, dark clouds form than rain comes with thunder and lightning. But the rain is soon over.”
Which of the following regions is described in the above passage?
A. Savannah
B. Equatorial
C. Monsoon
D. Mediterranean
QUESTION 10
GS
Hard
Indian Geography
Prelims 2015
Consider the following rivers :
- Vamsadhara
- Indravati
- Pranahita
- Pennar
Which of the above are tributaries of Godavari?
A. 1,2 and 3
B. 2,3 and 4
C. 1,2 and 4
D. 2 and 3 only
QUESTION 11
GS
Hard
Physical Geography
Prelims 2015
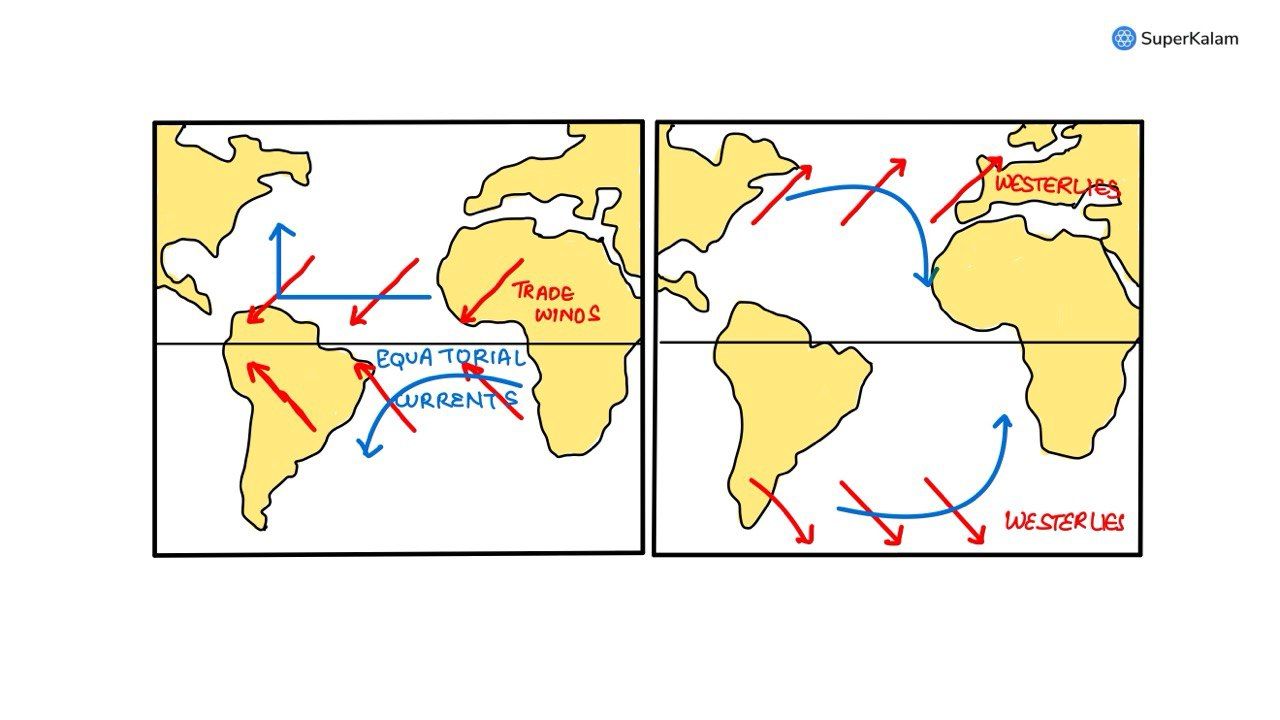
What explains the eastward flow of the equatorial counter-current?
