UPSC Prelims 2014 Analysis
Subject-Wise MCQ Distribution
- Economy (12 Questions): Covered economic growth indicators, fiscal policy, and banking. Questions were evenly split between static concepts and current affairs, requiring a strong grasp of government schemes and financial policies.
- Environment & Ecology (28 Questions): A major section, focusing on biodiversity, conservation policies, and climate change. Many questions demanded an interdisciplinary approach, linking geography, science, and governance.
- Indian Polity (10 Questions): Tested constitutional provisions, governance structures, and legal frameworks. Several questions required conceptual clarity over rote memorization.
- Modern History (5 Questions): Covered the freedom struggle, key personalities, and national movements. A mix of match the following and direct factual questions were asked.
- Science & Technology (11 Questions): Included topics on biotechnology, space technology, and applied sciences. Many questions required linking current affairs with static concepts, testing awareness of recent advancements.
- Art & Culture (15 Questions): Had a higher-than-usual weightage, emphasizing Buddhism, tribal culture, architecture, and performing arts. Required a detailed understanding of cultural heritage and traditions.
- International Relations (4 Questions): Covered global organizations, treaties, and India’s diplomatic engagements. Most questions were current affairs-driven, requiring knowledge of recent geopolitical developments.
- Medieval History (1 Question): Only one question appeared, focusing on administration in medieval India.
- Geography (Indian Geography: 8, Physical Geography: 1, World Geography: 3): A balanced mix, with emphasis on Indian geography and geophysical phenomena. Many questions included maps, requiring location-based knowledge.

Difficulty Analysis
- Medium Questions (49 Questions): The largest category, demanding a blend of factual knowledge and analytical reasoning. Found in Economy, Polity, and Science & Technology.
- Hard Questions (26 Questions): Required deep conceptual understanding, often framed in multi-statement formats. Common in Environment, Science & Technology, and International Relations.
- Easy Questions (25 Questions): Mostly from History and Polity, with straightforward factual recall. Provided scoring opportunities for well-prepared candidates.

Variations in Question Framing
- Multi-Statement Questions (64%) – Dominant in Polity, Economy, and Environment. Required careful reading, logical deduction, and elimination skills. Many were tricky due to wordplay, making conceptual clarity crucial.
- Direct Questions (36%) – Focused on factual recall, primarily in History and Geography. These were easier to answer for candidates with strong static knowledge.

Current Affairs vs. Static Questions
- Current Affairs-Driven Questions (40%) – Strong presence in Economy, Science & Technology, and Environment. Required awareness of government schemes, international developments, and technological advances.
- Static Knowledge-Based Questions (60%) – Covered fundamental concepts, particularly in Polity, History, and Geography. This highlights that despite the increasing weightage of current affairs, core syllabus topics remain crucial.
Key Learnings for Future Preparation
- Focus on Conceptual Clarity: The paper emphasized analytical thinking, especially in Polity, Economy, and Environment. A strong foundation is essential.
- Balanced Subject Preparation: No single subject dominated. Candidates must cover all subjects equally to adapt to changing trends.
- Master Elimination Techniques: Many multi-statement questions required logical reasoning. Practicing structured MCQs improves accuracy.
- Static Knowledge is Crucial: While current affairs had a presence, subjects like Polity, History, and Geography remained dominant.
- Practice & Revision Matters: Regular mock tests, PYQs, and revisions are essential for improving speed and accuracy.
