What is Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS)? What is the potential role of CCUS in tackling climate change?
What is Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS)? What is the potential role of CCUS in tackling climate change?
India's CO2 emissions are projected to peak by 2040, making Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS) a critical technology for achieving net-zero by 2070.
What is CCUS Technology
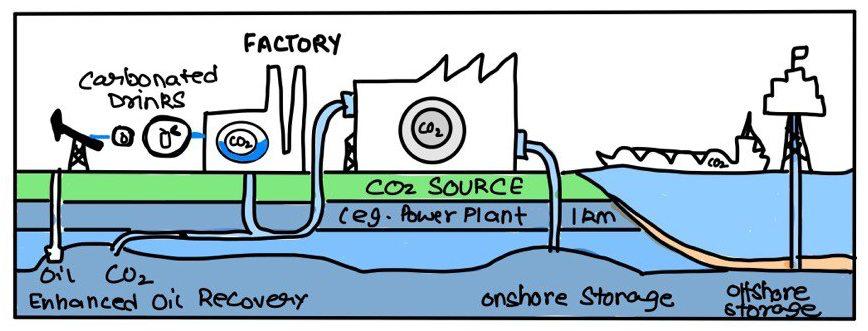
CCUS is an integrated process involving three key stages:
- Carbon Capture: Extracting CO2 from large emission sources like power plants using post-combustion capture, pre-combustion capture, or direct air capture technologies.
- Utilization: Converting captured CO2 into useful products like synthetic fuels, chemicals, concrete, and plastics.
- Storage: Permanently storing CO2 in deep geological formations, saline aquifers, or depleted oil/gas reservoirs.
- Example: Sleipner Project in Norway stores ~1 million tonnes of CO₂ per year beneath the North Sea.
Potential Role of CCUS in Tackling Climate Change
Industrial Decarbonization
- Enables hard-to-abate sectors like cement, steel, and chemicals to reduce emissions by 85-95%.
- Tata Steel's Jamshedpur plant is piloting CCUS to capture 5 million tonnes CO2 annually.
- ACC Cement implementing carbon capture at multiple facilities across India.
Power Sector Transformation
- Allows existing coal power plants to continue operating while reducing emissions.
- NTPC's Vindhyachal plant testing post-combustion capture technology.
Economic Opportunities
- Creates $1 trillion global market by 2030 for CCUS technologies.
- Generates revenue through carbon credits and CO2-derived products.
- Reliance Industries investing ₹75,000 crores in carbon-to-chemicals projects.
Climate Targets Achievement
- Essential for meeting Paris Agreement goals of limiting warming to 1.5°C.
- IEA estimates CCUS must capture 7.6 billion tonnes CO2 annually by 2050.
- India's Mission Innovation program allocating funds for CCUS research.
Challenges in Scaling CCUS
| Challenge | Details |
|---|---|
| High cost | Capture and storage technologies remain expensive |
| Lack of regulatory framework | Absence of legal clarity on liability and storage rights |
| Infrastructure needs | Pipeline and storage infrastructure is limited |
| Public perception | Concerns about leakage and "license to pollute" |
CCUS is not a silver bullet, but it is a critical piece of the climate mitigation puzzle, especially for countries like India with large industrial emissions. With right policy support, investment, and innovation, CCUS can help achieve deep decarbonization, bridge the net-zero gap, and enable a just energy transition.
Answer Length
Model answers may exceed the word limit for better clarity and depth. Use them as a guide, but always frame your final answer within the exam’s prescribed limit.
In just 60 sec
Evaluate your handwritten answer
- Get detailed feedback
- Model Answer after evaluation
Model Answers by Subject
Crack UPSC with your
Personal AI Mentor
An AI-powered ecosystem to learn, practice, and evaluate with discipline