A. The Earth’s rotation on its axis
B. Convergence of the two equatorial currents
C. Difference in salinity of the water
D. Occurrence of the belt of calm near the equator
QUESTION 12
GS
Medium
Indian Geography
Prelims 2015
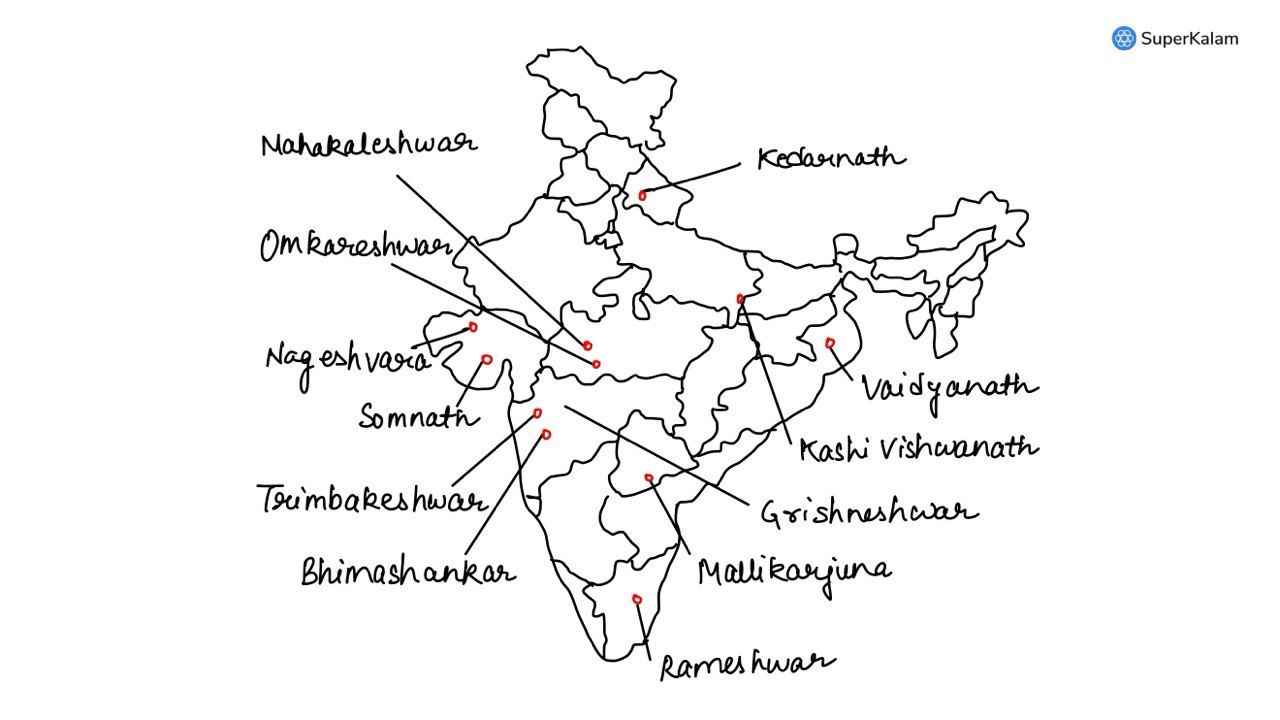
Consider the following pairs:
| Place of Pilgrimage | Location |
|---|---|
| 1. Srisailam | Nallamala Hills |
| 2. Omkareshwar | Satmala Hills |
| 3. Pushkar | Mahadeo Hills |
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1,2 and 3
QUESTION 13
