What is the main task of India’s third moon mission which could not be achieved in its earlier mission? List the countries that have achieved this task. Introduce the subsystems in the spacecraft launched and explain the role of the ‘Virtual Launch Control Centre’ at the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre which contributed to the successful launch from Sriharikota.
What is the main task of India’s third moon mission which could not be achieved in its earlier mission? List the countries that have achieved this task. Introduce the subsystems in the spacecraft launched and explain the role of the ‘Virtual Launch Control Centre’ at the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre which contributed to the successful launch from Sriharikota.
India’s third lunar mission, Chandrayaan-3, launched on 14 July 2023 from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, aimed to build upon Chandrayaan-1 (2008) and Chandrayaan-2 (2019). It marked a significant step in ISRO’s planetary exploration programme and in fulfilling an unfinished goal from Chandrayaan-2.
Main Task of Chandrayaan-3
- Primary Objective: Achieve soft landing on the Moon’s surface, specifically near the lunar south pole.
- Why important? Chandrayaan-2 failed to achieve a soft landing in 2019 due to a last-phase navigation anomaly.
- Significance of South Pole: Rich in permanently shadowed regions, possible water ice deposits, and unique geology.
Countries That Have Achieved a Successful Moon Soft Landing
- US – Surveyor program (1966–68), Apollo missions.
- USSR/Russia – Luna program (1966 onwards).
- China – Chang’e 3 (2013), Chang’e 4 (2019).
- India – With Chandrayaan-3 in 2023, became the 4th nation and first to land near the lunar south pole.
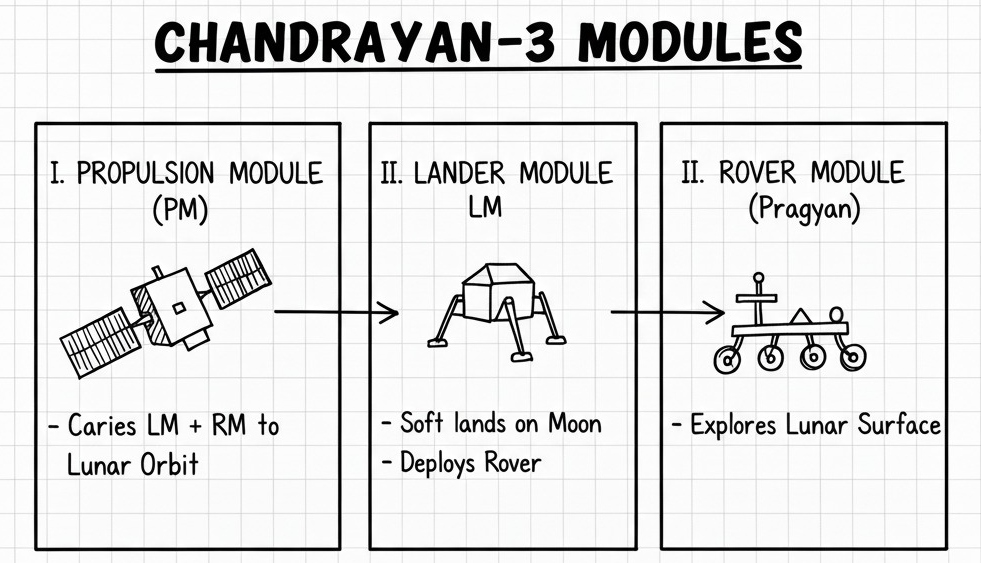
Subsystems in Chandrayaan-3 Spacecraft
-
Lander (Vikram)
-
Functions: Soft landing, payload deployment, scientific experiments.
-
Key Subsystems:
- Propulsion & navigation
- Hazard detection & avoidance cameras
- Altimeters & velocimeters
- Solar panels & thermal control
-
-
Rover (Pragyan)
-
Functions: Surface mobility & in-situ analysis.
-
Key Subsystems:
- Navigation cameras
- Spectrometers for elemental composition
- Solar-powered drive system
-
-
Propulsion Module
-
Functions: Transfer spacecraft from Earth’s orbit to lunar orbit and act as communication relay.
-
Key Subsystems:
- Liquid apogee motor
- High-gain antennas
- Power and thermal systems
-
IV. Role of the Virtual Launch Control Centre (VLCC)
- Location: Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), Thiruvananthapuram.
- Purpose: Functioned as a remote command, monitoring, and decision-making hub for launches.
Key Roles in Chandrayaan-3 Launch:
-
Redundancy & Safety – Enabled uninterrupted monitoring even in case of on-site technical issues.
-
Real-time Telemetry Analysis – Tracked propulsion, guidance, and health parameters remotely.
-
Coordination with Sriharikota – Worked in sync with Launch Control Centre at SDSC, sharing instant data and commands.
-
Enhanced Disaster Resilience – Could take over control in emergencies like adverse weather or technical disruptions at the launch site.
Chandrayaan-3’s successful soft landing fulfilled India’s unachieved goal from Chandrayaan-2, placing the nation in an elite lunar exploration club. The integration of advanced subsystems and innovative solutions like the Virtual Launch Control Centre demonstrate India’s growing self-reliance and sophistication in space technology, supporting future interplanetary missions.
Answer Length
Model answers may exceed the word limit for better clarity and depth. Use them as a guide, but always frame your final answer within the exam’s prescribed limit.
In just 60 sec
Evaluate your handwritten answer
- Get detailed feedback
- Model Answer after evaluation
Model Answers by Subject
Crack UPSC with your
Personal AI Mentor
An AI-powered ecosystem to learn, practice, and evaluate with discipline