Subject-Wise Answer Key
QUESTION 1
Medium
World Geography
Prelims 2014
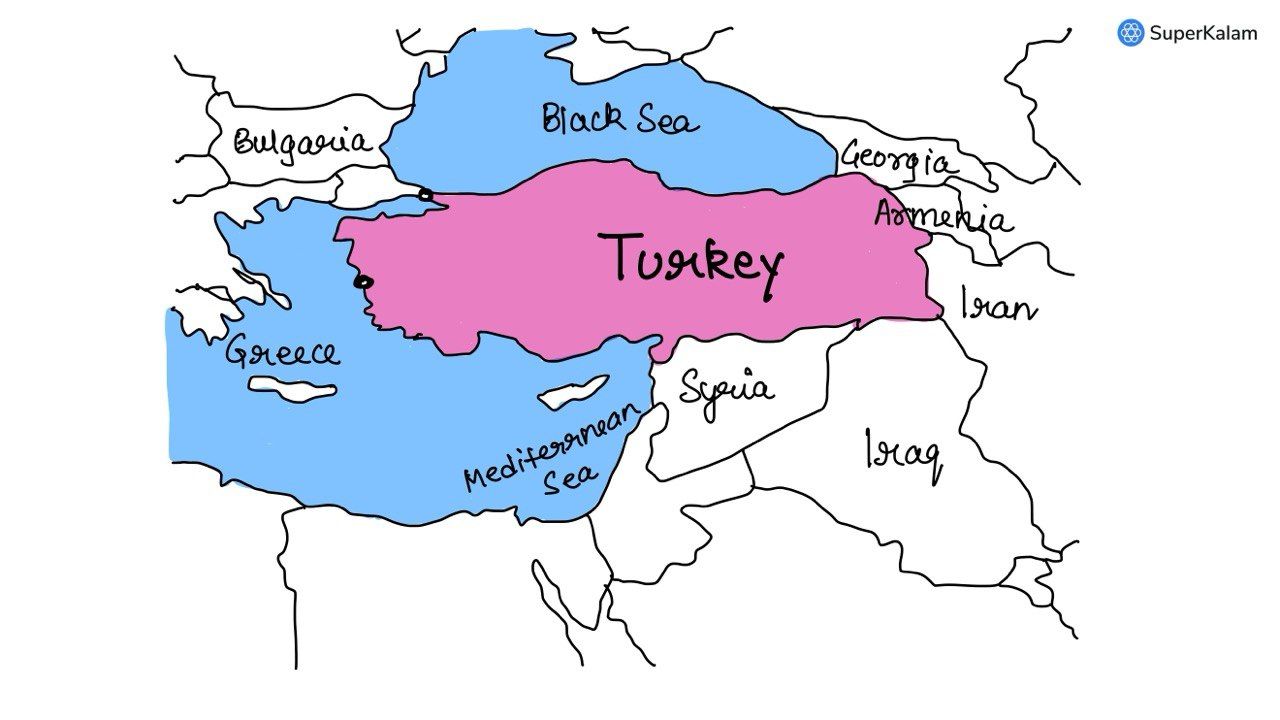
Turkey is located between
A. Black Sea and the Caspian Sea
B. Black Sea and the Mediterranean Sea
C. Gulf of Suez and the Mediterranean Sea
D. Gulf of Aqaba and the Dead Sea
QUESTION 2
Medium
Indian Geography
Prelims 2014
Consider the following pairs :
| National Highway | Cities Connected |
|---|---|
| 1. NH 4 | Chennai and Hyderabad |
| 2. NH 6 | Mumbai and Kolkata |
| 3. NH 15 | Ahmedabad and Jodhpur |
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 1, 2 and 3
D. None
QUESTION 3
Medium
Indian Geography
Prelims 2014
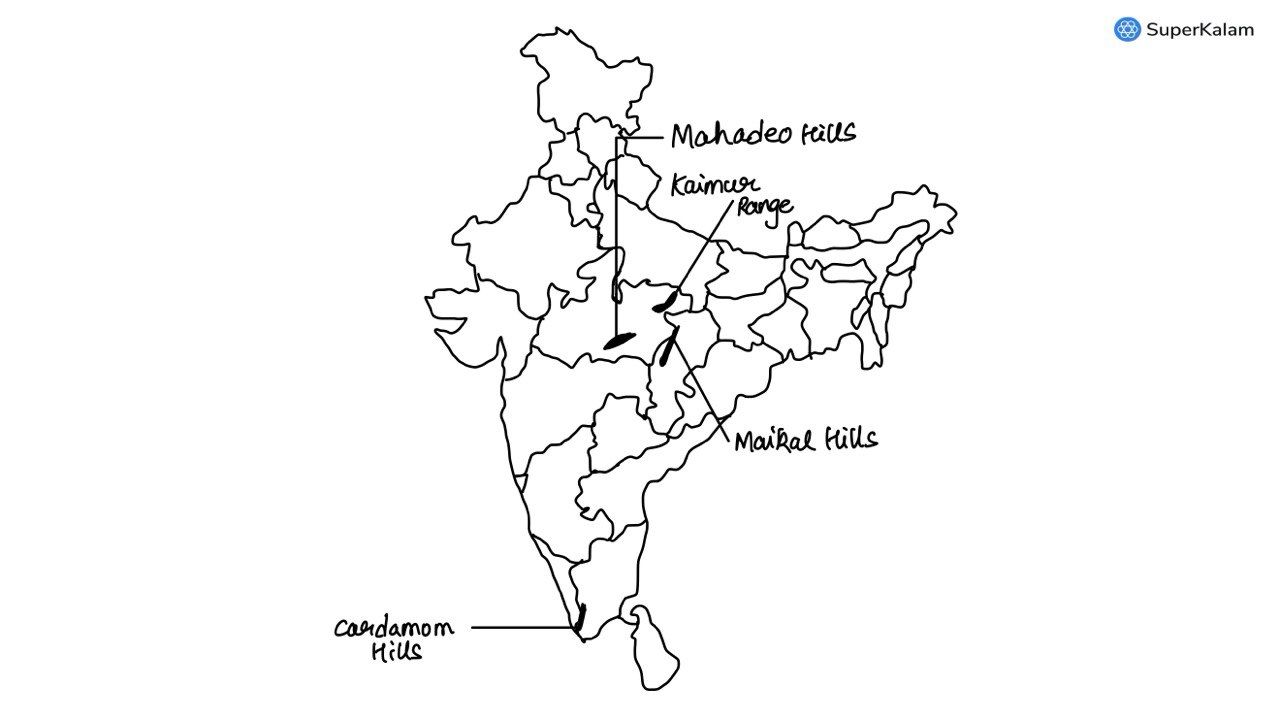
Consider these pairs -
- Cardamom Hills -- Coromandel Coast
- Kaimur Hills -- Konkan Coast
- Mahadeo Hills -- Central India
- Mikir Hills -- North-East India
