Describe the context and salient features of the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023.
Describe the context and salient features of the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023.
Subject: Internal Security
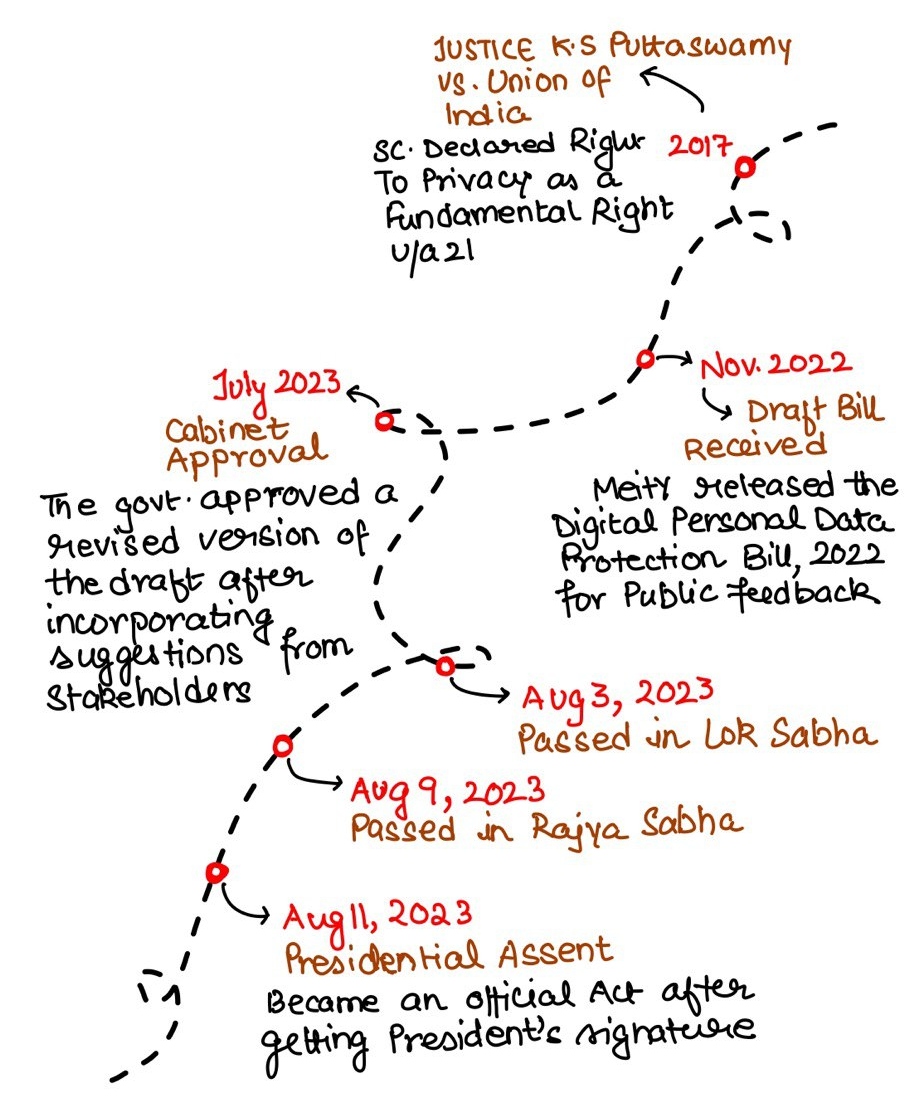
The Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 represents India's first comprehensive data protection legislation, enacted on August 11, 2023 after receiving Presidential assent. This landmark Act addresses the urgent need for robust data privacy regulations in India's rapidly digitizing economy.
Context
Background and Need
- India lacked a comprehensive data protection framework despite being home to the world's largest digital population
- Growing concerns over data breaches, privacy violations, and misuse of personal information by tech companies
- Need to balance individual privacy rights with legitimate business requirements for data processing
- Alignment with global privacy standards like GDPR while addressing India-specific challenges
Legislative Journey
Salient Features
Scope and Applicability
- Covers digital personal data collected online or offline and subsequently digitized
- Extraterritorial application for entities offering goods/services to Indians
- Applies to both domestic and international data processing activities
Key Provisions
- Consent Requirements: "Free, specific, informed, unconditional and unambiguous" consent mandatory for data processing
- Data Fiduciary Obligations: Security safeguards, data breach notifications, and grievance redressal mechanisms
- Children's Data Protection: Verifiable parental consent required for processing data of individuals under 18 years
- Data Principal Rights: Access, correction, erasure, and data portability rights
Institutional Framework
- Data Protection Board of India (DPBI): Regulatory authority for enforcement and compliance
- Significant Data Fiduciaries: Enhanced obligations for large-scale data processors including Data Protection Officer appointment
Penalties and Enforcement
- Financial penalties up to ₹250 crores for non-compliance
- No criminal penalties unlike previous drafts
- Graded responsibilities with lower compliance burden for startups and MSMEs
The DPDP Act 2023 establishes India's foundational data protection framework, balancing privacy rights with digital innovation while creating accountability mechanisms for responsible data handling in the digital economy.
Answer Length
Model answers may exceed the word limit for better clarity and depth. Use them as a guide, but always frame your final answer within the exam’s prescribed limit.
In just 60 sec
Evaluate your handwritten answer
- Get detailed feedback
- Model Answer after evaluation
Model Answers by Subject
Crack UPSC with your
Personal AI Mentor
An AI-powered ecosystem to learn, practice, and evaluate with discipline