Examine the need for electoral reforms as suggested by various committees with particular reference to the “one nation-one election” principle.
Examine the need for electoral reforms as suggested by various committees with particular reference to the “one nation-one election” principle.
Subject: Indian Polity
The need for electoral reforms in India has gained prominence due to the evolving nature of democracy and emerging challenges. The recent introduction of the "One Nation, One Election" bill in December 2024, securing 269 votes in favor, marks a significant step towards transforming India's electoral landscape. This was based on Ramnath Kovind Committee.
Electoral Reforms & their Need as Suggested by Various Committees
-
Appointment of Election Commissioners:
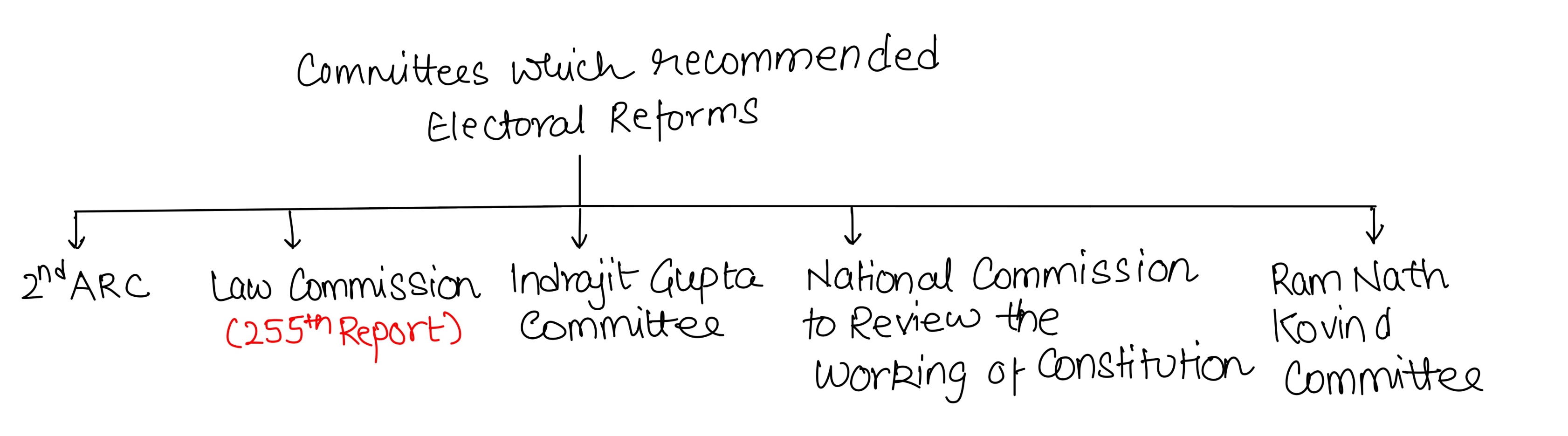
- Strengthening the autonomy of Election Commission of India (ECI) through transparent selection processes as recommended by the 2nd Administrative Reforms Commission.
- Implementation of a collegium system for appointment of Election Commissioners as suggested by the Supreme Court.
-
Financial Reforms:
- Indrajit Gupta Committee proposed regulation of election expenditure and implementation of State funding of elections.
- Introduction of digital payment systems to ensure transparency in political donations was emphasized by the Law Commission (255th Report, 2015).
-
Political Reforms:
- Decriminalization of politics through strict implementation of Section 8 of RPA, 1951 has been advocated by the Law Commission (244th Report, 2014).
- Enhanced voter verification methods using technology and Voter ID-Aadhaar linking, have been recommended by the Election Commission and endorsed by the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Law and Justice.
One Nation One Election: Analysis
-
Historical Context:
- Successfully implemented in India from 1951-1967.
- Gradual desynchronization occurred due to premature dissolution of assemblies.
-
Constitutional Implications:
- Requires amendments to Articles 83, 85, 172, 174, and 356.
- Need for political consensus and two-thirds majority in Parliament.
-
Implementation Challenges:
- Synchronization of electoral cycles across states.
- Constitutional provisions for handling premature dissolution.
- Protection of federal structure and regional autonomy.
Benefits and Concerns
| Benefits | Concerns |
|---|---|
| Frees governments from frequent MCC impositions, enabling consistent policy implementation. | May dilute the autonomy of states, undermining the spirit of cooperative federalism. |
| Reduces the financial burden of repeated elections on the exchequer. | Simultaneous elections demand massive infrastructure, personnel, and coordination. |
| Prevents repeated deployment of security and administrative staff. | Articles 83, 85, 172, and 174 must be amended to align terms. |
| Combined elections may improve voter engagement and turnout. | Different political parties may resist due to varied electoral interests and perceived disadvantages. |
Electoral reforms, particularly the "One Nation, One Election" principle, represent a transformative step towards efficient governance. The success of these reforms depends on balanced implementation, preserving democratic values while ensuring administrative efficiency, as demonstrated by successful models in countries like Sweden and South Africa.
Answer Length
Model answers may exceed the word limit for better clarity and depth. Use them as a guide, but always frame your final answer within the exam’s prescribed limit.
In just 60 sec
Evaluate your handwritten answer
- Get detailed feedback
- Model Answer after evaluation
Model Answers by Subject
Crack UPSC with your
Personal AI Mentor
An AI-powered ecosystem to learn, practice, and evaluate with discipline