Which of the above pairs are correctly matched?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 3 and 4 only
D. 2 and 4 only
QUESTION 4
Medium
World Geography
Prelims 2014
What is the correct sequence of occurrence of the following cities in South-East Asia as one proceeds from south to north?
- Bangkok
- Hanoi
- Jakarta
- Singapore
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
A. 4-2-1-3
B. 3-2-4-1
C. 3-4-1-2
D. 4-3-2-1
QUESTION 5
Hard
Indian Geography
Prelims 2014
If you travel through the Himalayas, you are Likely to see which of the following plants naturally growing there?
- Oak
- Rhododendron
- Sandalwood
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 6
Hard
Indian Geography
Prelims 2014
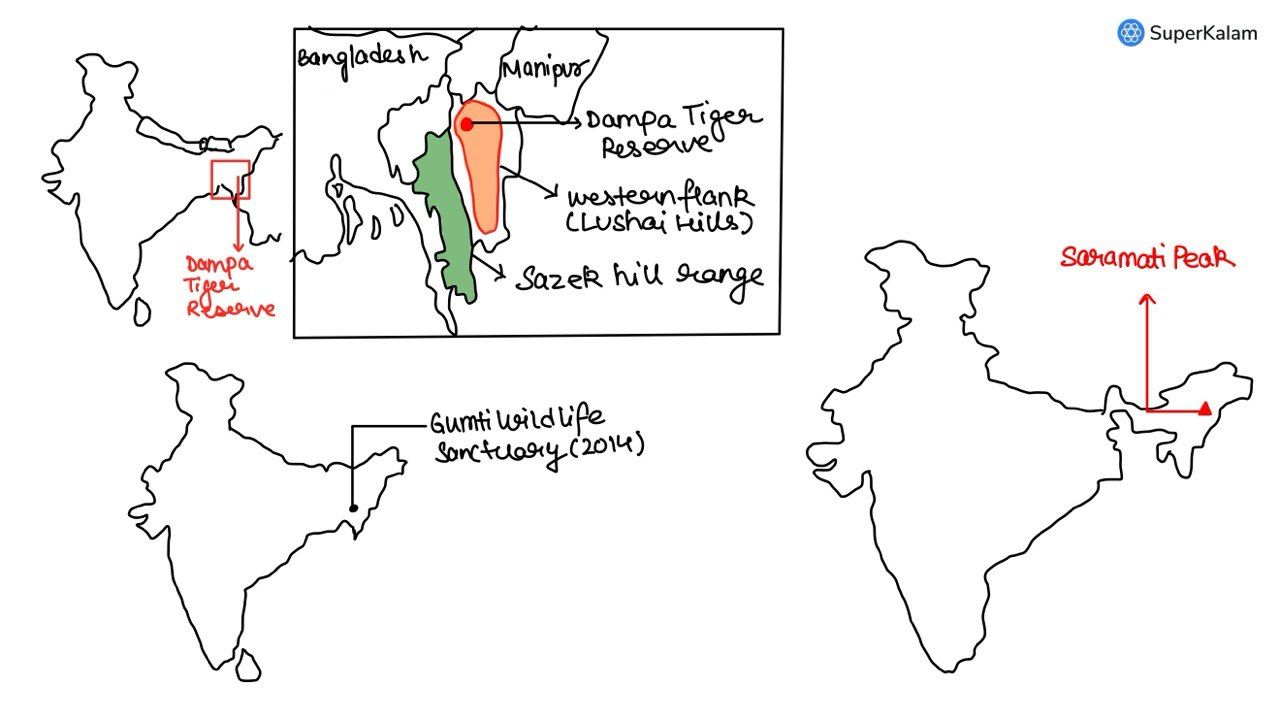
Consider the following pairs
- Dampa Tiger Reserve: Mizoram
- Gumti Wildlife Sanctuary: Sikkim
- Saramati Peak: Nagaland
Which of the above pairs is /are correctly matched?
