What is a twister? Why are the majority of twisters observed in areas around the Gulf of Mexico?
What is a twister? Why are the majority of twisters observed in areas around the Gulf of Mexico?
Subject: World Geography
A twister, also known as a tornado, is a violently rotating column of air extending from a thunderstorm cloud to the ground, characterized by its funnel-shaped appearance and devastating potential.
These natural phenomena represent one of nature's most intense and destructive atmospheric disturbances, capable of generating wind speeds exceeding 190 mph as recorded in Diaz, Arkansas in March 2025.
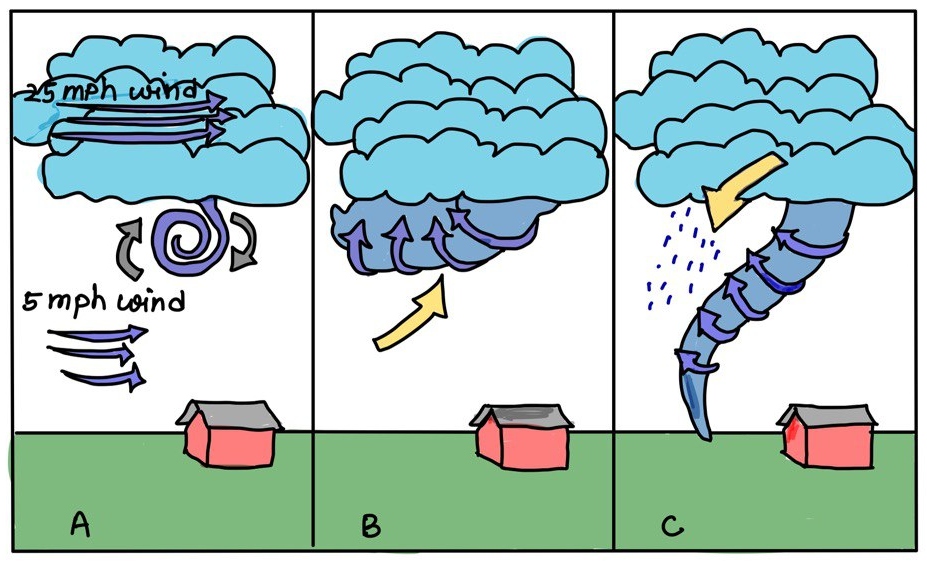
Formation of Twisters
Characteristics of Twisters
- Funnel Formation: Develop from supercell thunderstorms with a rotating updraft called a mesocyclone.
- Wind Speeds: Can range from mild to extremely violent, causing catastrophic damage to infrastructure and landscapes.
- Size Variation: Range from narrow ropes to massive wedges, sometimes over a mile wide.
- Duration: Usually last for a few minutes but can persist longer in favorable conditions.
Reasons for High Frequency in Gulf of Mexico Region
-
Atmospheric Conditions:
- The region serves as a meeting point between warm, moist air masses from the Gulf and cool, dry continental air from the north.
- This interaction creates ideal conditions for severe thunderstorm development.
-
Geographic Factors:
- Proximity to Tornado Alley: The Gulf region's location near the traditional Tornado Alley enhances tornado formation potential.
- The flat terrain allows unimpeded movement of air masses.
-
Meteorological Elements:
- Sea Breezes: Enhanced thunderstorm activity due to sea breeze convergence.
- Seasonal Timing: Earlier spring tornado season, as evidenced by 43 tornadoes in the northern Gulf Coast region during 2024.
- High moisture content from the Gulf waters provides fuel for storm development.
-
Climate Patterns:
- The region experiences consistent weather patterns conducive to tornado formation.
- Recent data shows 350 preliminary tornado reports in central Gulf Coast states, demonstrating the area's vulnerability.
The combination of these geographical and meteorological factors makes the Gulf of Mexico region a natural tornado laboratory, consistently producing conditions favorable for twister formation throughout the year, particularly during spring months.
Answer Length
Model answers may exceed the word limit for better clarity and depth. Use them as a guide, but always frame your final answer within the exam’s prescribed limit.
In just 60 sec
Evaluate your handwritten answer
- Get detailed feedback
- Model Answer after evaluation
Model Answers by Subject
Crack UPSC with your
Personal AI Mentor
An AI-powered ecosystem to learn, practice, and evaluate with discipline