From being net food importer in 1960s, India has emerged as a net food exporter to the world. Provide reasons.
From being net food importer in 1960s, India has emerged as a net food exporter to the world. Provide reasons.
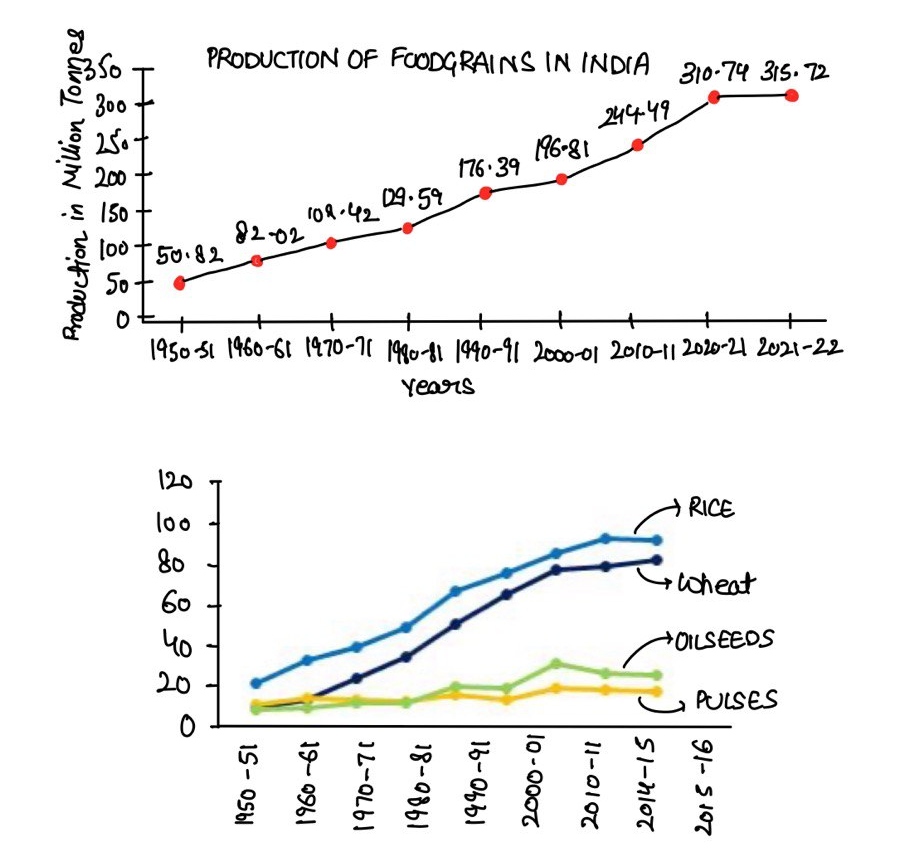
In the 1960s, India faced recurring famines and food shortages, leading to dependence on imports like PL-480 wheat from the US. However, by 2022–23, India had become the 2nd largest producer of rice and wheat and a significant net exporter of foodgrains, reflecting a structural transformation in its agricultural economy.
Reasons for the Shift from Net Food Importer to Exporter
-
Green Revolution (1965 onwards)
- Introduction of High Yielding Variety (HYV) seeds, chemical fertilizers, and irrigation in Punjab, Haryana, and western UP.
- Wheat production grew from 11 million tonnes (1960s) to over 110 million tonnes (2022).
-
Government Support & MSP Regime
- Institutional support via Minimum Support Price (MSP), procurement by Food Corporation of India (FCI), and public distribution system (PDS).
- Encouraged large-scale cultivation and marketable surplus.
-
Irrigation and Infrastructure Expansion
- Canal networks (like Indira Gandhi Canal), Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY), and rural electrification worked in synergy to expand irrigation facilities in India.
- Reduced monsoon dependence and stabilized yields.
-
Agri-Research and Extension Services: Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) and Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVK) helped develop region-specific cropping techniques and climate-resilient varieties.
-
Policy Shifts towards Agri-Exports
- Launch of Agri Export Policy 2018 and identification of 46 export hubs.
- India now exports rice, wheat, sugar, spices, marine products, and processed foods to over 100 countries.
-
Diversification and Value Addition
- Growth of horticulture, dairy, and fisheries with targeted schemes like Operation Greens, Blue Revolution, and PM Kisan Sampada Yojana.
- India became world’s largest producer of milk (220 MMT in 2022–23).
-
WTO-compliant Subsidies and Global Market Access
- Export subsidies phased out, replaced by infrastructure and logistics support.
- Enhanced competitiveness in global markets (e.g., Basmati rice to the Middle East & EU).
-
Use of Digital and Agri-Tech Tools: Use of eNAM, Kisan drones, and mobile apps for weather, pricing, and supply chain planning increased farmer efficiency.
India’s transition from food insecurity to food surplus is a testament to visionary policy, scientific innovation, and farmer resilience. As the world faces new food security challenges due to climate change and geopolitics, India’s role as a “grain basket of the Global South” will continue to grow, provided sustainability and inclusivity are ensured.
Answer Length
Model answers may exceed the word limit for better clarity and depth. Use them as a guide, but always frame your final answer within the exam’s prescribed limit.
In just 60 sec
Evaluate your handwritten answer
- Get detailed feedback
- Model Answer after evaluation
Model Answers by Subject
Crack UPSC with your
Personal AI Mentor
An AI-powered ecosystem to learn, practice, and evaluate with discipline