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 7
Easy
World Geography
Prelims 2014
The seasonal reversal of winds is the typical characteristic of -
A. Equatorial climate
B. Mediterranean climate
C. Monsoon climate
D. All of the above climates
QUESTION 8
Hard
Indian Geography
Prelims 2014
With reference to two non-conventional energy sources called ‘coal bed methane’ and ‘shale gas’, consider the following statements:
- Coal bed methane is the pure methane gas extracted from coal seams, while shale gas is a mixture of propane and butane only that can be extracted from fine-grained sedimentary rocks.
- In India abundant coal bed methane sources exist, but so far no shale gas sources have been found.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2
QUESTION 9
Easy
Physical Geography
Prelims 2014
Which of the following phenomena might have influenced the evolution of organisms?
- Continental drift
- Glacial cycles
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
A. 1 only
B. 2 only
C. Both 1 and 2
D. Neither 1 nor 2.
QUESTION 10
Easy
Indian Geography
Prelims 2014
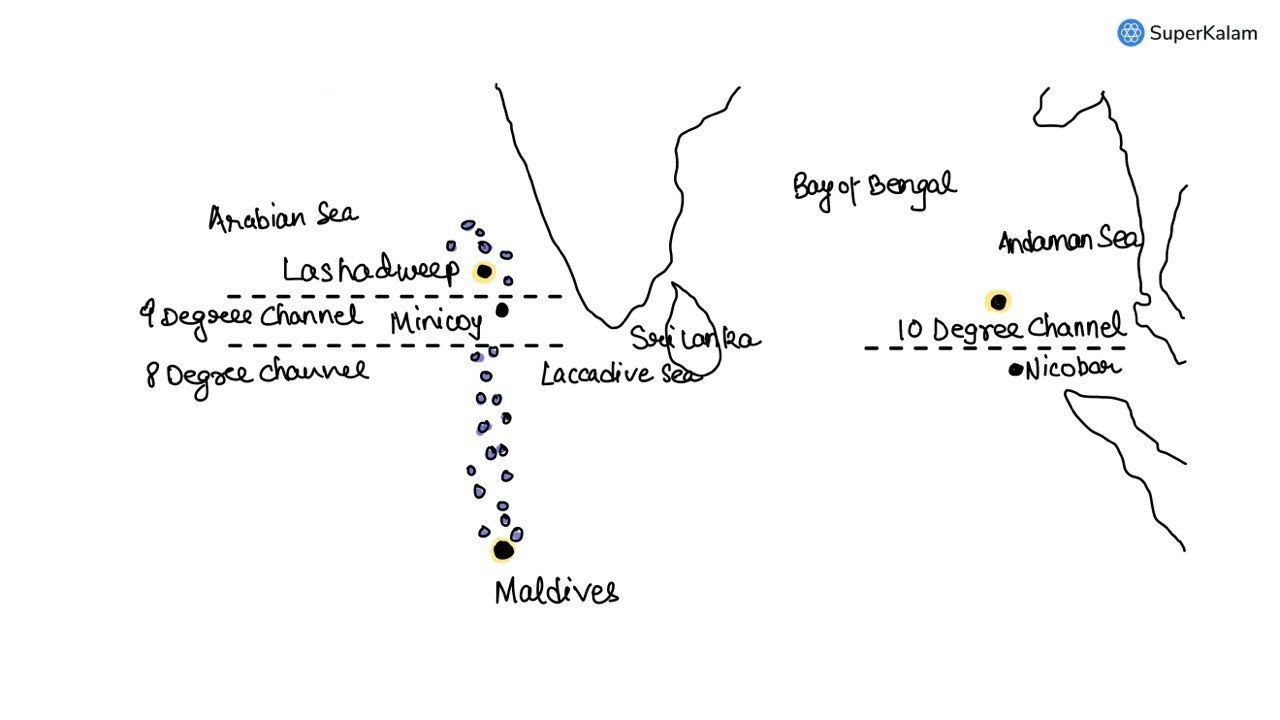
Which one of the following pairs of islands are separated from each other by the ‘Ten Degree Channel’?