GS
Medium
World Geography
Prelims 2015
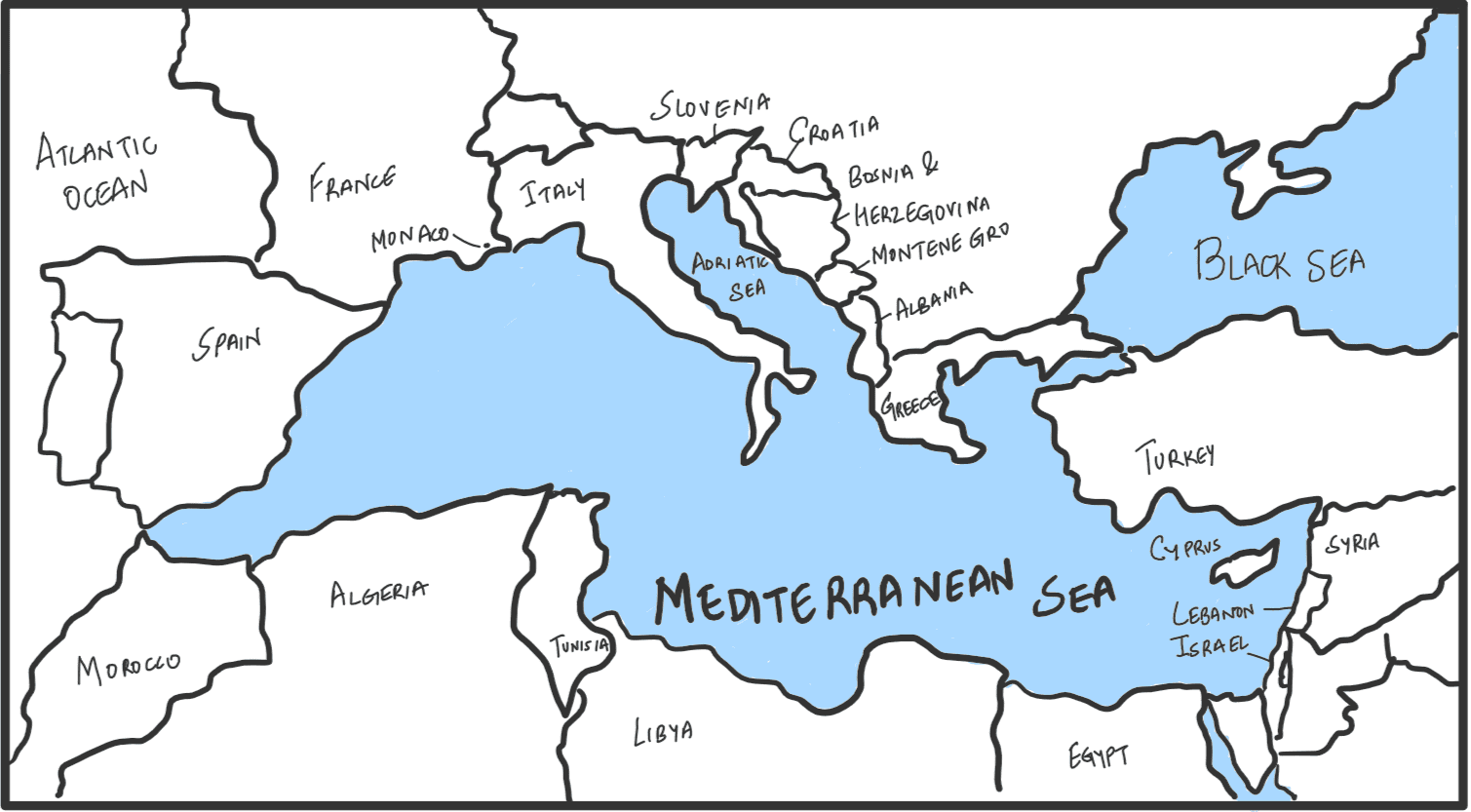
Which one of the following countries of South-West Asia does not open out to the Mediterranean Sea?
A. Syria
B. Jordan
C. Lebanon
D. Israel
QUESTION 14
GS
Easy
Indian Geography
Prelims 2015
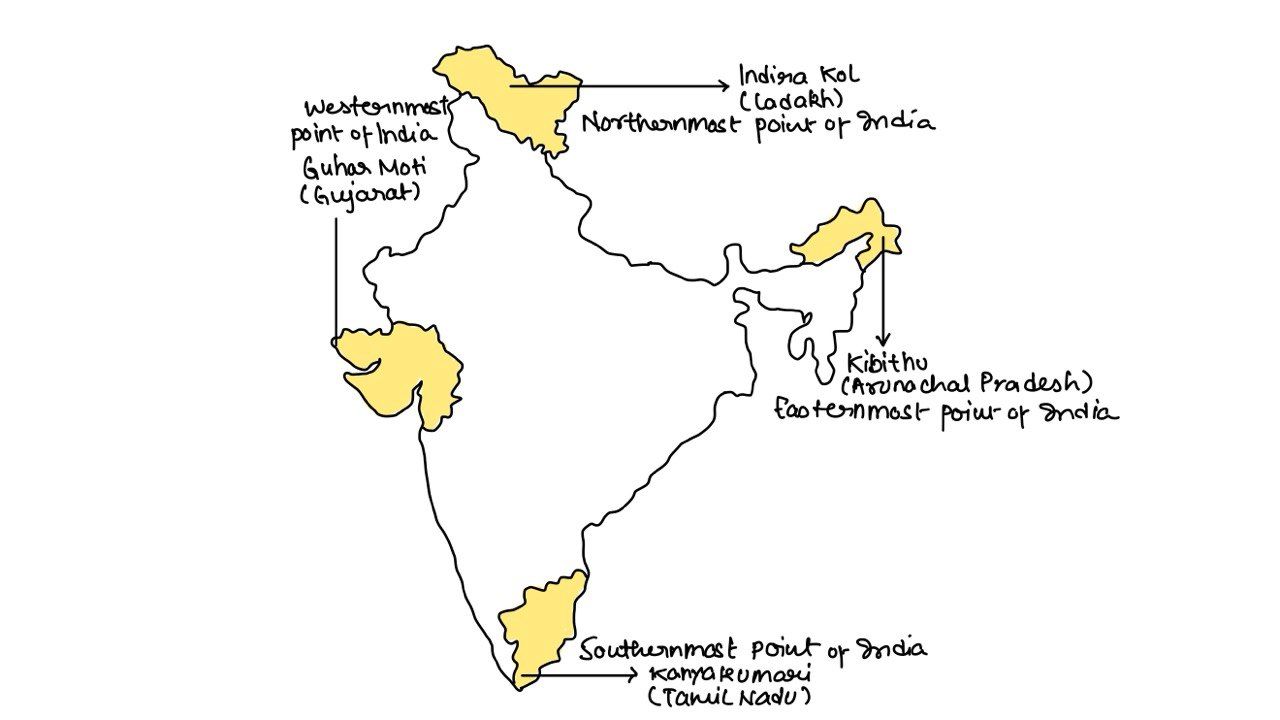
Which of the following pairs of States of India indicates the Easternmost and Westernmost State?
A. Assam and Rajasthan
B. Arunachal Pradesh and Rajasthan
C. Assam and Gujarat
D. Arunachal Pradesh and Gujarat