What is the technology being employed for electronic toll collection on highways? What are its advantages and limitations? What are the proposed changes that will make this process seamless? Would this transition carry any potential hazards?
What is the technology being employed for electronic toll collection on highways? What are its advantages and limitations? What are the proposed changes that will make this process seamless? Would this transition carry any potential hazards?
Subject: Science & Technology
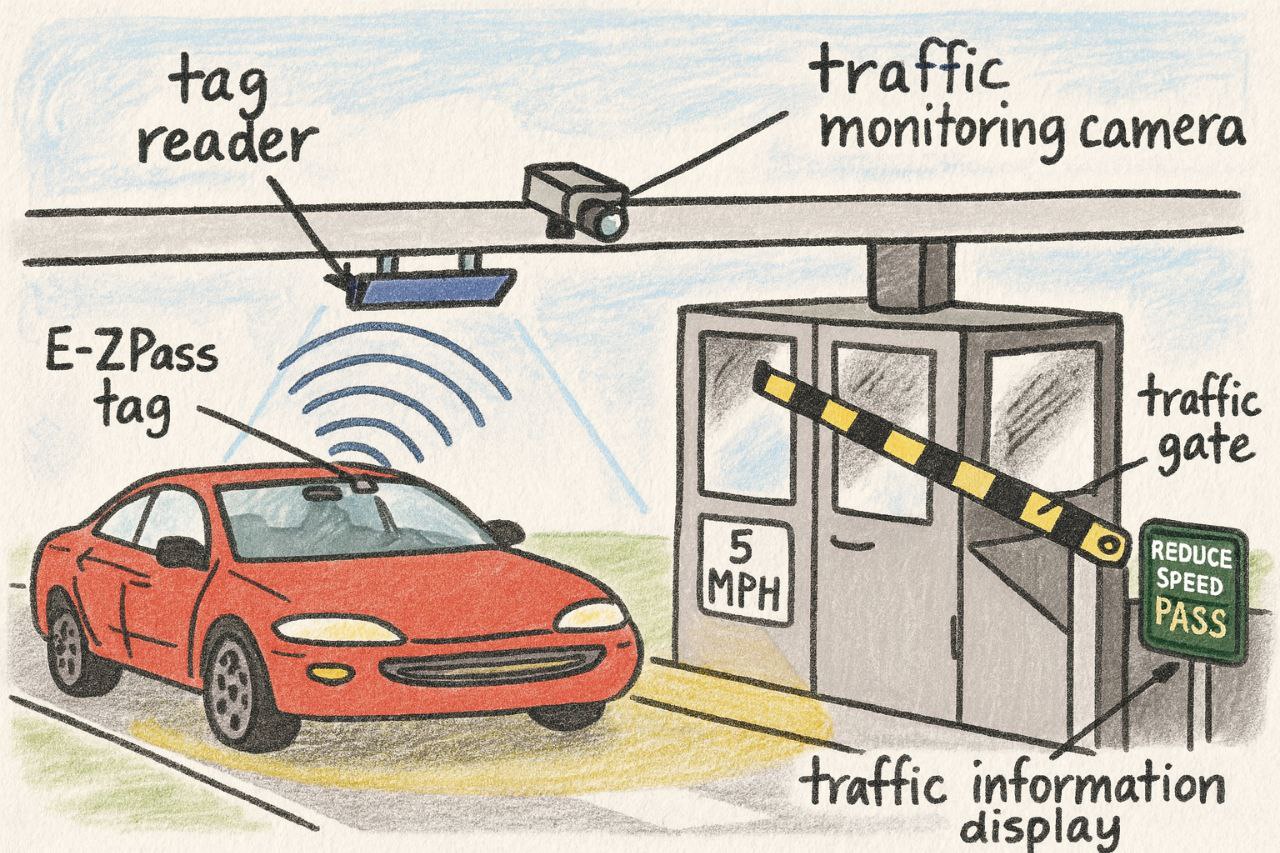
Electronic toll collection (ETC) in India primarily uses RFID-based FASTag technology for cashless highway tolling. Over 6.5 crore FASTags have been issued, with 97% of tolls now collected electronically on national highways.
Current Technology
FASTag System uses Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags on vehicle windshields that communicate with toll plaza readers for automatic payment deduction. Emerging technologies include Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR) and GPS-based tolling systems.
Advantages
Operational Benefits:
- Reduced waiting time by up to 30 minutes per vehicle
- Annual fuel savings of ₹12,000 crores due to reduced idling
- 50% increase in toll collection after FASTag mandate
- Transparent revenue collection preventing leakages
User Benefits:
- Cashless transactions across all highways
- Single FASTag works nationwide through National Electronic Toll Collection (NETC) system
- Better traffic data for infrastructure planning
Limitations
Technical Issues:
- RFID reader malfunctions and weather-related disruptions
- Heavy dependence on internet connectivity
- Insufficient ETC lanes causing peak-hour congestion
User Problems:
- Balance recharging difficulties
- Double toll charges for vehicles without functional FASTag
- Inconsistent implementation across state highways
Proposed Changes
Next-Generation Systems:
- GNSS-based tolling for distance-based charging
- Multi-Lane Free Flow (MLFF) technology eliminating toll booths
- Enhanced ANPR integration reducing dependency on physical tags
- Unified national platform for seamless interstate travel
Potential Hazards
Security Risks:
- Cybersecurity threats to financial and movement data
- Privacy concerns over vehicle tracking capabilities
Technical Risks:
- System downtime causing traffic disruptions
- GPS failures leading to incorrect toll charges
- High implementation costs
Social Challenges:
- Digital divide affecting rural and less tech-savvy users
- Public resistance to new technologies
- Temporary disruptions during system transitions
India's ETC system has evolved from RFID-based FASTag to advanced GNSS and ANPR technologies. While current systems improved efficiency and transparency, transitioning to satellite-based tolling offers seamless travel but requires addressing cybersecurity, privacy, and implementation challenges through careful planning and gradual rollout.
Answer Length
Model answers may exceed the word limit for better clarity and depth. Use them as a guide, but always frame your final answer within the exam’s prescribed limit.
In just 60 sec
Evaluate your handwritten answer
- Get detailed feedback
- Model Answer after evaluation
Model Answers by Subject
Crack UPSC with your
Personal AI Mentor
An AI-powered ecosystem to learn, practice, and evaluate with discipline