A. Andaman and Nicobar
B. Nicobar and Sumatra
C. Maldives and Lakshadweep
D. Sumatra and Java
QUESTION 11
Medium
Indian Geography
Prelims 2014
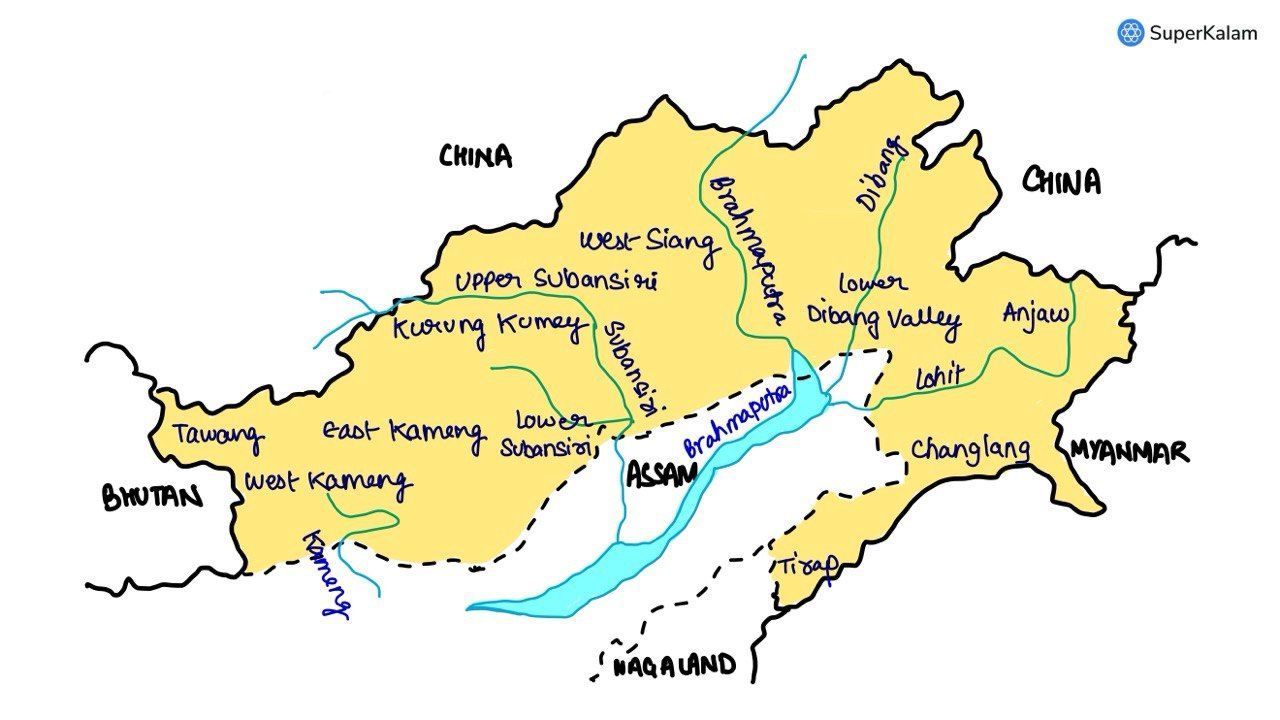
Consider the following rivers:
- Barak
- Lohit
- Subansiri
Which of the above flows / flow through Arunachal Pradesh?
A. 1 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
QUESTION 12
Hard
Indian Geography
Prelims 2014
| Region | Well known for the production of |
|---|---|
| 1. Kinnaur (Himachal) | Areca nut |
| 2. Mewat (Haryana) | Mango |
| 3. Coromandel (TN-Andhra) | Soya bean |
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 3 only
C. 1, 2 and 3
D. None