The citizen charter has been a landmark initiative in ensuring citizen- centric administration. But it is yet to reach its full potential. Identify the factors hindering the full realization of its promise and suggest measures to overcome them.
The citizen charter has been a landmark initiative in ensuring citizen- centric administration. But it is yet to reach its full potential. Identify the factors hindering the full realization of its promise and suggest measures to overcome them.
Subject: Governance
The Citizen's Charter, introduced in 1997 as part of the "Action Plan for Effective and Responsive Government", represents a significant step towards ensuring transparent and accountable public service delivery. It outlines the commitment of an organization towards standard, quality, and time frame of service delivery, grievance redressal mechanisms, and expectations from the citizens.
Despite being a landmark initiative, the Citizen’s Charter has not yet delivered on its full promise of ensuring citizen-centric governance.
Factors Hindering the Full Potential
Administrative Challenges
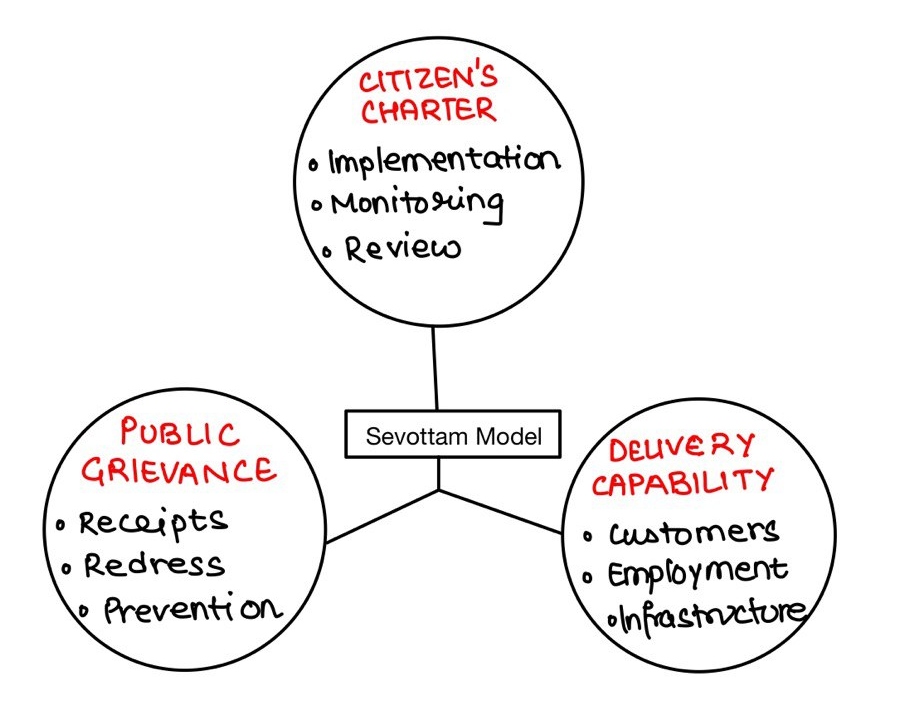
- Weak Implementation: Lack of proper monitoring mechanisms and accountability frameworks leads to ineffective execution of charter provisions.
- Bureaucratic Resistance: Traditional administrative mindset and resistance to change impede the adoption of citizen-centric approaches.
- Poor Design: Charters often contain vague promises and outdated service standards, making implementation difficult.
Legal and Institutional Issues
- Absence of Legal Backing: Unlike the Right to Information Act, citizen charters lack statutory status, making them merely advisory in nature.
- Inadequate Infrastructure: Insufficient resources and technological capabilities hamper effective service delivery.
- Limited Coordination: Poor coordination between different departments affects seamless service delivery.
Awareness and Participation
- Low Public Awareness: Citizens are often unaware of their rights and the provisions outlined in the charter.
- Communication Gap: Ineffective communication between service providers and citizens affects service quality.
- Limited Stakeholder Consultation: Top-down approach in charter formulation without adequate public participation.
Measures for Improvement
Institutional Reforms
- Implementation of Sevottam Model for service delivery excellence.
- Regular updating of service standards based on citizen feedback and changing needs.
- Establishment of robust grievance redressal mechanisms.
Legal and Policy Measures
- Enact a Citizen Services Delivery Guarantee Act, as done in states like Madhya Pradesh and Karnataka, to make charters enforceable.
- Integration with e-governance initiatives like Digital India.
- Setting up independent monitoring and evaluation mechanisms.
Capacity Building
- Regular training of public officials in citizen-centric service delivery.
- Enhancing public awareness through media campaigns and social outreach.
- Promoting citizen participation in charter formulation and review.
The transformation of citizen charters from mere documents to effective tools of governance requires a multi-pronged approach involving legal reforms, technological integration, and cultural change. Success stories like Mysore City Corporation's Citizen Charter demonstrate that with proper implementation, charters can significantly enhance public service delivery and citizen satisfaction.
Answer Length
Model answers may exceed the word limit for better clarity and depth. Use them as a guide, but always frame your final answer within the exam’s prescribed limit.
In just 60 sec
Evaluate your handwritten answer
- Get detailed feedback
- Model Answer after evaluation
Model Answers by Subject
Crack UPSC with your
Personal AI Mentor
An AI-powered ecosystem to learn, practice, and evaluate with discipline