How did the colonial rule affect the tribals in India and what was the tribal response to the colonial oppression?
How did the colonial rule affect the tribals in India and what was the tribal response to the colonial oppression?
The tribal communities of India, with their distinct socio-economic and cultural systems, were deeply affected by colonial rule from the late 18th century onward. British policies disrupted their traditional livelihoods, land rights, autonomy, and cultural identity, leading to widespread resentment and rebellions across regions.
Impact of Colonial Rule on Tribals
-
Land Alienation: Introduction of Permanent Settlement (1793) and other land revenue systems led to alienation of tribal land to non-tribals (moneylenders, zamindars, settlers - Dikus).
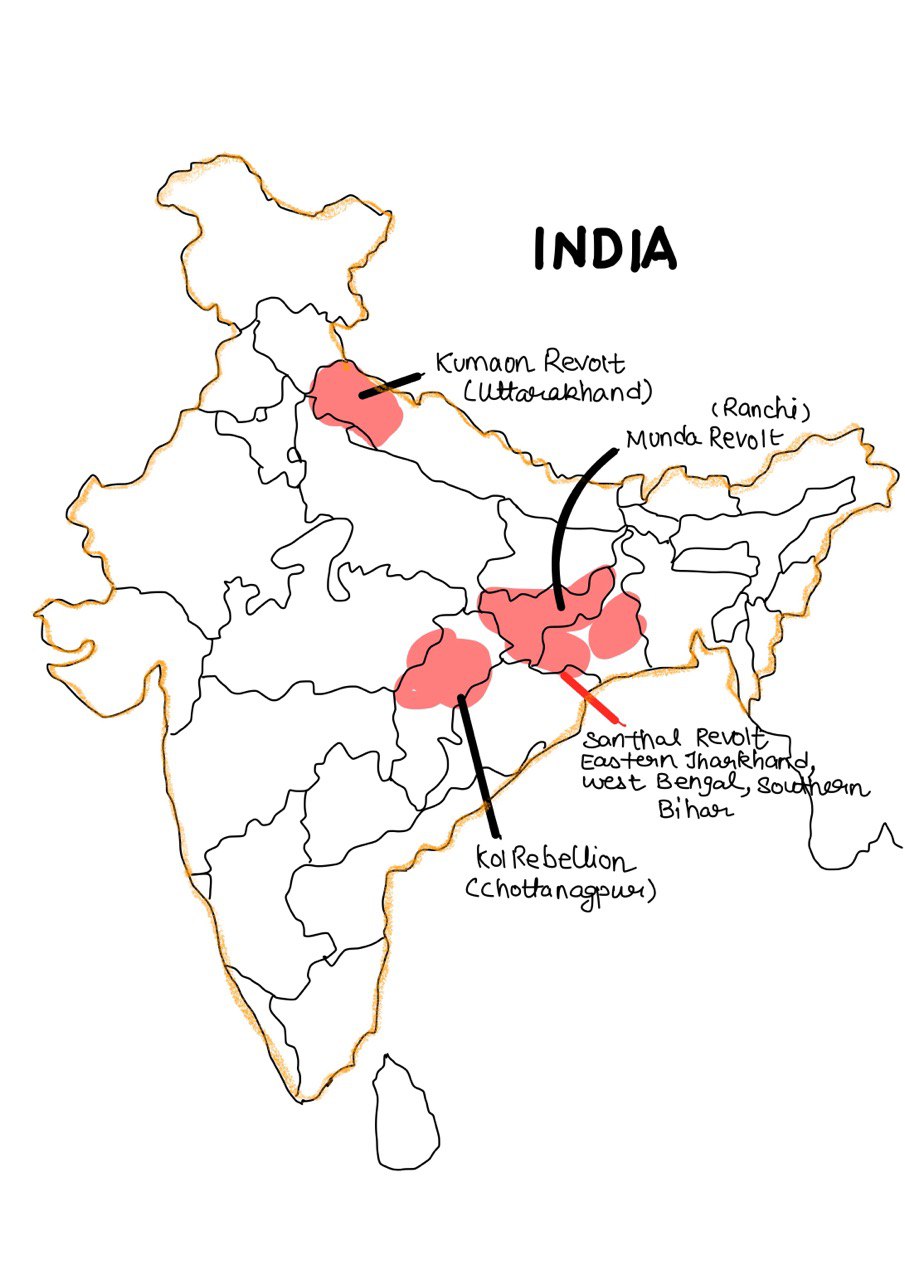
- Example: Santhals of Bihar and Mundas of Chotanagpur lost land to dikus (outsiders).
-
Forest Rights Violation: Indian Forest Acts (1865, 1878, 1927) criminalized tribal practices like shifting cultivation, hunting, and forest grazing.
- Criminalization of entire tribes under Criminal Tribes Act 1871.
-
Economic Exploitation:
- Tribals were turned into indentured labourers on tea plantations (Assam), mines (Jharkhand), and railways.
- Tribal economy, based on barter and subsistence, was replaced by exploitative cash economy.
-
Indebtedness: Settlement of outsider in tribal lands and exhorbitant land rates pushed tribal towards moneylenders who charged high interest rates and manipulated records.
-
Cultural Marginalization: Missionary activities and Western education attempted to ""civilize"" tribals, undermining their belief systems and traditional institutions.
-
Social Displacement and Disintegration:
-
Construction of dams, roads, and railways led to physical displacement of tribal populations.
-
Depopulation of tribal areas occurred due to migration and forced labour.
-
Data: By early 20th century, tribals formed a disproportionate share of labour in Assam’s tea estates and coal mines in eastern India.
-
-
Introduction of western legal system: It eroded customary tribal laws and authority of village heads leading to their marginalization without legal recourse.
Tribal Response to Colonial Oppression
Tribal resistances were both armed and non-violent, rooted in the desire to protect land, identity, and autonomy.
-
Rebellions and Uprisings
- Santhal Rebellion (1855–56): Against exploitation by moneylenders and British officials.
- Munda Ulgulan (1899–1900): Led by Birsa Munda, against land alienation and missionary influence.
- Bhil Revolts (1818–1831): Western India against British taxation and forest restrictions.
- Rampa Rebellion (1922–24): Led by Alluri Sitarama Raju in Andhra Pradesh against forest laws.
-
Religious and Cultural Movements
- Emergence of messianic leaders like Birsa Munda and Kanhu Murmu who revived tribal religion and identity.
- Movements like Tana Bhagat Movement among Oraons combined Gandhian ideas with tribal resistance.
-
Alliance with National Movement
- Some tribal movements eventually merged with the Indian national movement, especially during the Non-Cooperation Movement and Quit India Movement.
The colonial rule systematically dispossessed and disempowered tribal communities, yet it also ignited their political consciousness. The resilience and resistance of the tribals formed an integral part of the broader freedom struggle. Their revolts, though often localized, laid the foundation for the later constitutional recognition of tribal rights and autonomy post-Independence.
Answer Length
Model answers may exceed the word limit for better clarity and depth. Use them as a guide, but always frame your final answer within the exam’s prescribed limit.
In just 60 sec
Evaluate your handwritten answer
- Get detailed feedback
- Model Answer after evaluation
Model Answers by Subject
Crack UPSC with your
Personal AI Mentor
An AI-powered ecosystem to learn, practice, and evaluate with discipline